Bioinformatics
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
-

Dart Seq data gathered on Blue Shark in the framework of the PSTBS-IO project supported by funding from FAO, CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, AZTI Tecnalia, Institut de recherche pour le développement (IRD), and Research Institute for Tuna Fisheries (RITF) and financial assistance of the European Union (GCP/INT/233/EC – Population structure of IOTC species in the Indian Ocean), and POPSIZE project supported by FEAMP (2014-2020 UE N°508/2014), and Institut français de recherche pour l'Exploitation de la mer (Ifremer).
-
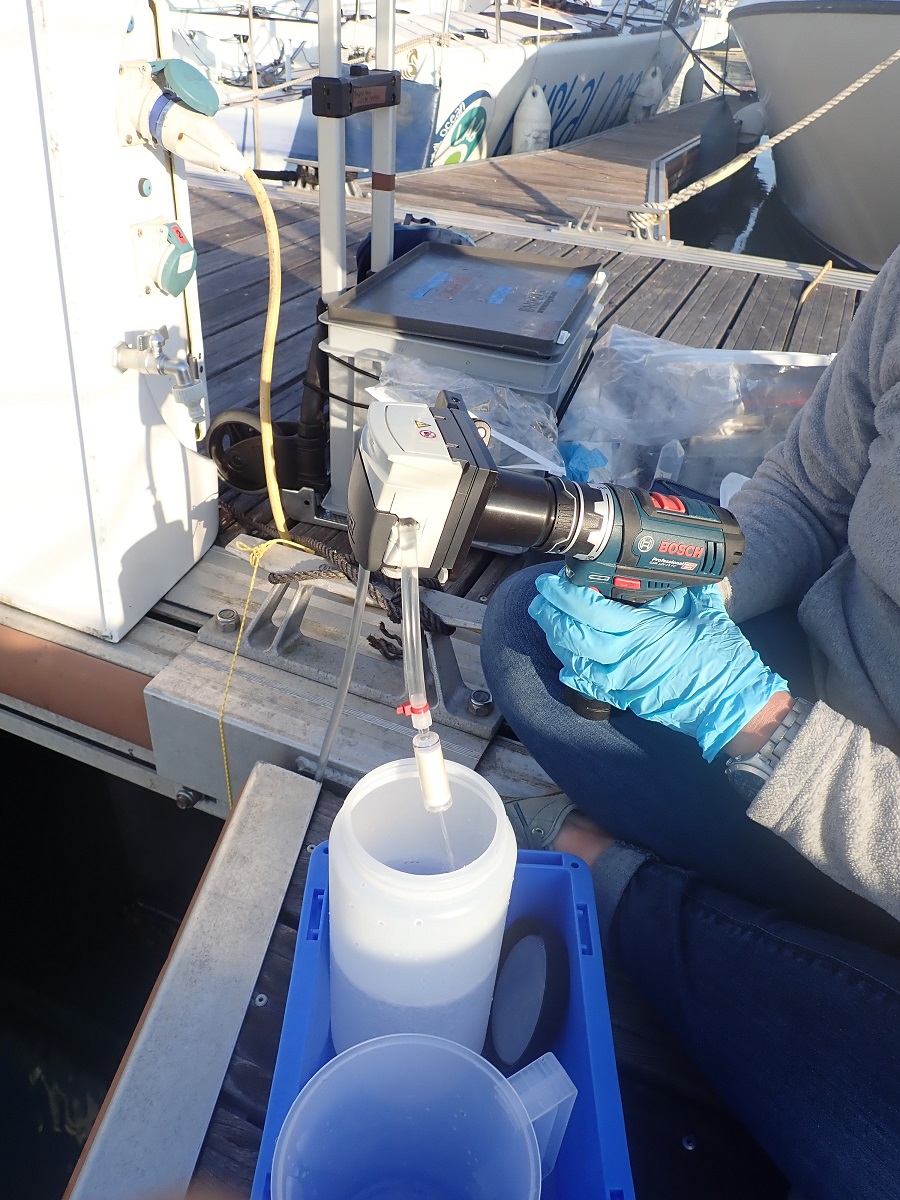

Metabarcoding data were produced based on samples gathered at Ifremer where the DNA was extracted; PCR libraries were built at Ifremer and Genseq; libraries were sequenced at Novogene. The data to download contain: 1/d emultiplexed raw data, 2/ metadata, and 3) Scripts to process data and taxonomically assign DNA sequences 4) Rmarkdown to analyze communities.
-

Successive infections with Vibrio harveyi were conducted in two populations of the European abalone in order to examine which genes may be involved in improved survival to the disease in the St. Malo population.
-

Land-sea continuum microbiome analyses in 4 coastal French sites and in oysters aimed at evaluating human impact on coastal ecosystems and new potentiel microbiological sanitary risks.
-

WGS of SARS-CoV-2 by Oxford Nanopore Technology from raw wastewater samples collected in France, 2020-2021
-

DNA sequencing of Crassostrea gigas Pacific oyster spat infected in the wild with OsHV-1 virus in 4 French oyster basins (Marennes Oleron Bay, Arcachon bay, Rade de Brest and Thau lagoon).
-
The present data set concerne metabarcoding raw reads produced using 4 different PCR targeting polymerase or capside coding region of the genoyupe I and II of norovirus. Test samples of norovirus with serial dilutions in pure water and after a bio-accumulation in oysters. Sequencing was made after VirCapSeq-VERT approach.
-

ddRAD genotyping was used to evaluate population connectivity and putative loci under selection in honeycomb worm from 13 sites spanning its distribution in the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts.
-

In European sea bass like in other animals, the tongue plays a fundamental role in the mechanics of food ingestion. It is composed from the surface in depth of mucosa, submucosa, musculature and fibro cartilaginous skeleton. The tunica mucosa exhibits a stratified epithelium interrupted by numerous teeth differently distributed that erupt more or less completely from the layers below. The European sea bass tongue is composed of canine-like teeth, surrounded by taste buds and numerous fungiform and conical papillae. The tongue beeing directly in contact with external environment, the success of the adaptation of fishes to different environments in the context of global change, depends oamong other on the modifications occurring on the tongue structures. The present study investigates the potential effect of ocean acidification on the lingual transcriptome.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA