Salinity
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
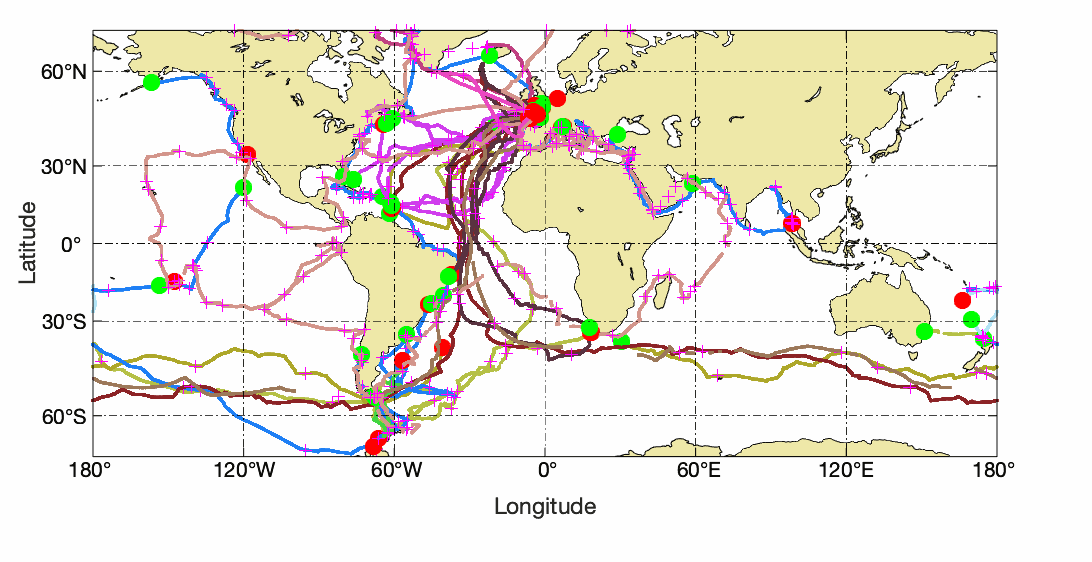
Observations of Sea surface temperature and salinity are now obtained from voluntary sailing ships using medium or small size sensors. They complement the networks installed on research vessels or commercial ships. The delayed mode dataset proposed here is upgraded annually as a contribution to GOSUD (http://www.gosud.org )
-
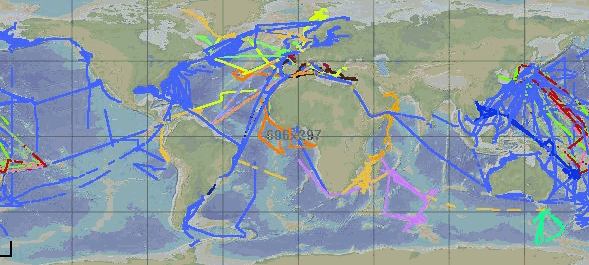
GOSUD aims at assembling in-situ observations of the world ocean surface collected by a variety of ships and at distributing quality controlled datasets. At present time the variables considered by GOSUD are temperature and salinity. The GOSUD data are mostly collected using thermosalinographs (TSG) installed on research vessels, on commercial ships and in some cases on sailing exploration ships GOSUD manages both near-real time data and delayed mode (reprocessed) data.
-
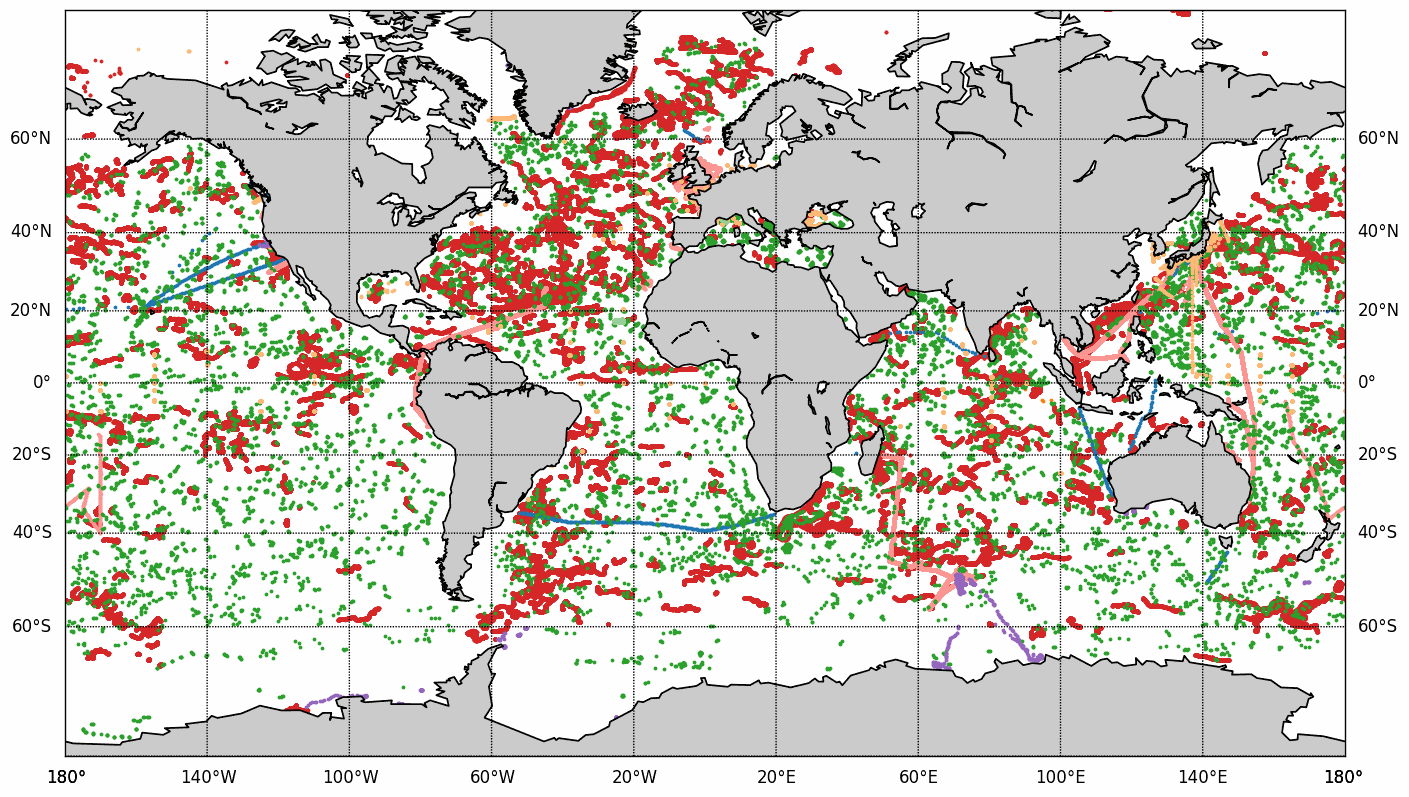
The COriolis Ocean Dataset for Reanalysis (hereafter "CORA") product is a global dataset of in situ temperature and salinity measurements. The CORA observations comes from many different sources collected by Coriolis data centre in collaboration with the In Situ Thematic Centre of the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS INSTAC). The observation integrated in the CORA product have been acquired both by autonomous platforms (Argo profilers, fixed moorings , gliders , drifters, sea mammals) , research or opportunity vessels (CTDs, XBTs, ferrybox). From the near real time CMEMS In Situ Thematic Centre product validated on a daily and weekly basis for forecasting purposes, a scientifically validated product is created. It s a "reference product" updated on a yearly basis since 2007. This product has been controlled using an objective analysis (statistical tests) method and a visual quality control (QC). This QC procedure has been developed with the main objective to improve the quality of the dataset to the level required by the climate application and the physical ocean re-analysis activities. It provides T and S weekly gridded fields and individual profiles both on their original level with QC flags and interpolated level. The measured parameters, depending on the data source, are : temperature, salinity. The reference level of measurements is immersion (in meters) or pressure (in decibars). CORA contains historical profiles extracted from the EN.4 global T&S dataset, World Ocean Atlas, SeaDataNet, ICES and other data aggregators . The last version of the CORA product are also available freely from the Copernicus WEB site : - Global Ocean- CORA- In-situ Observations Yearly Delivery in Delayed Mode - Global Ocean- Delayed Mode gridded CORA- In-situ Observations objective analysis in Delayed Mode
-

The Mytilobs network, carried out by IFREMER (French Research Institute for Exploitation of the Sea), is a national network dedicated to building long-term physiological variations time series of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis), across a large spatial scale. This observation network, initially designed to survey production yields, also provides valuable data to track environmental variations of coastal ecosystems. Mussels exhibit high phenotypic plasticity in response to environmental variations. Collection of data describing phenotypic variations, over an extended period, reveals small-scale climate and habitat variations. With its broad deployment across time and space, the data produced under Mytilobs will be useful for the establishment of a baseline condition when studying the effect of a perturbation affecting an ecosystem’s functioning. Finally, the monitoring of mussel biometric traits and mortality was coupled with high-frequency measurements of salinity, temperature, and sea level, complementing this multi-layer observational framework.
-

Measurements by drifting surface buoys. This system is a drifting mooring consisting of a surface buoy fastened to a floating anchor by a cable (trip line, buoy rope). It has to monitor as precisely as possible the water volume in which the floating anchor is immersed. The surface buoys are traced by Argos satellites.
-
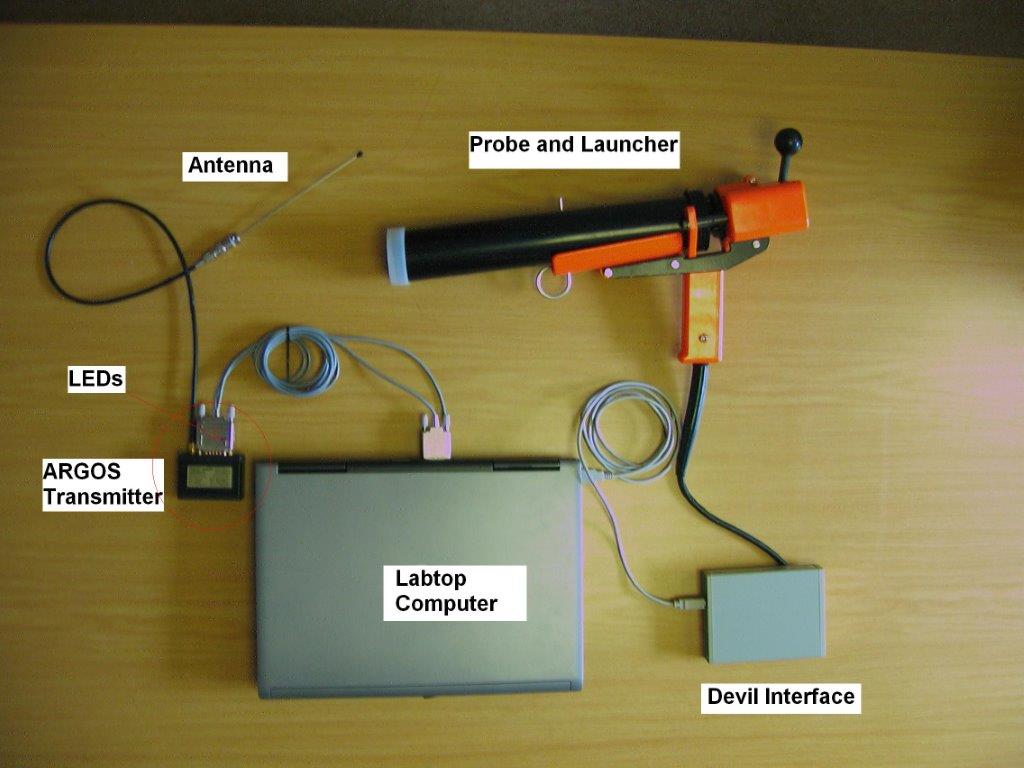
X : eXpendable; B : Bathy; T: Thermograph. Thermal profile measurement with real-time transmission
-
.jpg)
The Sir Alister Hardy Foundation for Ocean Science (SAHFOS) is an international charity that operates the Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR) Survey. The dataset covers the North Atlantic and the North Sea on since 1958.
-
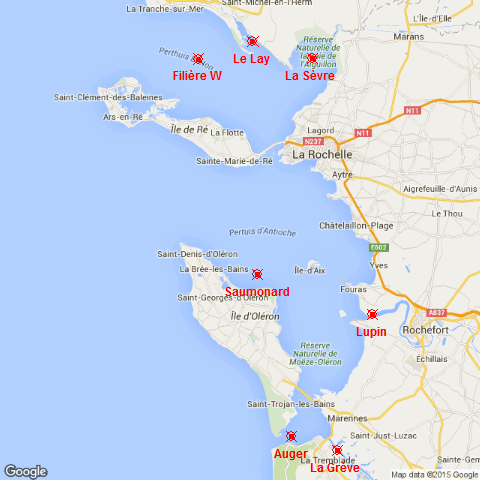
The SAPERCHAIS program (Suivi des Apports marins et terrigènes dans la mer des PERtuis CHarentAIS) was developed to monitor environmental fluctuations in the Pertuis Charentais Sea by an hydrological watchfulness. Seven stations, representatives of terrigenous or marine inputs, have been followed from 2011 to 2014. From north to south, the main four rivers of the Pertuis, Le Lay, La Sèvre, Charente and Seudre, and the three maritime inputs of each strait, Breton, Antioche and Maumusson. At each station, temperature and salinity were recorded in situ, just below the surface, with a high frequency resolution (10 minutes) . This work was supported by grants from Région Poitou-Charentes and European Regional Development Fund to the Ifremer "Developpement Durable de la Pêche et de la Conchyliculture" project.
-
The SeaDataNet aggregated datasets over the Atlantic Ocean are regional ODV historical collections of all temperature and salinity measurements contained within SeaDataNet database and covering 3 European sea basins: North Arctic Ocean, North Sea, North Atlantic Ocean. Two versions have been published during SeaDataNet 2 and they represent a snapshot of the SeaDataNet database content at two different times: • V1.1 January 2014 • V2 March 2015 Each of them is the result of the Quality Check Strategy (QCS) implemented during SeaDataNet 2 that contributed to highly improve the quality of temperature and salinity data. The QCS is made by four main phases: 1. data harvesting from the central CDI 2. file and parameter aggregation 3. quality check analysis at regional level 4. analysis and correction of data anomalies. The aggregated datasets have been prepared and quality checked using ODV software.
-
GOSUD aims at assembling in-situ observations of the world ocean surface collected by a variety of ships and at distributing quality controlled datasets. At present time the variables considered by GOSUD are temperature and salinity. The GOSUD data are mostly collected using thermosalinographs (TSG) installed on research vessels, on commercial ships and in some cases on sailing exploration ships. GOSUD manages both near-real time (RT and NRT) data and delayed mode (DM-reprocessed) data. The GOSUD GDAC is hosted by the Coriolis data centre (France) and a back-up (permanent archived) is performed on a daily basis by NCEIS (NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information).
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA