Oceanographic geographical features
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Sediment Profile Images (SPIs) are commonly used to map physical, biological and chemical/nutrient gradients in benthic habitats. SpiArcBase is a software that has been developed for the analysis of Sediment Profile Images (SPIs). It has been conceived to improve the objectivity of extracted information (especially the apparent Redox Potential Discontinuity (aRPD). The software presents a graphical user interface designed to enhance the interpretation of features observed on SPIs in an objective manner and to facilitate image management and structures visualization via a data base.The software also allows for the storage of generated data and the automatic computation of a benthic habitat quality index. The facilities provided within JERICONext include access to the software through free downloading and assistance in its utilization.
-

SpiArcBase is a software developed for the treatment of Sediment Profile images (SPIs). Sediment Profile Images (SPIs) are widely used for benthic ecological quality assessment under various environmental stressors. The processing of the information contained in SPIs is slow and its interpretation is largely operator dependent. SpiArcBase enhances the objectivity of the information extracted from SPIs, especially for the assessment of the apparent Redox Potential Discontinuity (aRPD). This software allows the user to create and manage a database containing original SPIs and corresponding derived pieces of information. Once you have downloaded it, you can ask for help and stablish a helpdesk.
-

Surface current data measured by the CNR-ISMAR HF radar network are made available in graphical format for the last 48 hours and in real time and delayed mode via a THREDDS catalog which provides metadata and data access. The web site gives information on HF radar technology, sites position and operational parameters, and links to the THREDDS catalog. The catalog offers different remote-data-access protocols such as Open-source Project for a Network Data Access Protocol (OpenDaP), Web Coverage Service (WCS), Web Map Service (WMS) (OGS standards), as well as pure HTTP or NetCDF-Subsetter. They allow for metadata interrogation and data download (even sub-setting the dataset in terms of time and space) while embedded clients, such as GODIVA2, NetCDF-JavaToolsUI and Integrated Data Viewer, grant real-time data visualization directly via browser and allow for navigating within the plotted maps, saving images, exporting-importing on Google Earth, generating animations in selected time intervals. The data on the THREDDS catalog are organized in two folders, collecting the hourly current files of the last five days and grouping all the historical data. The two folders are accessible both in aggregated and in non-aggregated configuration. The data set consists of maps of radial and total velocity of the sea water surface current collected by the HF radars within the Italian Coastal Radar Network established in the framework of the Italian flagship project RITMARE. Surface ocean velocities estimated by HF Radar are representative of the upper 0.3-2.5 meters of the ocean. The radar sites are operated according to Quality Assessment procedures and data are processed for Quality Control. Data access tools are compliant to Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), Climate and Forecast (CF) convention and INSPIRE directive. The use of netCDF format allows an easy implementation of all the open source services developed by UNIDATA.
-

ERA‐40 is a re‐analysis of meteorological observations from September 1957 to August 2002 produced by the European Centre for Medium‐Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)
-
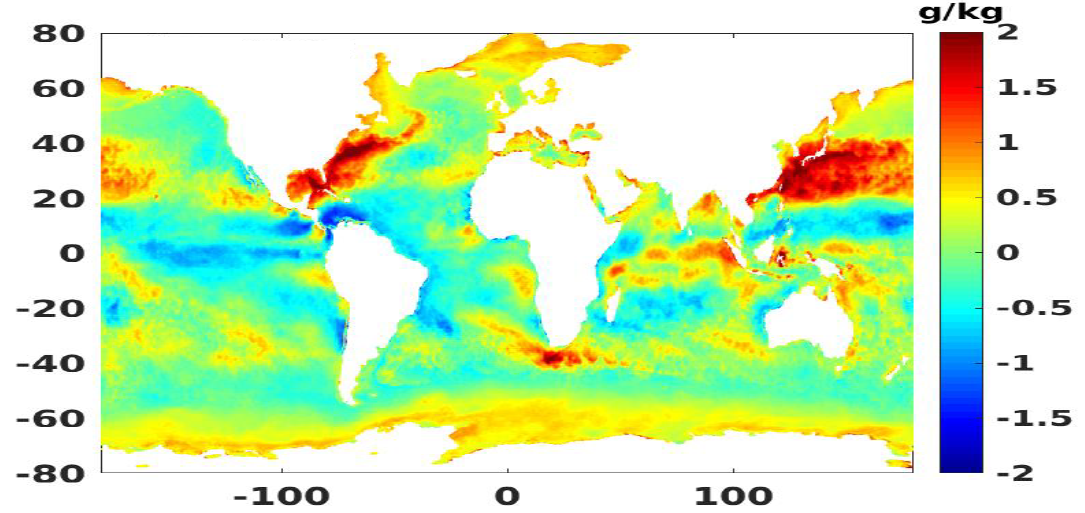
Daily air-sea heat fluxes dataset on the last 27 years (1992-2018). Global coverage with 0.25° resolution. Data is mainly coming from aggregated calibrated scatterometer datasets and numerical models. Main geophysical parameters are: sensible heat flux, latent heat flux, wind speed, SST, air temperature. Latest version : 4.1 released in June 2019.
-
A Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) Level 4 sea surface temperature analysis produced daily on an operational basis at the UK Met Office using optimal interpolation (OI) on a global 0.054 degree grid. The Operational Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Analysis (OSTIA) analysis uses satellite data from sensors that include the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR), the Advanced Along Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR), the Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI), the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS (AMSRE), the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission Microwave Imager (TMI), and in situ data from drifting and moored buoys. This analysis has a highly smoothed SST field and was specifically produced to support SST data assimilation into Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models.
-
A Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) Level 4 sea surface temperature analysis produced daily on an operational basis at the UK Met Office using optimal interpolation (OI) on a global 0.054 degree grid. The Operational Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Analysis (OSTIA) analysis uses satellite data from sensors that include the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR), the Advanced Along Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR), the Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI), the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS (AMSRE), the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission Microwave Imager (TMI), and in situ data from drifting and moored buoys. This analysis has a highly smoothed SST field and was specifically produced to support SST data assimilation into Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models.
-

This HF radar system is composed by two CODAR Seasonde antennas (transmit frecuency 4.525 MHz) and offers many benefits for the Basque Operational Oceanography Network such as: the improvement of the knowledge about surface currents and their forcing physical processes, marine safety, search and rescue, pollution response, validation and calibration of both hydrodynamic and pollutant drift forecasting models, data assimilation on progress, etc. The access from raw radial data to processes 2D surface current is provided for scientific and applied purposes (Coastal processes, marine safety, search and rescue, pollution response, etc).
-
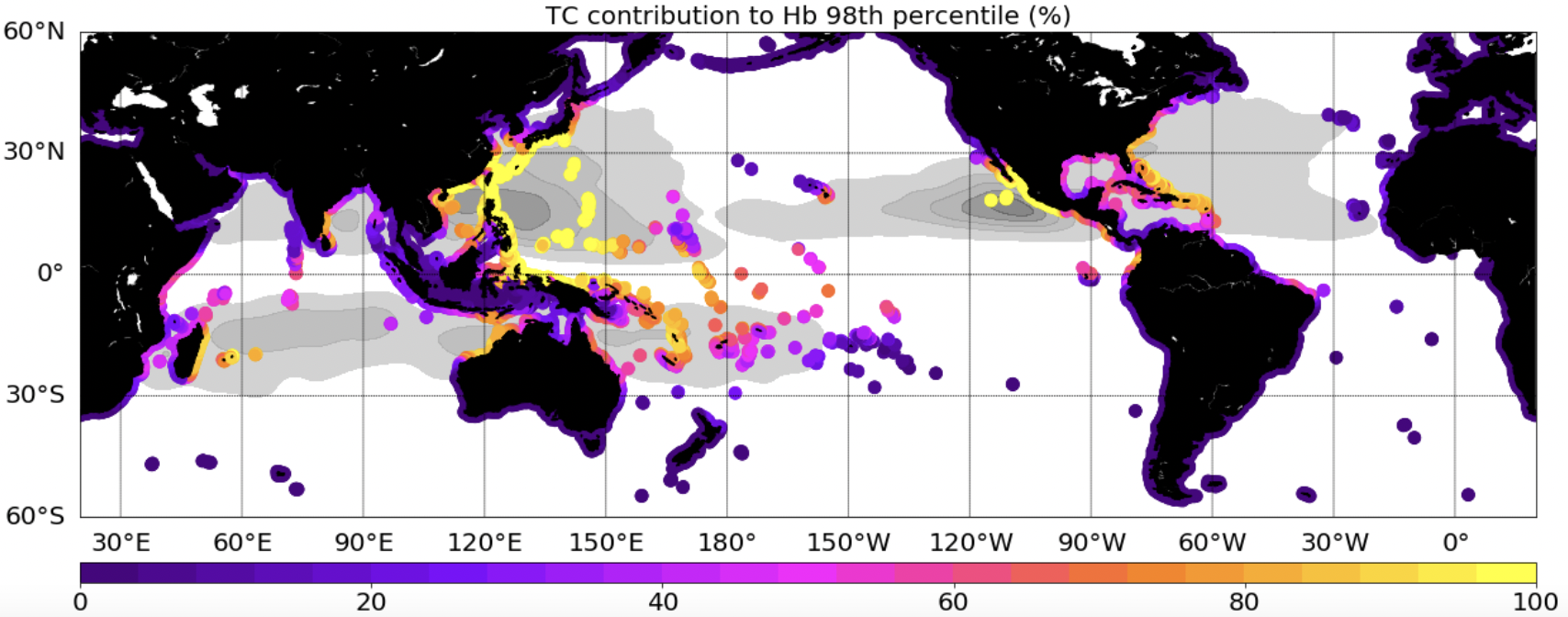
This dataset provides extreme waves (Hs: significant wave height, Hb:breaking wave height, a proxy of the wave energy flux) simulated with the WWIII model, and extracted along global coastlines. Two simulations, including or not Tropical Cyclones (TCs) in the forcing wind field, are provided.
-
A regional Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) Level 2P dataset based on multi-channel sea surface temperature (SST) retrievals generated in real-time from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) on the NOAA-19 platform (launched 6 Feb 2009) produced and used operationally in oceanographic analyses and forecasts by the US Naval Oceanographic Office (NAVO). The AVHRR is a space-borne scanning sensor on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) family of Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellites (POES) having a operational legacy that traces back to the Television Infrared Observation Satellite-N (TIROS-N) launched in 1978. AVHRR instruments measure the radiance of the Earth in 5 (or 6) relatively wide spectral bands. The first two are centered around the red (0.6 micrometer) and near-infrared (0.9 micrometer) regions, the third one is located around 3.5 micrometer, and the last two sample the emitted thermal radiation, around 11 and 12 micrometers, respectively. The legacy 5 band instrument is known as AVHRR/2 while the more recent version, the AVHRR/3 (first carried on the NOAA-15 platform), acquires data in a 6th channel located at 1.6 micrometer. Typically the 11 and 12 micron channels are used to derive SST sometimes in combination with the 3.5 micron channel. The NOAA platforms are sun synchronous generally viewing the same earth location twice a day (latitude dependent) due to the relatively large AVHRR swath of approximately 2400 km. The highest ground resolution that can be obtained from the current AVHRR instruments is 1.1 km at nadir. AVHRR data are acquired in three formats: High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT), Local Area Coverage (LAC), and Global Area Coverage (GAC). HRPT data are full resolution image data transmitted to a ground stations as they are collected. LAC are also full resolution data, but the acquisition is prescheduled and recorded with an on-board tape recorder for subsequent transmission during a station overpass. GAC data provide daily subsampled global coverage recorded on tape recorders and then transmitted to a ground station. This particular dataset is derived from LAC data. Further binning and averaging of the 1.1 km LAC pixels results in a final dataset resolution of 2.2 km. The coverage of the LAC data can vary but generally contains scenes over the oceans adjacent to Australia and the North Indian Ocean.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA