2023
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
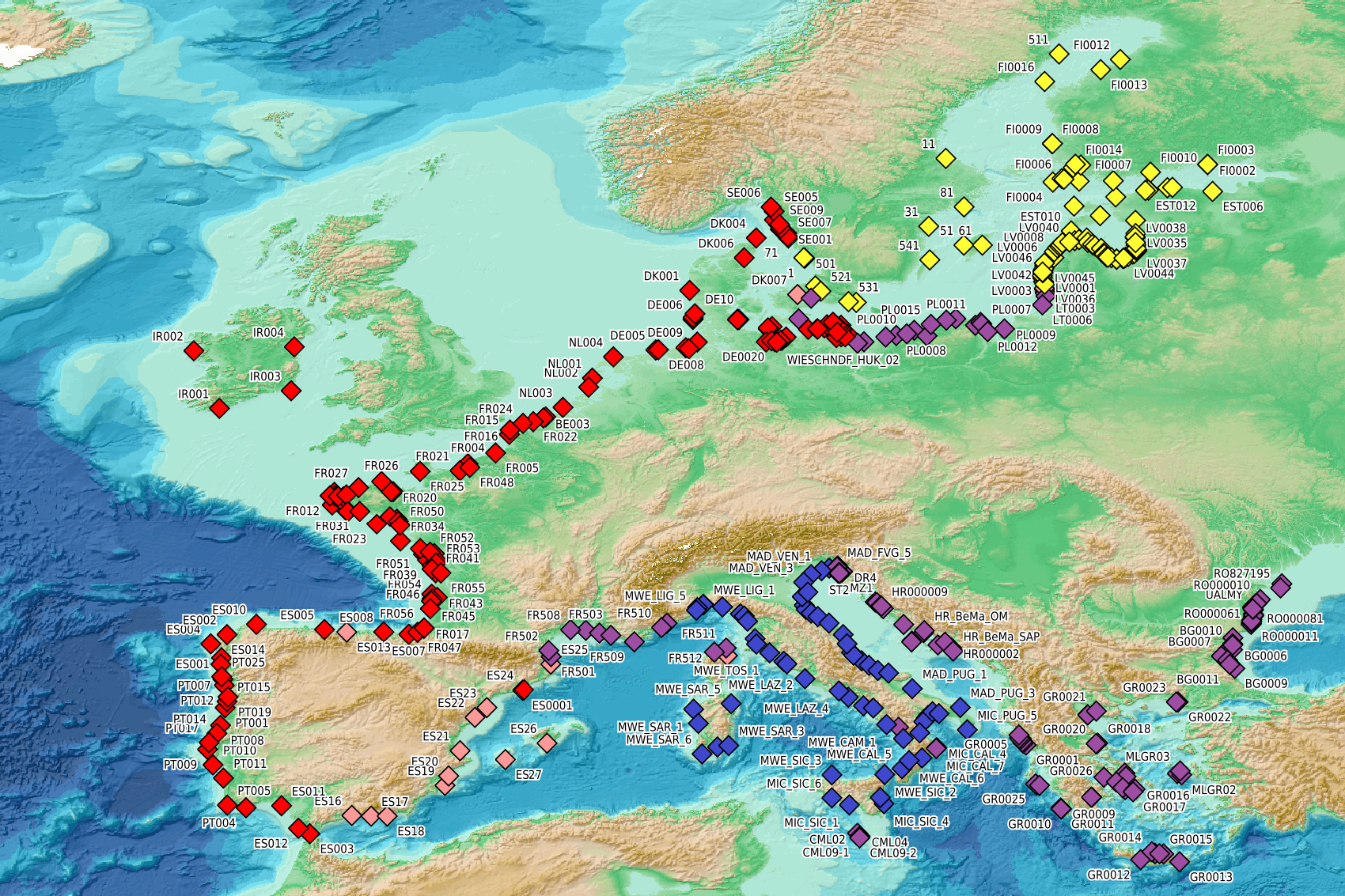
This visualization product displays beaches locations where the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) monitoring protocol has been applied to collate data on macrolitter (> 2.5 cm). Reference lists associated with these protocols have been indicated with different colors in the map. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of MSFD surveys only (exclusion of other monitoring, cleaning and research operations); - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Some categories & some litter types like organic litter, small fragments (paraffin and wax; items > 2.5cm) and pollutants have been removed. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines and EU Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines from JRC (these two documents are attached to this metadata). More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map doesn't necessarily mean that they don't exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of Solitary Scleractinian fields assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image sample. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the north-east Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
-
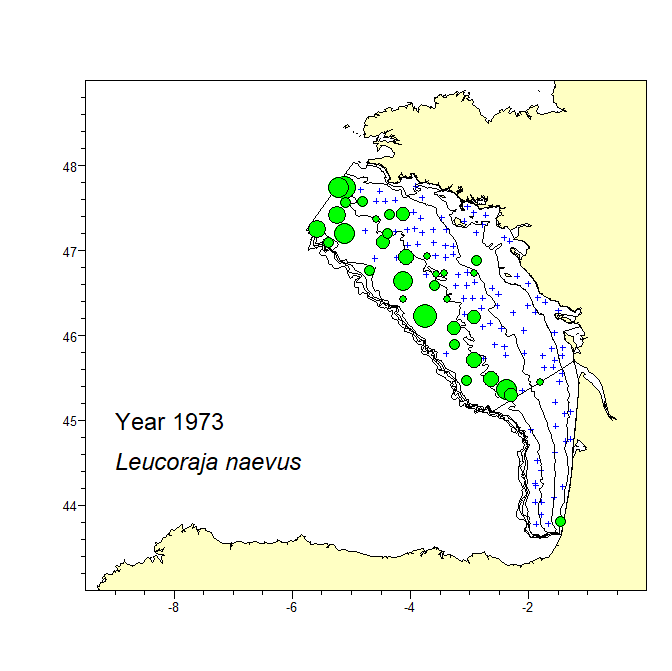
A consistent dataset of bottom trawl survey data spanning 47 years in the Bay of Biscay was assembled. The dataset includes data from the current EVHOE survey from 1987 to 2019 and two previous surveys carried out in 1973 and 1976. The recent EVHOE time-series from 1997 is also available from DATRAS (https://www.ices.dk/data/data-portals/Pages/DATRAS.aspx). The catch in numbers and weight (kg) per haul of all Rajiformes species caught in these surveys is provided. Haul information is provided for all hauls, including those with no catch of Rajiformes. Areas of the sampling strata of the survey and spatial polygones of these strata are provided in separate files.
-

'''DEFINITION''' The OMI_EXTREME_SL_NORTHWESTSHELF_slev_mean_and_anomaly_obs indicator is based on the computation of the 99th and the 1st percentiles from in situ data (observations). It is computed for the variable sea level measured by tide gauges along the coast. The use of percentiles instead of annual maximum and minimum values, makes this extremes study less affected by individual data measurement errors. The annual percentiles referred to annual mean sea level are temporally averaged and their spatial evolution is displayed in the dataset omi_extreme_sl_northwestshelf_slev_mean_and_anomaly_obs, jointly with the anomaly in the target year. This study of extreme variability was first applied to sea level variable (Pérez Gómez et al 2016) and then extended to other essential variables, sea surface temperature and significant wave height (Pérez Gómez et al 2018). '''CONTEXT''' Sea level (SLEV) is one of the Essential Ocean Variables most affected by climate change. Global mean sea level rise has accelerated since the 1990’s (Abram et al., 2019, Legeais et al., 2020), due to the increase of ocean temperature and mass volume caused by land ice melting (WCRP, 2018). Basin scale oceanographic and meteorological features lead to regional variations of this trend that combined with changes in the frequency and intensity of storms could also rise extreme sea levels up to one metre by the end of the century (Vousdoukas et al., 2020, Tebaldi et al., 2021). This will significantly increase coastal vulnerability to storms, with important consequences on the extent of flooding events, coastal erosion and damage to infrastructures caused by waves (Boumis et al., 2023). The increase in extreme sea levels over recent decades is, therefore, primarily due to the rise in mean sea level. Note, however, that the methodology used to compute this OMI removes the annual 50th percentile, thereby discarding the mean sea level trend to isolate changes in storminess. The North West Shelf area presents positive sea level trends with higher trend estimates in the German Bight and around Denmark, and lower trends around the southern part of Great Britain (Dettmering et al., 2021). '''COPERNICUS MARINE SERVICE KEY FINDINGS''' The completeness index criteria is fulfilled by 33 stations in 2023, one less than in 2022 (32). The mean 99th percentiles present a large spatial variability related to the tidal pattern, with largest values found in East England and at the entrance of the English channel, and lowest values along the Danish and Swedish coasts, ranging from the 3.08 m above mean sea level in Immingan (East England) to 0.45 m above mean sea level in Tregde (Norway). The standard deviation of annual 99th percentiles ranges between 2-3 cm in the western part of the region (e.g.: 2 cm in Harwich, 3 cm in Dunkerke) and 7-8 cm in the eastern part and the Kattegat (e.g. 8 cm in Stenungsund, Sweden). The 99th percentile anomalies for 2023 show overall slightly negative values except in the Kattegat (Eastern part), with maximum significant values of +11 cm in Hornbaek (Denmark), and +10 cm in Ringhals (Sweden). '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00272
-
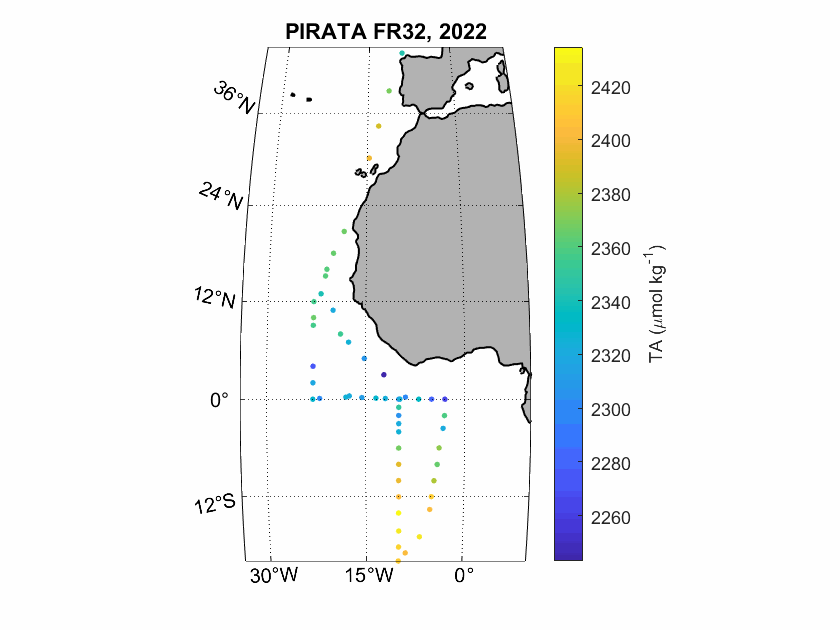
Seawater samples (500 mL) were taken during the PIRATA FR-32 cruise to measure surface inorganic carbon and alkalinity. The analyses were realised by potentiometric titration using a closed-cell at the SNAPO-CO2, LOCEAN in Paris.
-
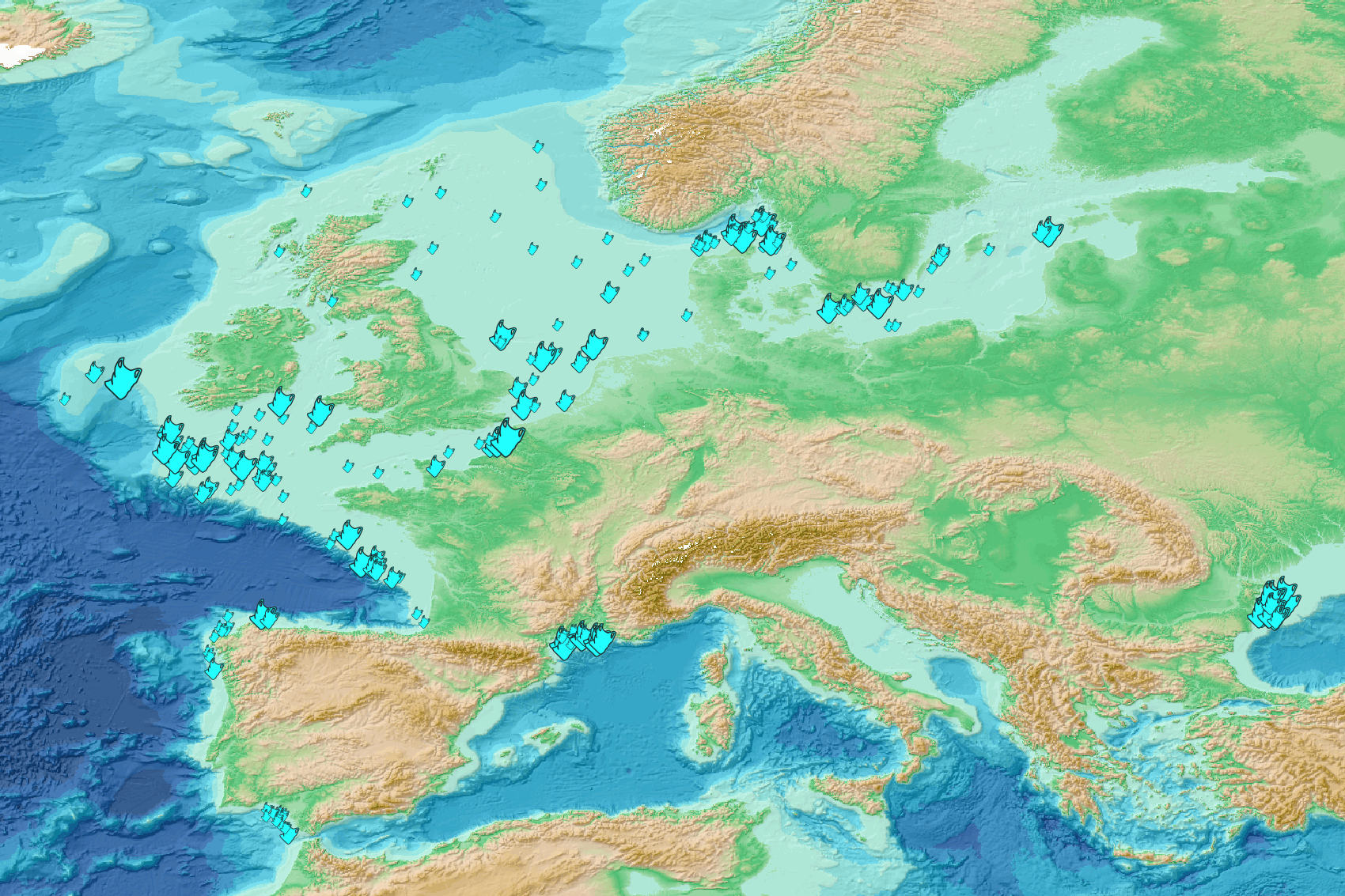
This visualization product displays plastic bags density per trawl. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of seafloor litter collected by international fish-trawl surveys have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols (OSPAR and MEDITS protocols) and reference lists used on a European scale. Moreover, within the same protocol, different gear types are deployed during fishing bottom trawl surveys. In cases where the wingspread and/or number of items were unknown, data could not be used because these fields are needed to calculate the density. Data collected before 2011 are affected by this filter. When the distance reported in the data was null, it was calculated from: - the ground speed and the haul duration using this formula: Distance (km) = Haul duration (h) * Ground speed (km/h); - the trawl coordinates if the ground speed and the haul duration were not filled in. The swept area is calculated from the wingspread (which depends on the fishing gear type) and the distance trawled: Swept area (km²) = Distance (km) * Wingspread (km) Densities have been calculated on each trawl and year using the following computation: Density of plastic bags (number of items per km²) = ∑Number of plastic bags related items / Swept area (km²) Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account data for all years. The list of selected items for this product is attached to this metadata. Information on data processing and calculation is detailed in the attached methodology document. Warning: the absence of data on the map doesn't necessarily mean that they don't exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of Acanella arbuscula assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image sample. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the North East Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
-

'''DEFINITION''' The OMI_EXTREME_SL_MEDSEA_slev_mean_and_anomaly_obs indicator is based on the computation of the 99th and the 1st percentiles from in situ data (observations). It is computed for the variable sea level measured by tide gauges along the coast. The use of percentiles instead of annual maximum and minimum values, makes this extremes study less affected by individual data measurement errors. The annual percentiles referred to annual mean sea level are temporally averaged and their spatial evolution is displayed in the dataset omi_extreme_sl_medsea_slev_mean_and_anomaly_obs, jointly with the anomaly in the target year. This study of extreme variability was first applied to sea level variable (Pérez Gómez et al 2016) and then extended to other essential variables, sea surface temperature and significant wave height (Pérez Gómez et al 2018). '''CONTEXT''' Sea level (SLEV) is one of the Essential Ocean Variables most affected by climate change. Global mean sea level rise has accelerated since the 1990’s (Abram et al., 2019, Legeais et al., 2020), due to the increase of ocean temperature and mass volume caused by land ice melting (WCRP, 2018). Basin scale oceanographic and meteorological features lead to regional variations of this trend that combined with changes in the frequency and intensity of storms could also rise extreme sea levels up to one meter by the end of the century (Vousdoukas et al., 2020, Tebaldi et al., 2021). This will significantly increase coastal vulnerability to storms, with important consequences on the extent of flooding events, coastal erosion and damage to infrastructures caused by waves (Boumis et al., 2023). The increase in extreme sea levels over recent decades is, therefore, primarily due to the rise in mean sea level. Note, however, that the methodology used to compute this OMI removes the annual 50th percentile, thereby discarding the mean sea level trend to isolate changes in storminess. The Mediterranean Sea shows statistically significant positive sea level trends over the whole basin. However, at sub-basin scale sea level trends show spatial variability arising from local circulation (Calafat et al., 2022; Meli et al., 2023). '''COPERNICUS MARINE SERVICE KEY FINDINGS''' The completeness index criteria is fulfilled by 41 stations in 2023, 3 more than in 2022, including the first station in the African coast, in the Alboran Sea (Melilla). The mean 99th percentiles reflect the spatial variability of the tide, a microtidal regime, along the Spanish, French and Italian coasts, ranging from around 0.20 m above mean sea level in Sicily and the Balearic Islands (e.g.: 0.22 m in Porto Empedocle; 0.23 m in Ibiza) to around 0.60 m above mean sea level in the Northern Adriatic Sea (e.g.: 0.63 m in Trieste, 0.61 m in Venice). The annual 99th percentiles standard deviation ranges between 2 cm in the Alboran Sea and Sicily to 8 cm in Marseille. The 2023 99th percentile anomalies present positive values in the central and northern part of the Mediterranean Sea, with the exception of Ibiza, in the Balearic Islands, and zero or slightly negative anomalies in the Spanish coast and South of Italy. However, these anomalies are only significant, when compared with the standard deviation of the annual percentiles in the record, at a few stations: Marseille (+12 cm), Ibiza (+8 cm), Trieste (+8 cm) and Venice (+7 cm). '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00265
-
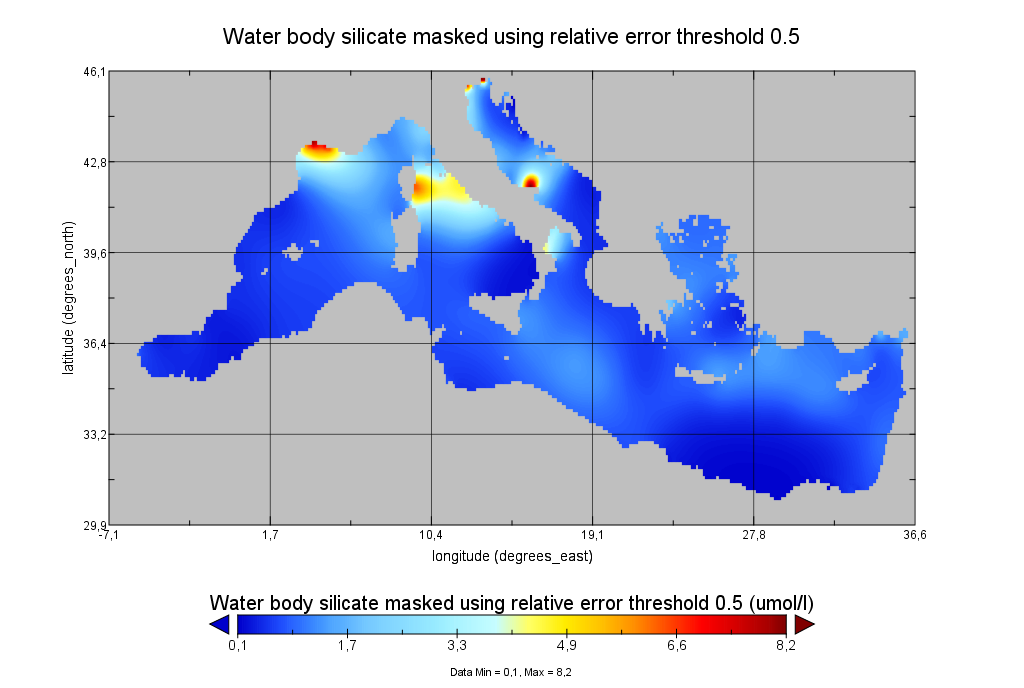
Moving 6-year analysis of Water body silicate in the Mediterranean Sea for each season: - winter: January-March, - spring: April-June, - summer: July-September, - autumn: October-December. Every year of the time dimension corresponds to the 6-year centered average of the season. 6-years periods span from 1970-1975 until 2017-2022. Data Sources: observational data from SeaDataNet/EMODNet Chemistry Data Network. Units: umol/l. Description of DIVA analysis: The computation was done with the DIVAnd (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis in n dimensions), version 2.7.9, using GEBCO 30sec topography for the spatial connectivity of water masses. The horizontal resolution of the produced DIVAnd maps grids is dx=dy=0.125 degrees (around 13.5km and 10.9km accordingly). The vertical resolution is 25 depth levels: [0.,5.,10.,20.,30.,50.,75.,100.,125.,150.,200.,250.,300.,400.,500.,600.,700.,800.,900.,1000.,1100.,1200.,1300.,1400.,1500.]. The horizontal correlation length is 200km. The vertical correlation length (in meters) was set twices the vertical resolution: [10.,10.,20.,20.,40.,50.,50.,50.,50.,100.,100.,100.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.,200.]. Duplicates check was performed using the following criteria for space and time: dlon=0.001deg., dlat=0.001deg., ddepth=1m, dtime=1hour, dvalue=0.1. The error variance (epsilon2) was set equal to 1 for profiles and 10 for time series to reduce the influence of close data near the coasts. An anamorphosis transformation was applied to the data (function DIVAnd.Anam.loglin) to avoid unrealistic negative values: threshold value=200. A background analysis field was used for all years (1970-2022) with correlation length equal to 600km and error variance (epsilon2) equal to 20. Quality control of the observations was applied using the interpolated field (QCMETHOD=3). Residuals (differences between the observations and the analysis (interpolated linearly to the location of the observations) were calculated. Observations with residuals outside the minimum and maximum values of the 99% quantile were discarded from the analysis. Originators of Italian data sets-List of contributors: - Brunetti Fabio (OGS) - Cardin Vanessa, Bensi Manuel doi:10.6092/36728450-4296-4e6a-967d-d5b6da55f306 - Cardin Vanessa, Bensi Manuel, Ursella Laura, Siena Giuseppe doi:10.6092/f8e6d18e-f877-4aa5-a983-a03b06ccb987 - Cataletto Bruno (OGS) - Cinzia Comici Cinzia (OGS) - Civitarese Giuseppe (OGS) - DeVittor Cinzia (OGS) - Giani Michele (OGS) - Kovacevic Vedrana (OGS) - Mosetti Renzo (OGS) - Solidoro C.,Beran A.,Cataletto B.,Celussi M.,Cibic T.,Comici C.,Del Negro P.,De Vittor C.,Minocci M.,Monti M.,Fabbro C.,Falconi C.,Franzo A.,Libralato S.,Lipizer M.,Negussanti J.S.,Russel H.,Valli G., doi:10.6092/e5518899-b914-43b0-8139-023718aa63f5 - Celio Massimo (ARPA FVG) - Malaguti Antonella (ENEA) - Fonda Umani Serena (UNITS) - Bignami Francesco (ISAC/CNR) - Boldrini Alfredo (ISMAR/CNR) - Marini Mauro (ISMAR/CNR) - Miserocchi Stefano (ISMAR/CNR) - Zaccone Renata (IAMC/CNR) - Lavezza, R., Dubroca, L. F. C., Ludicone, D., Kress, N., Herut, B., Civitarese, G., Cruzado, A., Lefèvre, D.,Souvermezoglou, E., Yilmaz, A., Tugrul, S., and Ribera d'Alcala, M.: Compilation of quality controlled nutrient profiles from the Mediterranean Sea, doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.771907, 2011.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of discrete Lophelia pertusa - Desmophylum pertusum colonies assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image samples. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the North East Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA