/Biological Environment/Habitats
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Scale
Resolution
-
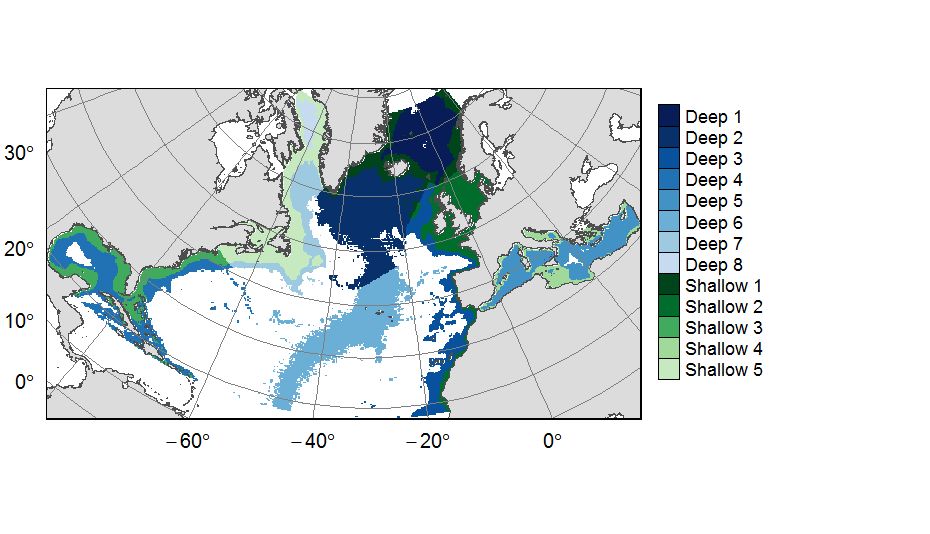
Planning units layers used for ATLAS EU prioritization scenarios on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). This raster layer is designed on a grid of 25km * 25km resolution, that served to extract all the spatial data used prioritization. The 31 518 planning units (cells with value) corresponded to areas containing depths shallower or equal to 3500m, even if they could also contain deeper areas locally. For connectivity scenarios, only the planning units matching with the extent of available connectivity data were selected. One layer allocates planning units to the 13 geographical provinces (values ranging from 1 to 13) created for the purpose of prioritization. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-

The code and files contained in this repository support replication of a broad-scale benthic habitat classification of the South Atlantic produced by McQuaid et al. (2023). We used statistical clustering algorithms to classify broad-scale (10km2) environmental data into distinct habitat classes, which reflect variation in physical conditions and we assume support distinct biological communities. We request that any use of the input data is referenced as per the table below, and that classification outputs are referenced as: McQuaid K. A. Bridges A. E. H., Howell K. L., Gandra T. B. R., de Souza V., Currie J. C., Hogg O. T., Pearman T. R. R., Bell J. B. B., Atkinson L. J., Baum D., Bonetti J., Carranza A., Defeo O., Furey T., Gasalla M. A., Golding N, Hampton S. L., Horta S., Jones D. O. B., Lombard A. T., Manca E., Marin Y., Martin S., Mortensen P., Passdore C., Piechaud N., Sink K. J. & Yool A. 2023. Broad-scale benthic habitat classification of the South Atlantic. Progress in Oceanography. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2023.103016
-
The raster corresponds to the predicted Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities.
-
The rasters correspond to the prediction uncertainties associted with the production of Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities
-
These rasters correspond to the environmental predictors used in the production of Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities
-
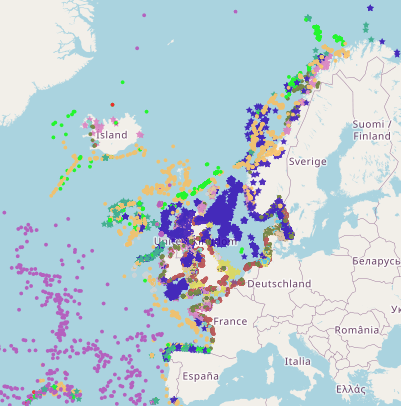
This is a compilation of OSPAR habitat point data for the northeast Atlantic submitted by OSPAR contracting parties. The compilation is coordinated by the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee, working with a representative from each of the OSPAR coastal contracting parties. This public dataset does not contain records relating to sensitive species (e.g. Ostrea edulis) in specific areas, or where data are restricted from public release by the owner's use limitations. This version (v2020) was published in July 2021.
-
The shapefile corresponds to areas where predicted bioregions were extrapolated for lack of benthic in-situ observations.
-

Portal to view and download observations of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystem (VME) indicators and habitats in the North Atlantic. A central portal for data on the distribution and abundance of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs), (and organisms considered to be indicators of VMEs) across the North Atlantic has been set up by the Joint ICES/NAFO Working Group on Deep-water Ecology (WGDEC). Criteria used to select habitats and indicators for inclusion in the database were those described in the FAO International Guidelines for the Management of Deep-sea Fisheries in the High Seas (FAO, 2009). The database is comprised of: - 'VME habitats' that are records for which there is unequivocal evidence for a VME, e.g. ROV observations of a coral reef - 'VME indicators' which are records that suggest the presence of a VME with varying degrees of uncertainty. For VME indicators a weighting system of vulnerability and uncertainty is provided as part of the database to aid interpretation. The VME database may be used for many purposes. ICES uses it when providing scientifically-robust advice on the distribution of VMEs and recommending possible management solutions such as bottom fishing closures within North East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) waters to protect VMEs.
-
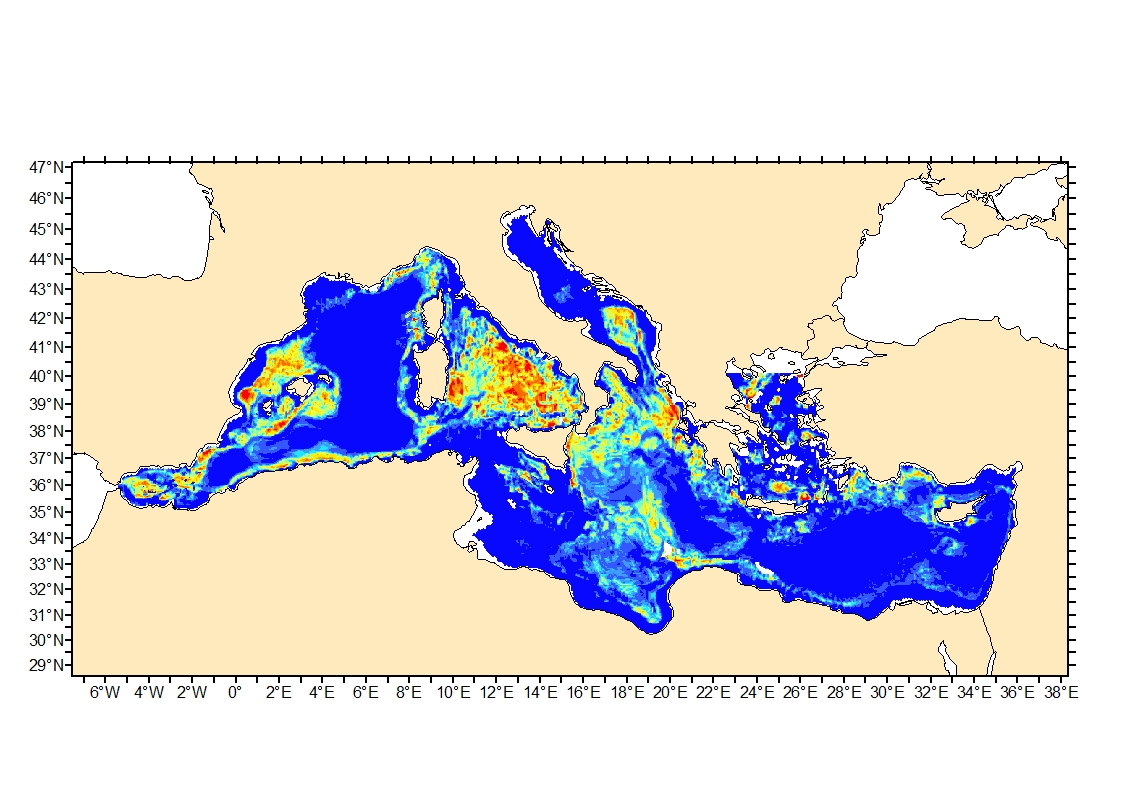
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-
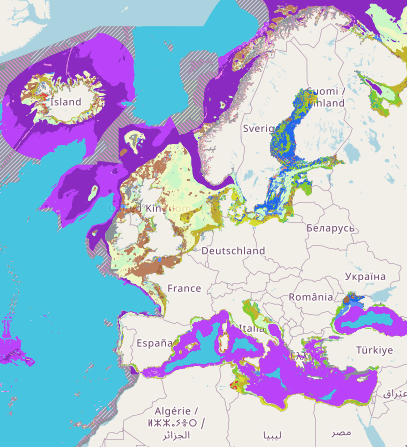
Output of the 2019 EUSeaMap broad-scale predictive model, produced by EMODnet Seabed Habitats and aggregated into the Benthic Broad Habitat Types of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (as defined in the Commission Decision 17 May 2017). The extent of the mapped area includes the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea, and areas of the North Eastern Atlantic extending from the Canary Islands in the south to the Barents Sea in the north. The map was produced using a "top-down" modelling approach using classified habitat descriptors to determine a final output habitat. Habitat descriptors differ per region but include: - Biological zone - Energy class - Oxygen regime - Salinity regime - Seabed substrate - Riverine input Habitat descriptors (excepting Substrate) are calculated using underlying physical data and thresholds derived from statistical analyses or expert judgement on known conditions.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA