2020
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-

Itinéraires de randonnée et pistes cyclables du Département des Landes. Le Département des Landes propose 3 500 km d’itinéraires inscrits au Plan départemental des itinéraires de promenade et de randonnée (PDIPR) et près de 2 500 km d’itinéraires cyclables. Ces circuits sont entretenus et balisés avec des niveaux de difficultés mentionnés sur chaque parcours.
-

Cette couche recense les Zones d’Activités Economiques (ZAE) présentes sur le département de la Charente. Initialement crée par Charente Développement, il s'agit d'un surfacique qui permet d'identifier précisément le contour de ces zones en se calant sur les données du Cadastre.
-
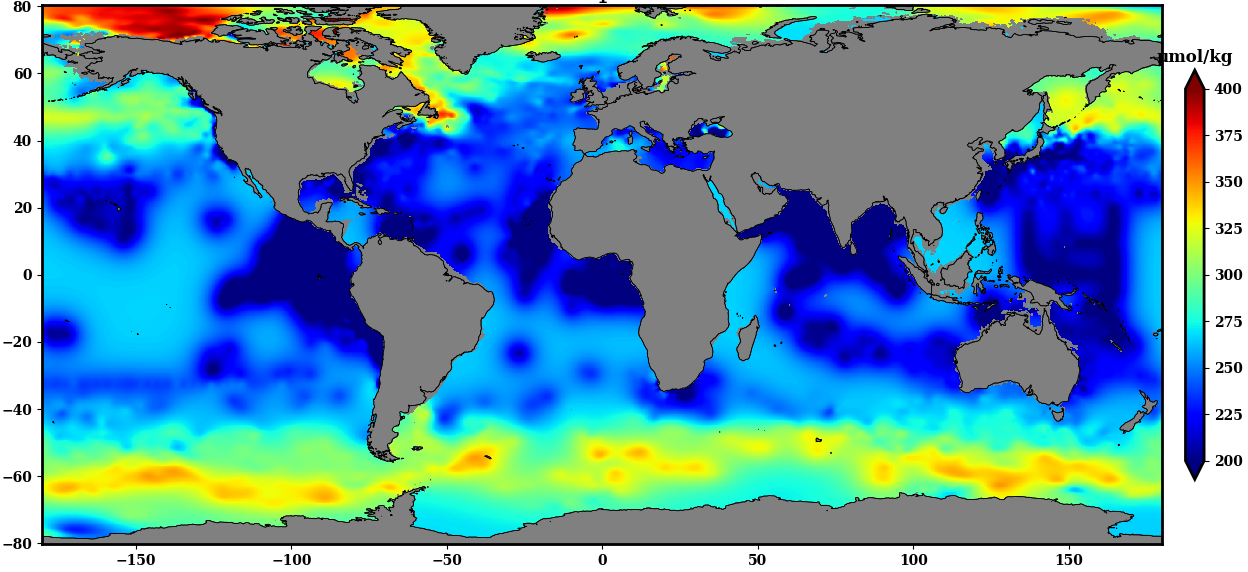
The SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2_AOU product contains two different monthly climatology for dissolved Oxygen and Apparent Oxygen Utilization, SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2 and SDC_GLO_CLIM_AOU respectively from the World Ocean Data (WOD) database. Only basic quality control flags from the WOD are used. The first climatology, SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2, considers Dissolved Oxygen profiles casted together with temperature and salinity from CTD, Profiling Floats (PFL) and Ocean Station Data (OSD) for time duration 2003 to 2017. The second climatology, SDC_GLO_CLIM_AOU, apparent Oxygen utilization, is computed as a difference of dissolved oxygen and saturation O2 profiles. The gridded fields are computed using DIVAnd (Data Interpolating Variational Analysis) version 2.3.1.
-

This dataset is the coastal zone land surface region from Europe, derived from the coastline towards inland, as a series of 10 consecutive buffers of 1km width each. The coastline is defined by the extent of the Corine Land Cover 2018 (raster 100m) version 20 accounting layer. In this version all Corine Land Cover pixels with a value of 523, corresponding to sea and oceans, were considered as non-land surface and thus were excluded from the buffer zone.
-

This metadata refers to a dataset that shows the percentage of cities' administrative area (core city based on the Urban Morphological Zones dataset) inundated by the sea level rise of 2 metres, without any coastal flooding defences present for a series of individual coastal European cities (included in Urban Audit). The dataset has been computed using the CReSIS (Centre for Remote Sensing of Ice Sheets) dataset for 2018.
-
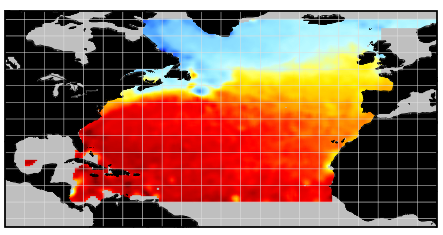
The SDC_NAT_CLIM_TS_V2 product contains Temperature and Salinity Climatologies for the North Atlantic Ocean including the seasonal and monthly fields for 7 decades starting from 1950 to 2019. One resolution has been processed : 1/2°. The climatic fields were computed from the integrated North Atlantic Ocean dataset that combines data extracted from the 2 major sources: SeaDataNet infrastructure and Coriolis Ocean Dataset for Reanalysis (CORA). The computation was done with the DIVAnd software.
-

The Marine Reporting Units (MRUs) are used within the reporting obligations of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) in order to link the implementation of the different articles to specific marine areas. The MRUs can be of varying sizes, according to the appropriate scale for the different reports (e.g. region, sub-region, regional or sub-regional subdivision, Member State marine waters, WFD coastal waters, etc.), as indicated in the Good Environmental Status 2017 Decision. The present data set is the second public version released of the MRUs used during the MSFD 2018 reporting exercise on the update of Articles 8, 9 and 10. Only the MRUs of those countries that have gone through the reporting exercise by June 2020 have been included in this data set. Apart from the countries included already in version 1 of the dataset (SE, FI, EE, LV, PL, DE, DK, NL, BE, FR, ES, HR and RO), this version also includes seven more countries, namely MT, LT, IT, SI, CY, PT and IE. The data set is distributed in SHP and in INSPIRE-compliant GML format, made available also through an INSPIRE compliant ATOM service.
-

This data set corresponds to the global offshore wind farm boundaries with the following attributes for each project: + WindfarmId (ID of the windfarm) + Name (Name of the windfarm) + Country (Country code) + Status (Status code) + WindfarmStatus (Windfarm Status or Project Status) + StatusComments (Comments on the Windfarm Status or Project Status) + CapacityMWMin (Capacity of the windfarm - Min) + CapacityMWMax (Capacity of the windfarm - Max) + NoTurbinesMin (Number of turbines - Min) + NoTurbinesMax (Number of turbines - Max) + Comments (Comments) + TurbineMWMin (Capacity of the turbine (set-up in the windfarm) - Min) + TurbineMWMax (Capacity of the turbine (set-up in the windfarm) - Max) + OtherNames (Other name of the windfarm) + CountryName (Country where the windfarm is set) + Lat (Geographic coordinate - centre latitude) + Lon (Geographic coordinate - centre longitude) + IsEstimatedLocation (This is where we know that a project exists but we don't know its exact location.) + IsOnHold + Developers (Developer(s) of the windfarm) + Owners (Owner of the windfarm) + Operators (Operator of the windfarm) + OffshoreConstructionStarts The frequency of the database release is monthly. This data set corresponds to the release of January 2020. This data set is strictly for internal EEA use as is subjected to a commercial license. Given the limited user subscriptions available, interested users should contact the SDI Team (sdi@eea.europa.eu) to be granted access to the data set.
-
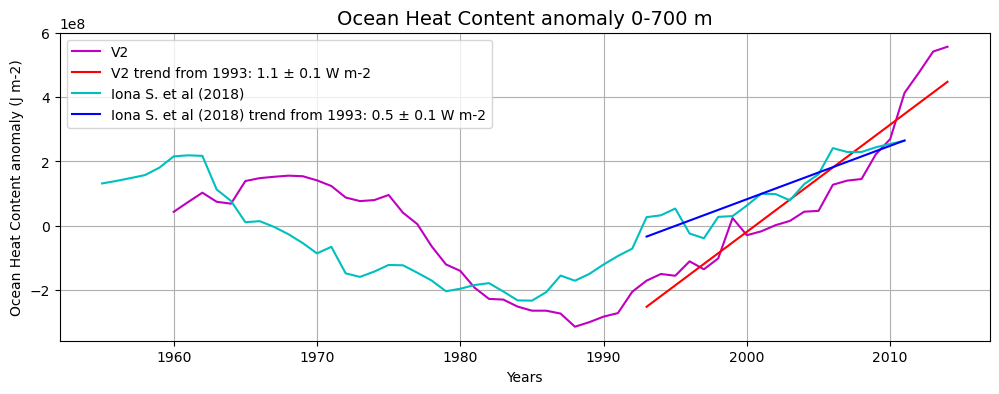
The SDC_MED_DP2 product contains 55 sliding decadal temperature fields (1955-1964, 1956-1965, 1957-1966, …, 2009-2018) at 1/8° horizontal resolution obtained in the 0-2000m layer and two derived OHC annual anomaly estimates for the 0-700m and the 0-2000m layers. Sliding decades of annual Temperature fields were obtained from an integrated Mediterranean Sea dataset covering the time period 1955-2018, which combines data extracted from SeaDataNet infrastructure at the end of July 2019 (SDC_MED_DATA_TS_V2, https://doi.org/10.12770/3f8eaace-9f9b-4b1b-a7a4-9c55270e205a) and the Coriolis Ocean Dataset for Reanalysis (CORA 5.2, accessed in July 2020, https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00595/70726/). The resulting annual OHC anomaly time series span the 1960-2014 period. The analysis was performed with the DIVAnd (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis in n dimensions), version 2.6.1.
-

'''DEFINITION''' The CMEMS NORTHWESTSHELF_OMI_tempsal_extreme_var_temp_mean_and_anomaly OMI indicator is based on the computation of the annual 99th percentile of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) from model data. Two different CMEMS products are used to compute the indicator: The North-West Shelf Multi Year Product (NWSHELF_MULTIYEAR_PHY_004_009) and the Analysis product (NORTHWESTSHELF_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_PHY_004_013). Two parameters are included on this OMI: * Map of the 99th mean percentile: It is obtained from the Multi Year Product, the annual 99th percentile is computed for each year of the product. The percentiles are temporally averaged over the whole period (1993-2019). * Anomaly of the 99th percentile in 2020: The 99th percentile of the year 2020 is computed from the Analysis product. The anomaly is obtained by subtracting the mean percentile from the 2020 percentile. This indicator is aimed at monitoring the extremes of sea surface temperature every year and at checking their variations in space. The use of percentiles instead of annual maxima, makes this extremes study less affected by individual data. This study of extreme variability was first applied to the sea level variable (Pérez Gómez et al 2016) and then extended to other essential variables, such as sea surface temperature and significant wave height (Pérez Gómez et al 2018 and Alvarez Fanjul et al., 2019). More details and a full scientific evaluation can be found in the CMEMS Ocean State report (Alvarez Fanjul et al., 2019). '''CONTEXT''' This domain comprises the North West European continental shelf where depths do not exceed 200m and deeper Atlantic waters to the North and West. For these deeper waters, the North-South temperature gradient dominates (Liu and Tanhua, 2021). Temperature over the continental shelf is affected also by the various local currents in this region and by the shallow depth of the water (Elliott et al., 1990). Atmospheric heat waves can warm the whole water column, especially in the southern North Sea, much of which is no more than 30m deep (Holt et al., 2012). Warm summertime water observed in the Norwegian trench is outflow heading North from the Baltic Sea and from the North Sea itself. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The 99th percentile SST product can be considered to represent approximately the warmest 4 days for the sea surface in Summer. Maximum anomalies for 2020 are up to 4oC warmer than the 1993-2019 average in the western approaches, Celtic and Irish Seas, English Channel and the southern North Sea. For the atmosphere, Summer 2020 was exceptionally warm and sunny in southern UK (Kendon et al., 2021), with heatwaves in June and August. Further north in the UK, the atmosphere was closer to long-term average temperatures. Overall, the 99th percentile SST anomalies show a similar pattern, with the exceptional warm anomalies in the south of the domain. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product)''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00273
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA