Sorbonne Université, CNRS, IRD, MNHN, Laboratoire d'Océanographie et du Climat: Expérimentations et approches numériques, UMR 7159, Paris, France
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
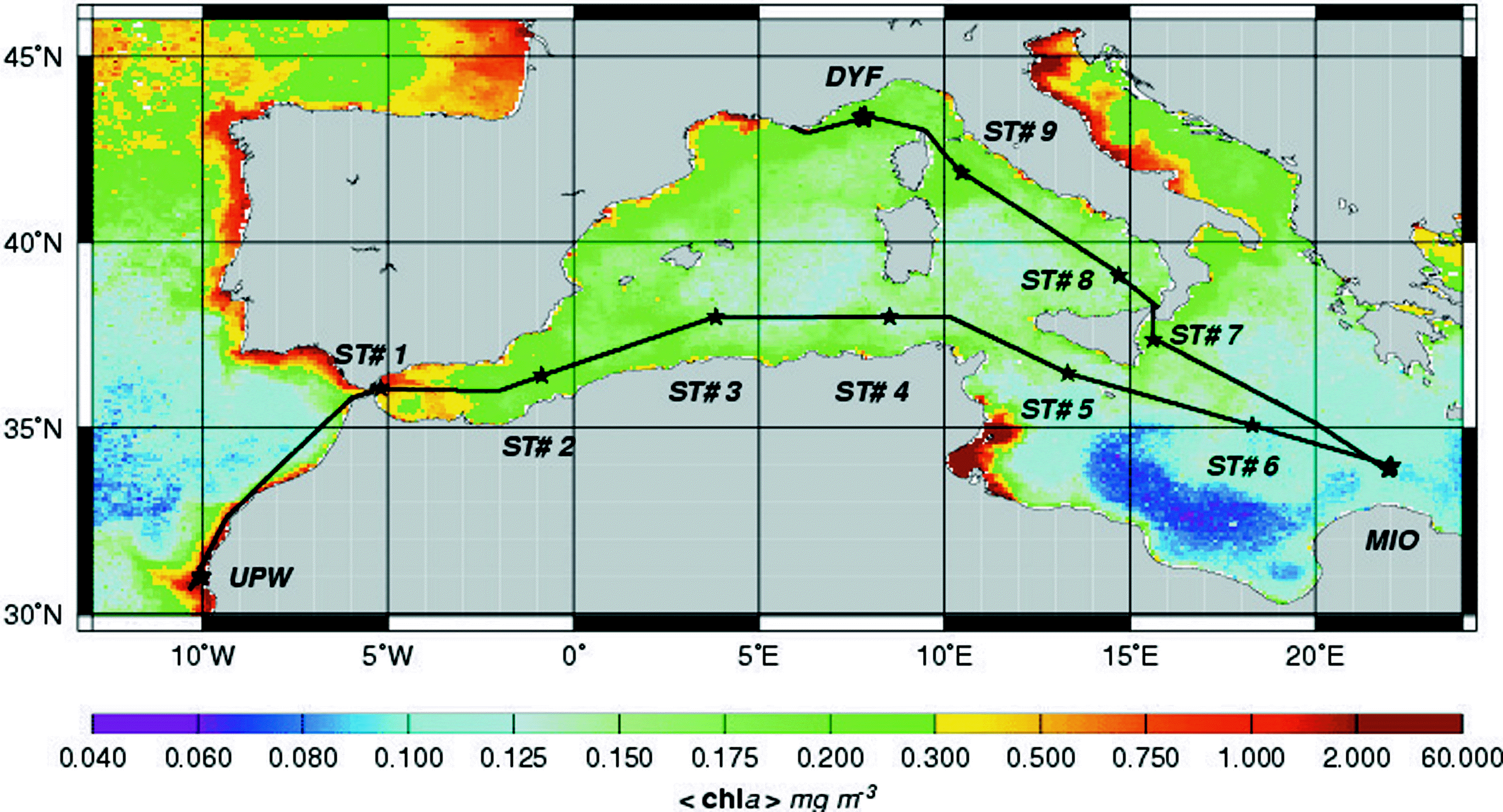
The PROSOPE (PROductivity of Oceanic PElagic Systems) cruise took place from the 4th of September (Agadir, Morocco) to the 4th of October (Toulon, France) 1999 aboard the RV Thalassa. There were four main scientific objectives: 1, carry out classical process studies, typical of the Joint Global Ocean Flux Study (JGOFS), 2, focus on small scale biogeochemical processes, in particular at a daily scale, 3, study the influence of nitrogen, phosphorus and iron on oceanic fertility and 4, conduct a calibration/validation operation for the SeaWIFS (Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor) color sensor. To reach these objectives, the studied areas, as well as the cruise plan, were designed : To investigate different trophic regimes, to investigate systems characterized by different degrees of limitation in nitrogen and phosphorus and to study stable ("steady state") systems for a sufficiently long period. The cruise track encompassed a variety of trophic systems ranging from eutrophic conditions associated to the Moroccan upwelling to the typical ultra-oligotrophic conditions of the eastern Mediterranean sea during summer stratification. Two main types of stations were occupied : - 9 short (4-hour) stations. These sites were occupied around the solar noon and were essentially designed to conduct objectives 1 (JGOFS process studies) and 4 (SeaWIFS validation/calibration) - 3 "long" (5-day) stations, where all four objectives were investigated with a particular emphasis on objectives 2 (processes at a daily scale) and 3 (nutrient resources and oceanic fertility). Between each station, continuous multiparametric (hydrological, optical, biological and chemical) surface acquisitions were performed.
-
The general objective of the PEACETIME cruise is to study the fundamental processes and their interactions at the ocean-atmosphere interface, occurring after atmospheric deposition (especially Saharan dust) in the Mediterranean Sea, and how these processes impact the functioning of the pelagic ecosystem. During the proposed 33 days cruise in the western and central Mediterranean Sea in May 2017, we will study the impact of atmospheric deposition on the cycles of chemical elements, on marine biogeochemical processes and fluxes, on marine aerosols emission and how ongoing changes will impact the functioning of Mediterranean Sea communities in the future. The cruise is designed to explore a variety of oligotrophic regimes. Combining in situ observations both in the atmosphere and the ocean, and in situ and minicosm-based on-board process studies, the 40 embarking scientists from atmosphere and ocean sciences will characterize the chemical, biological and physical/optical properties of both the atmosphere and the sea-surface microlayer, mixed layer and deeper waters. The PEACETIME strategy (season and cruise track) associated to a combination of dust transport forecasting tools and near real-time satellite remote sensing is designed to maximize the probability to catch a Saharan dust deposition event in a stratified water column in order to follow the associated processes in-situ. This coordinated multidisciplinary effort will allow us to fill the current weaknesses/lacks in our knowledge of atmospheric deposition impact in the ocean and feedbacks to the atmosphere in such oligotrophic systems. As a key joint-project between MERMEX and CHARMEX : The PEACETIME project comes in the scope of the regional multidisciplinaryprogramme MISTRALS (Mediterranean Integrated STudies at Regional And Local Scales ), which aims at predicting the evolution of this region following strong expected changes in climate and human pressures. In this framework, the PEACETIME project constitutes a key joint project between the ChArMEx (the Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment) and MERMEx (Marine Ecosystems Response in the Mediterranean Experiment) initiatives, enabling to gather communities of atmospheric chemists and marine biogeochemists around the common question of assessing the impact of atmospheric deposition on the marine biogeochemical processes and air-sea exchanges.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA