*
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
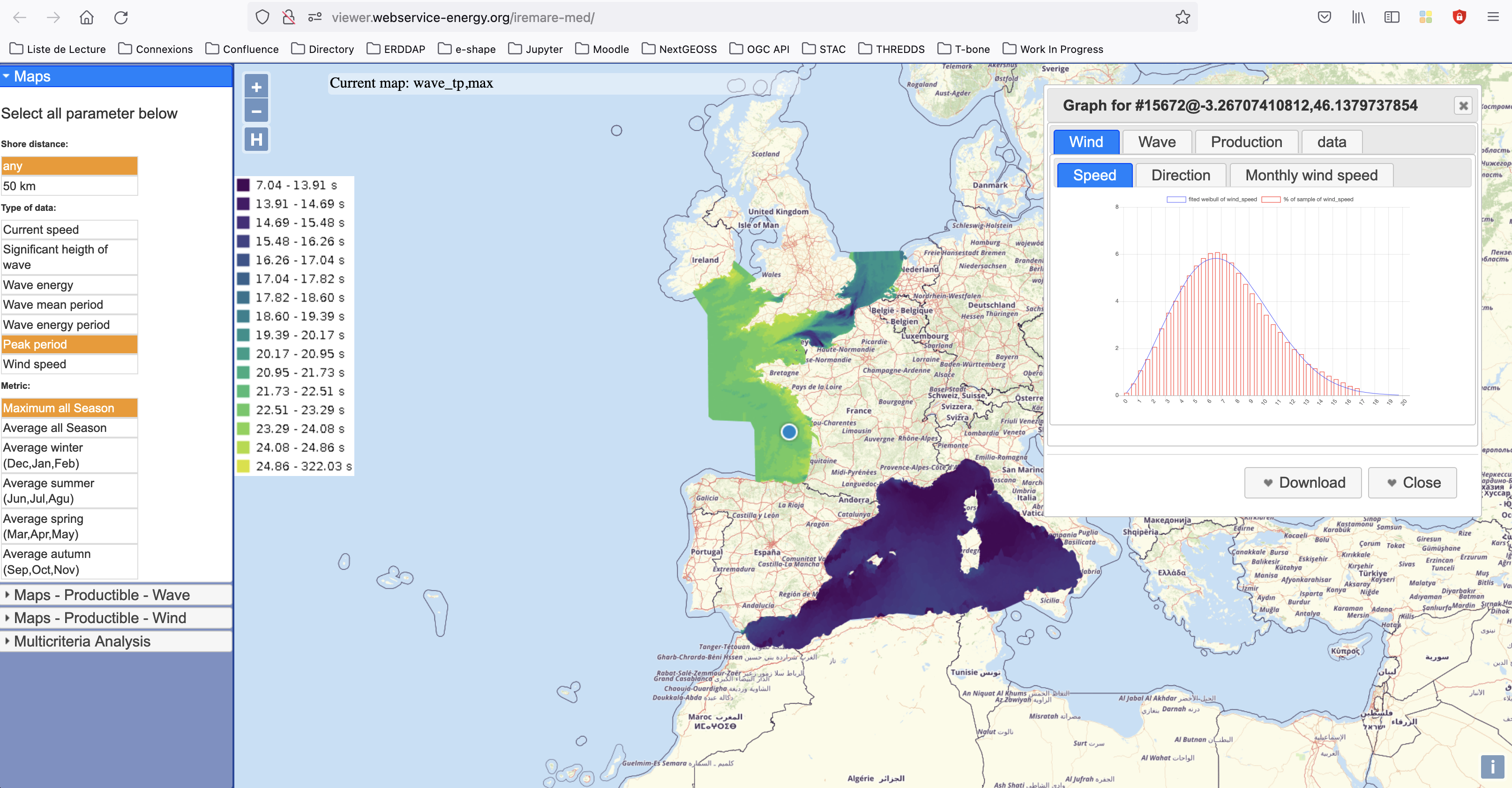
IREMARE (Marine Renewable Energie Resource Information) is a project funded by ADEME (Agency for the Environment and Energy Control, French Public Institution), convention n°1505C0027. It is dedicated to the production and dissemination of high level information about Marine Renewable Energy (MRE) resource. The information produced during IREMARE project covers the western coast of France (Atlantic, English Channel and North Sea) and can be used for national down to local scale studies. IREMARE-MED (Informations sur la Ressource pour les Energies MArines REnouvelables en MEDiterranée/Marine Renewable Energie Resource Information in the Mediterranean) is a project funded by ADEME (Agence de l'Environnement et de la Maitrise de l'Energie/Agency for the Environment and Energy Control, French Public Institution), convention n°1705C0016. It is dedicated to the production and dissemination of high level information about Marine Renewable Energy (MRE) resource. The data comes from the HOMERE database (Boudiere et al. 2013) for the zone Atlantic, Channel and North Sea and from the ANEMOC-2 dataset (Tiberi-Wadier et al. 2016) for the Mediterranean Sea.
-
Conversion into the EMODnet format of the published grid for the Capbreton Canyon in 2007: http://dx.doi.org/10.12770/72e2f750-c255-11df-a9b6-005056987263
-

-

The abundance of ichthyoplankton in samples from dedicated plankton surveys by Cefas with positional and sample data. Surveys took place off the Western Coast of the UK and Ireland between 1986 and 2004. Series of cruises undertaken to contribute to the estimation of the spawning stock biomass of the western mackerel and horse mackerel stocks by plankton survey. The triennial mackerel egg surveys were begun in 1977 to estimate the SSB of the western mackerel stock. Since 1986 the surveys have also been used to estimate the SSB of horse mackerel. Plankton sampling is undertaken to estimate the egg production and trawling is carried out to estimate the mean fecundity of the mature female fish. Various designs of Gulf VII type samplers have been used with various apertures of nosecones and 270 micron nets. Samplers are now standardised to the 53cm version, fitted with 20cm aperture nosecones. Analysis at Cefas involved separating all fish eggs and larvae from samples. Where possible all eggs were identified. Eggs lacking identifiable features were measured. Where >100 eggs were found, sub-sampling was undertaken. Eggs that were unmeasured were apportioned across the size distribution of measured eggs. All mackerel and horse mackerel eggs were staged.
-
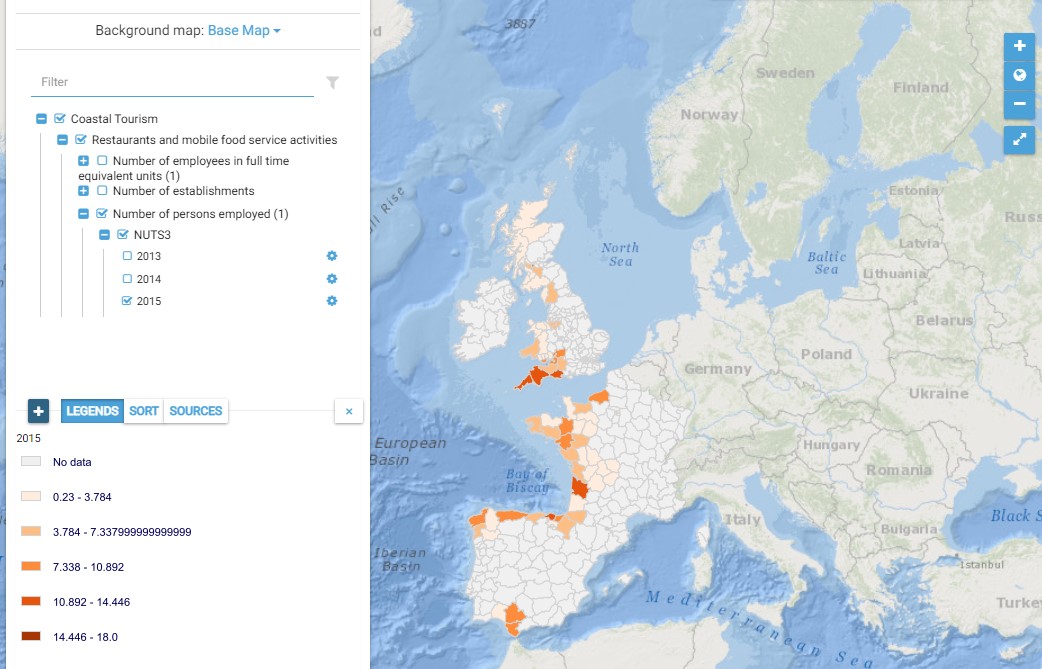
This map presents all layers corresponding to "Restaurants and mobile food service activities" activities in the Atlantic area. For more information about this NACE code : https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/ramon/nomenclatures/index.cfm?TargetUrl=DSP_NOM_DTL_VIEW&StrNom=NACE_REV2&StrLanguageCode=EN&IntPcKey=18514004&IntKey=18514034&StrLayoutCode=HIERARCHIC&IntCurrentPage=1 Indicators collected are : Number of persons employed and number of employees in full time equivalent units per NUTS 3 unit of the Atlantic Area Number of establishments per NUTS3 unit of the Atlantic Area
-

This dataset contains the biological outputs of a global ocean simulation coupling dynamics and biogeochemistry at ¼° over the year 2019. The simulation has been performed using the coupled circulation/ecosystem model NEMO/PISCES (https://www.nemo-ocean.eu/), which is here enhanced to perform an ensemble simulation with explicit simulation of modeling uncertainties in the physics and in the biogeochemistry. This dataset is one of the 40 members of the ensemble simulation. This study was part of the Horizon Europe project SEAMLESS (https://seamlessproject.org/Home.html), with the general objective of improving the analysis and forecast of ecosystem indicators. See Popov et al. (https://os.copernicus.org/articles/20/155/2024/) for more details on the study.
-

-

This dataset gathers results of monthly sampling with a WP2 plankton net within the Gironde plume (Bay of Biscay) in 2008 from March to August, as part of the ECLAIR suite of surveys. The sampling in May was part of the ECLAIR time-series but was performed onboard the THALASSA vessel during the PELGAS 2008 survey. Results are made of anchovy and sardine egg abundances, as well as size-fractionnated zooplankton biomass.
-

This dataset contains the dynamical outputs of a global ocean simulation coupling dynamics and biogeochemistry at ¼° over the year 2019. The simulation has been performed using the coupled circulation/ecosystem model NEMO/PISCES (https://www.nemo-ocean.eu/), which is here enhanced to perform an ensemble simulation with explicit simulation of modeling uncertainties in the physics and in the biogeochemistry. This dataset is one of the 40 members of the ensemble simulation. This study was part of the Horizon Europe project SEAMLESS (https://seamlessproject.org/Home.html), with the general objective of improving the analysis and forecast of ecosystem indicators. See Popov et al. (https://os.copernicus.org/articles/20/155/2024/) for more details on the study.
-
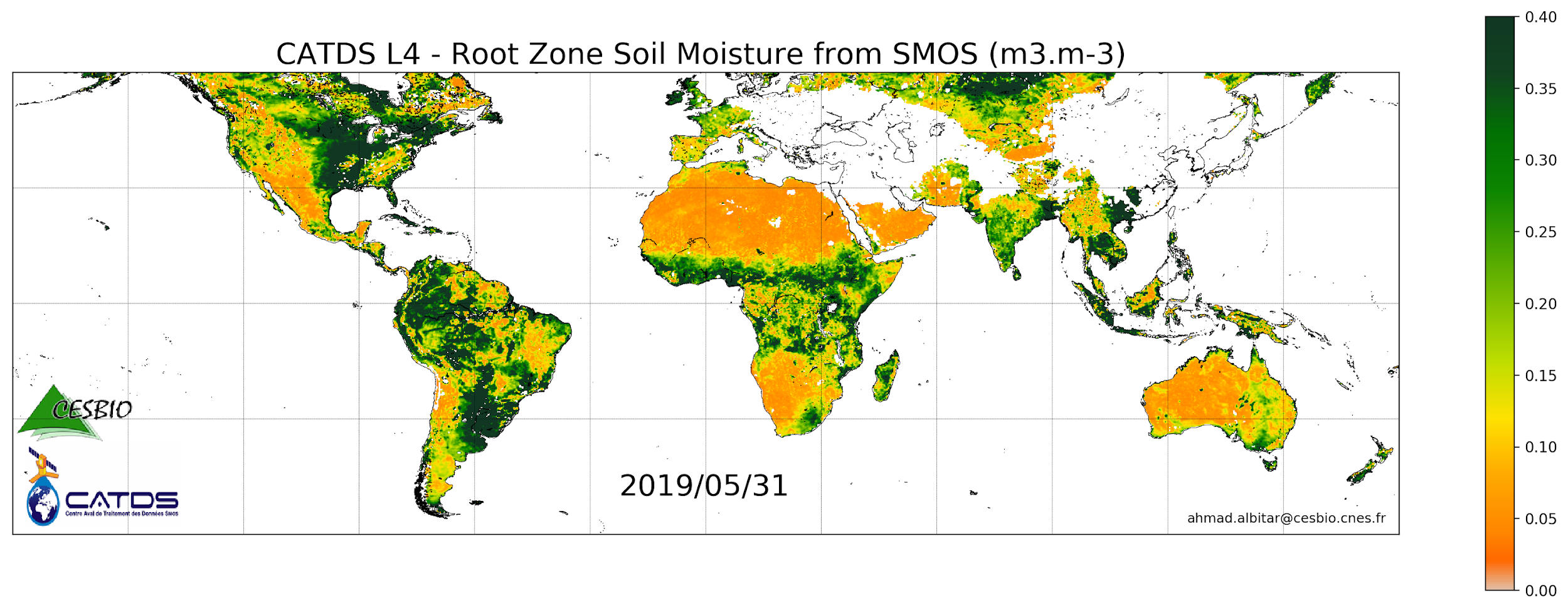
This product is a daily product of root zone soil moisture representative of the 0-1 m depth of the soil. The base products, for all the CATDS-PDC (Centre Aval de Traitement des Données SMOS - Production & Dissemination Center) processing chains, are the SMOS L1B products from ESA (European Space Agency). The L4SM RZSM is the daily product of root zone soil moisture (m3/m3) representative of the 0-1 m depth of the soil. The product contains also a quality index taking into account the presence of Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), low quality of retrieval of the input surface soil moisture, and a high fraction of non-nominal surfaces. Products from reprocessing RE07 are available for the period 01/2010 - 05/2021. Products from operational (OPER) processing are available since 06/2021. Reprocessed products and operational products are derived using the same algorithm and configuration, hence ensuring the temporal continuity.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA