Area management/restriction/regulation zones and reporting units
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
The territorial organization of flood warning has two components: - The SCHAPI or central service for Hydrometeorology and support for flood forecasting, - 22 services for flood forecasting (SPC), replacing, since 2002, the 52 flood warning services (SAC) existing. The legal framework for flood forecasting is defined in the law relating to natural and technological hazards, adopted on 30 July 2003.
-
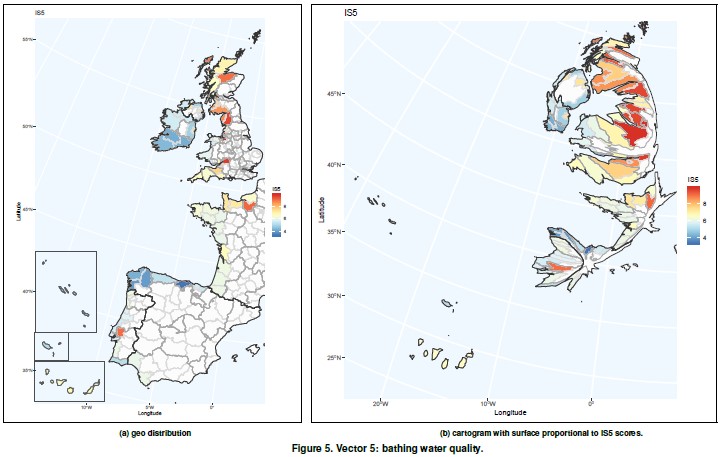
This vector uses information from two European directives: the Bathing Water Directive (76/160/EEC, 2006/7/EC) which aims “to preserve, protect and improve the quality of the environment and to protect human health” and the Waste Framework Directive (75/442/EEC , 2008/98/EC) whose essential objective is “the protection of human healthand the environment against harmful effects caused bythe collec- tion, transport, treatment, storage and tipping of waste”.
-
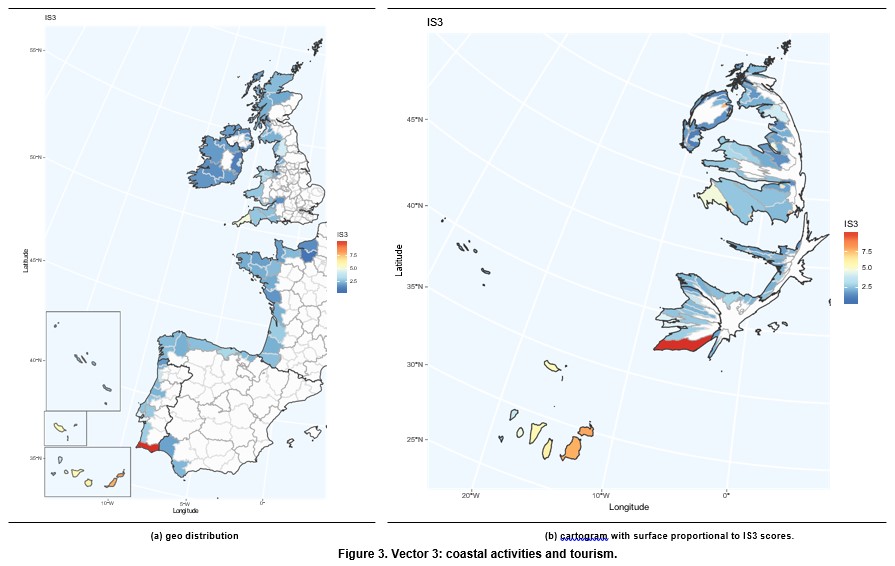
It covers indicators related to demographic pressure, tourism and recreation, economic devel- opment and land use and infrastructure development. This vector captures the impact of human coastal activities on vulnera- bility. In this framework, we are particularly interested in the tourism sector, which is one of the main economic activities in the coast. Tourism is an important economic sector due to its contribution to GDP and employment. According to the World Travel & Tourism Council, Tourims generates 10.4% of all global economic activity. It contributes 319 million jobs, representing one in ten of all jobs globally. It is a sector that has been growing faster than the global economy for the last eight years. Europe plays an important role in this sector with 51% of international tourits arrivals and 39% of international tourist revenues. Taking into account the countries included in the European Atlantic Arc, it is worth pointing out that France and Spain are first and second, respectively, in the world ranking of international tourist arrivals, with United Kingdom in the seventh position. With respect to international tourism revenues, Spain and France are second and third in the world ranking, respectively, while United Kingdom occupies the fifth position. Coastal tourism contributes significantly in theses coun- tries. It represents 75.6% of total tourism in Spain, 28% in Portugal, 23% in France, 10% in Ireland and 6% in the United Kingdom (Foley et al., 2014, p.204).
-
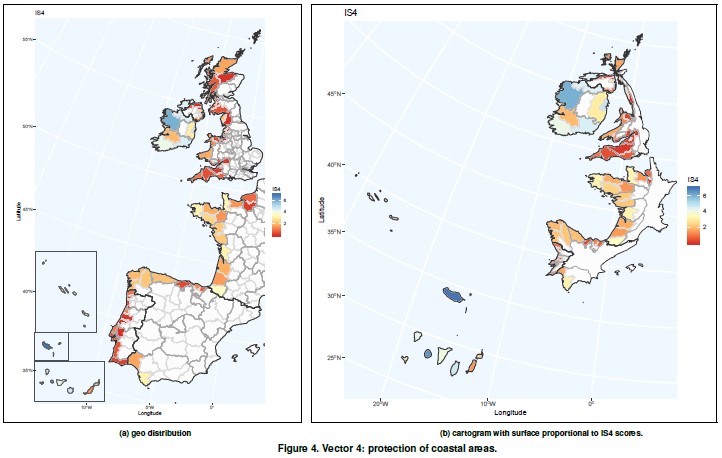
It is related to EU SCIs (Coastal Sites of Community Importance). Natura 2000 is the largest coordinated network of protected areas in the world. The aim of the network is to ensure the long-term survival of Europe’s most valuable and threatened species and habitats, listed under both the Birds Directive and the Habitats Directive. This vector tries to capture the effect of the Natura 2000 network on maintaining the resilience of ecosystems, especially in the marine environment.
-
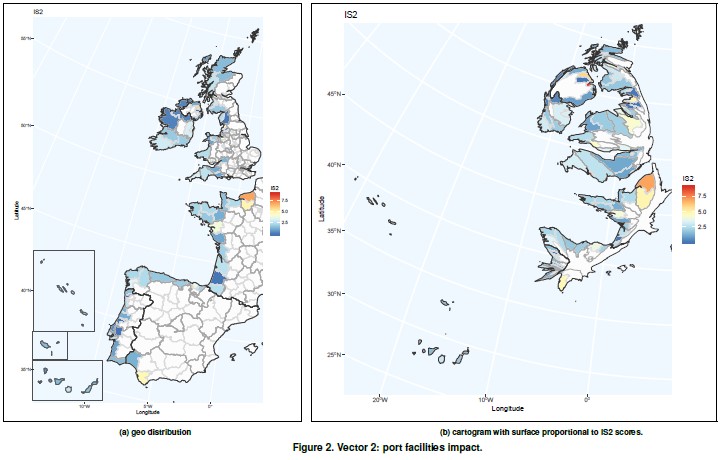
It contemplates the assessment of vulnerability due to passengers and goods transportation and cov- ers indicators related to sustainability awareness (energy efficiency, land use, etc.). Shipping has an environmental impact both in ports, as well as in the immediate vicinity of the ports. This vector tries to capture the impact of the port activity on vulnerability. Vector 2 indicators have been obtained from Eurostat and EcoPorts, a environmental initiative of the European port sector fully integrated into the European Sea Ports Organisation (ESPO) since 2011.
-
The objective of this tender is to examine the current data collection, observation and data assembly programmes in the Meditterranean Sea, identify gaps and to evaluate how they can be optimised.
-
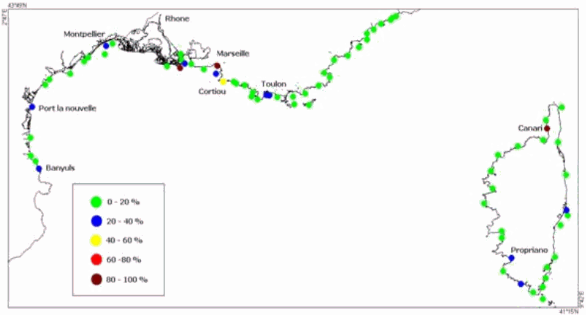
-
The objective of this tender is to examine the current data collection, observation and data assembly programmes in the Meditterranean Sea, identify gaps and to evaluate how they can be optimised.
-
The objective of this tender is to examine the current data collection, observation and data assembly programmes in the Meditterranean Sea, identify gaps and to evaluate how they can be optimised.
-
The challenge attempts to collect data on landings for the North Atlantic sea basin (i.e. north of the equator, excluding Caribe, Baltic, North Sea and Artic) and to compute: mass and number of discards by species and year, including fish, mammals, reptiles and seabirds. Data are presented in an Excel spreadsheet.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA