Univ Brest, CNRS, Ifremer, Geo-Ocean, F-29280 Plouzané, France
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
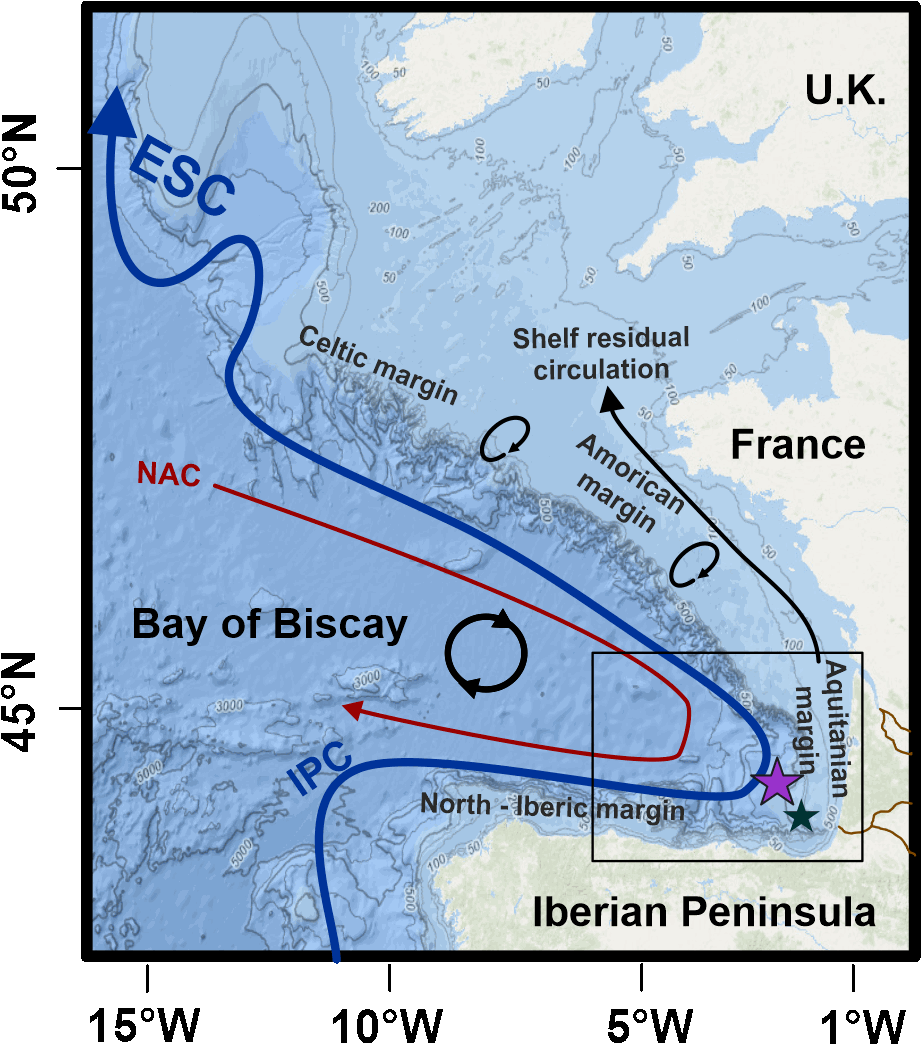
In the mid-latitudes of the northeast Atlantic, the study of the upper branch of the AMOC is poorly documented. This study provides a complete record of the glacial, deglacial and Holocene dynamics of the easternmost portion of the upper branch of the AMOC, namely the European Slope Current and its glacial equivalent know as the Glacial Eastern Boundary Current (GEBC). To do so, we use core SU81-44 (~1000 m water depth) from the of southern Bay of Biscay (BoB) upper slope, .The aim of this study is to reconstruct paleoenvironmental and hydrodynamic changes using a multiproxy approach (i.e. benthic foraminiferal assemblage, grain size proxies, oxygen and carbon stable isotopes, and foraminiferal εNd). During the glacial period and the onset of the deglaciation, our results show that the grain size proxies together with the relative densities of the high-energy indicator species Trifarina angulosa and the low oxygen tolerant Globobulimina spp. showed significant fluctuations. These were concomitant with the main climate changes recognized over this period and with the glacial slope paleoflow reconstruction from the northern BoB. This highlights a strong climatic/oceanographic forcing on the sedimentary characteristics of the region and a prominent forcing by changes in near-bottom flow speed. Our data also provide a new constraint on the strength of the slope current in the region during the late deglaciation and Holocene periods. We observe a reinvigoration of the upper branch of the AMOC during the Bølling-Allerød warming, preceding the abrupt resumption of the deeper branch of the AMOC in the western North Atlantic. This seems to confirm the crucial role of the European Slope Current in deep water formation, as it is the case today. Finally, our data show a progressive weakening of the ESC during the Holocene and we hypothesize a link with the long-term dynamics of the subpolar gyre.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA