International and global data portals
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Resolution
-

The ODATIS Ocean Cluster (Ocean Data Information and Services) is the entry point to access all the French Ocean observation data. Its aim is to promote and facilitate the use of Ocean observations sampled by way of in situ and remote sensing measurements. ODATIS contributes to describing, quantifying and understanding the ocean as a whole — offshore and coastal.
-

Marine research is truly multidisciplinary as evidenced by e.g. the EMODnet I, II, and III projects that have been running since 2009. EMODnet Geology has succeeded in bringing together harmonised offshore data including sea-floor geology, seabed substrates, rates of coastline migration, geological events and probabilities and mineral resources. The EMODnet Geology Portal aims at providing harmonised information on marine geology in Europe. It is one of several EMODnet portals with the purpose to strengthen blue growth in Europe.
-

The Human Activities portal was not included in the first phase of EMODnet, and its development only begun in September 2013. Nonetheless, in the previous EMODnet phase, the Human Activities team caught up with the other portals, and now work towards providing a seamless multi-resolution digital map of European waters, with the highest resolution possible. EMODnet Human Activities aims to facilitate access to existing marine data on activities carried out in EU waters, by building a single entry point for geographic information on 14 different themes. The portal makes available information such as geographical position, spatial extent of a series of activities related to the sea, their temporal variation, time when data was provided, and attributes to indicate the intensity of each activity. The data are aggregated and presented so as to preserve personal privacy and commercially-sensitive information. The data also include a time interval so that historic as well as current activities can be included. The information provided through the portal is collated from a variety of sources, harmonised and made interoperable. Data are free and free of any restrictions, in such a way as to ensure their use from a multitude of stakeholders (policy makers, researchers, students, spatial planners, etc.).
-
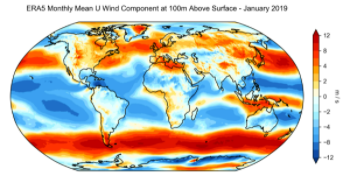
ERA5 is the fifth generation ECMWF reanalysis for the global climate and weather for the past 4 to 7 decades. Currently data is available from 1950, split into Climate Data Store entries for 1950-1978 (preliminary back extension) and from 1979 onwards (final release plus timely updates, this page). ERA5 replaces the ERA-Interim reanalysis. Reanalysis combines model data with observations from across the world into a globally complete and consistent dataset using the laws of physics. This principle, called data assimilation, is based on the method used by numerical weather prediction centres, where every so many hours (12 hours at ECMWF) a previous forecast is combined with newly available observations in an optimal way to produce a new best estimate of the state of the atmosphere, called analysis, from which an updated, improved forecast is issued. Reanalysis works in the same way, but at reduced resolution to allow for the provision of a dataset spanning back several decades. Reanalysis does not have the constraint of issuing timely forecasts, so there is more time to collect observations, and when going further back in time, to allow for the ingestion of improved versions of the original observations, which all benefit the quality of the reanalysis product. ERA5 provides hourly estimates for a large number of atmospheric, ocean-wave and land-surface quantities. An uncertainty estimate is sampled by an underlying 10-member ensemble at three-hourly intervals. Ensemble mean and spread have been pre-computed for convenience. Such uncertainty estimates are closely related to the information content of the available observing system which has evolved considerably over time. They also indicate flow-dependent sensitive areas. To facilitate many climate applications, monthly-mean averages have been pre-calculated too, though monthly means are not available for the ensemble mean and spread. ERA5 is updated daily with a latency of about 5 days (monthly means are available around the 6th of each month). In case that serious flaws are detected in this early release (called ERA5T), this data could be different from the final release 2 to 3 months later. So far this has not been the case and when this does occur users will be notified. The data set presented here is a regridded subset of the full ERA5 data set on native resolution. It is online on spinning disk, which should ensure fast and easy access. It should satisfy the requirements for most common applications. An overview of all ERA5 datasets can be found in this article. Information on access to ERA5 data on native resolution is provided in these guidelines. Data has been regridded to a regular lat-lon grid of 0.25 degrees for the reanalysis and 0.5 degrees for the uncertainty estimate (0.5 and 1 degree respectively for ocean waves). There are four main sub sets: hourly and monthly products, both on pressure levels (upper air fields) and single levels (atmospheric, ocean-wave and land surface quantities). The present entry is "ERA5 monthly mean data on single levels from 1979 to present".
-
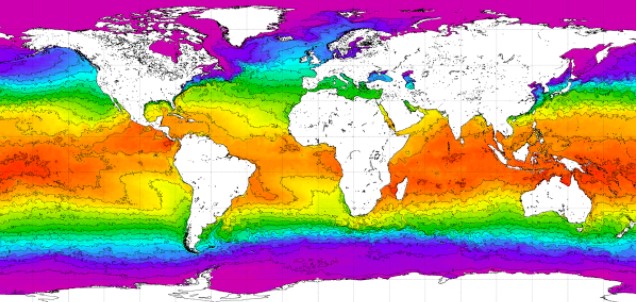
World Ocean Atlas 2018 (WOA18) is a set of objectively analyzed (one degree grid and quarter degree grid) climatological fields of in situ temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, Apparent Oxygen Utilization (AOU), percent oxygen saturation, phosphate, silicate, and nitrate at standard depth levels for annual, seasonal, and monthly compositing periods for the World Ocean. Quarter degree fields are for temperature and salinity only. It also includes associated statistical fields of observed oceanographic profile data interpolated to standard depth levels on quarter degree, one degree, and five degree grids. Temperature and salinity fields are available for six decades (1955-1964, 1965-1974, 1975-1984, 1985-1994, 1995-2004, and 2005-2017) an average of all decades representing the period 1955-2017, as well as a thirty year "climate normal" period 1981-2010. Oxygen fields (as well as AOU and percent oxygen saturation) are available using all quality controlled data 1960-2017, nutrient fields using all quality controlled data from the entire sampling period 1878-2017. This accession is a product generated by the National Centers for Environmental Information's (NCEI) Ocean Climate Laboratory Team. The analyses are derived from the NCEI World Ocean Database 2018.
-

The EMODnet Bathymetry portal is operated and further developed by a European partnership. This comprises members of the SeaDataNet consortium together with organisations from marine science, the hydrographic survey community, and industry. The partners combine expertises and experiences of collecting, processing, and managing of bathymetric data together with expertises in distributed data infrastructure development and operation and providing OGC services (WMS, WFS, and WCS) for viewing and distribution. SeaDataNet is a leading infrastructure in Europe for marine & ocean data management, initiated and managed by the National Oceanographic Data Centres (NODC's). It is actively operating and further developing a Pan-European infrastructure for managing, indexing and providing access to ocean and marine data sets and data products, acquired via research cruises and other in-situ observational activities. The basis of SeaDataNet is interconnecting Data Centres into a distributed network of data resources with common standards for metadata, vocabularies, data transport formats, quality control methods and flags, and access. SeaDataNet is aiming for an extensive coverage of available data sets for the various marine environmental disciplines, such as physical oceanography, marine chemistry, biology, biodiversity, geology, geophysics and bathymetry. This is implemented by seeking active cooperation at a national scale with institutes and at a European scale with communities, that are engaged in data management for these disciplines, and by seeking opportunities for including their data centres and data collections in the SeaDataNet metadata and data provision.
-

EMODnet Physics provides a combined array of services and functionalities to obtain free-of-charge data, meta-data and data products on the physical conditions of European sea basins and oceans as recorded by more than 20.000 platforms (fixed stations, surface loads, ARGOs, HF radars, etc.) The system provides full interoperability with third-party software through WMS services, Web Services and Web catalogues in order to exchange data and products according to the most recent standards. EMODnet Physics builds on and is based on the cooperation and collaboration with the three established pillars of the European Oceanographic Community: 1) EuroGOOS and its Regional Operational Oceanographic Systems (ROOSs); 2) Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) , and in particular with the In Situ Thematic Assembly Center (INSTAC); 3) SeaDataNet network of National Oceanographic Data Centres (NODCs). Data are made available by EMODnet Physics, funded by the European Commission Directorate General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries, in collaboration with Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS) and EuroGOOS ROOSs INSTAC. Delayed mode data integrates the best available version of in situ data. These data are collected from national observing systems operated by EuroGOOS ROOS members, SeaDataNet NODCs completed by main global networks
-

EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data Network) is the long term marine data initiative supported by the European Commission since 2009 to ensure that European marine data will become easily accessible, interoperable, and free on restrictions on use. EMODnet Chemistry provides access to standardized, harmonized and validated chemical data collections for water quality evaluation at a regional scale, as defined by the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). The data portal has adopted and adapted SeaDataNet standards and services, establishing interoperability between the data sets from the many different providers (more than 60 in EMODnet Chemistry network). Concentration maps of nutrients, chlorophyll-a and dissolved oxygen are computed on a standard grid, providing information at a regular time interval, per season and over several vertical layers, including the deepest one. Dedicated OGC standard services for browsing, viewing and downloading chemistry observation, data and data products for the European waters have been developed, and are actively maintained and monitored.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA