temperature
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
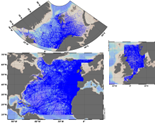
The SeaDataNet aggregated datasets over the Atlantic Ocean are regional ODV historical collections of all temperature and salinity measurements contained within SeaDataNet database and covering 3 European sea basins: North Arctic Ocean, North Sea, North Atlantic Ocean. Two versions have been published during SeaDataNet 2 and they represent a snapshot of the SeaDataNet database content at two different times: • V1.1 January 2014 • V2 March 2015 Each of them is the result of the Quality Check Strategy (QCS) implemented during SeaDataNet 2 that contributed to highly improve the quality of temperature and salinity data. The QCS is made by four main phases: 1. data harvesting from the central CDI 2. file and parameter aggregation 3. quality check analysis at regional level 4. analysis and correction of data anomalies. The aggregated datasets have been prepared and quality checked using ODV software.
-
Shom uses HYCOM 3D (Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model) digital models to model changes to the ocean environment (currents, temperature, salinity, water depth). These HYCOM 3D models include a scalable (space and time) vertical grid, which is particularly suitable for the coastal regions and physical phenomena modelled (particularly the transition from a deep sea zone to the continental shelf, and the presence of frontal zones). These models were adapted to coastal models at Shom, particularly by integrating tides and the effects of rivers. These models focus on changes and variability in the different physical processes affecting coastal areas (continental shelves and slopes), such as tidal fronts, river plumes, tides and internal waves, upwelling and the dynamics of the mixed layer at an hourly frequency and with high spatial resolution (1/60 deg for the Biscay Channel model).
-
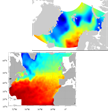
SeaDataNet gridded climatologies are based on the SeaDataNet Temperature and Salinity historical data collection v1.1. For the Atlantic Ocean there are covering 2 European sea basins: North Arctic Ocean, and North Atlantic Ocean The preparation of the products has also improved the quality, the consistency and the overall coherence of the data made available by SeaDataNet. They have been computed using DIVA software.
-

Unveiling the implications of hybridization on fitness stands as a primary focus in the realms of ecology and evolution. Numerous investigations elucidate how evolutionary mechanisms regulate the intricate pattern of introgression across genomes, yet few have examined the consequential impact of genetic admixture on fitness attributes. Leveraging the Western Mediterranean population of the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), a population formed through hybridization of the Atlantic and Mediterranean lineages in the Alboran Sea, we utilized the Axiom Sea Bass 57k SNP DlabChip array to genotype 1850 hybrid individuals. This enabled us to evaluate the correlation between individual admixture levels and fitness traits under varying thermal conditions (19°C, 21°C, 23°C, and 25°C). Our initial findings unveil a male-biased sex ratio and high temperature sensitivity among admixed individuals with a greater proportion of Atlantic ancestry. Subsequently, our analysis demonstrates that individuals with a higher Atlantic genetic background also exhibit reduced body weight (a parameter linked to fecundity in fish) compared to those with lower Atlantic ancestry. These outcomes underscore the disadvantageous nature of Atlantic ancestry introgression in the Mediterranean region, aligning with previous observations of the elimination of Atlantic ancestry segments subsequent to hybridization.
-
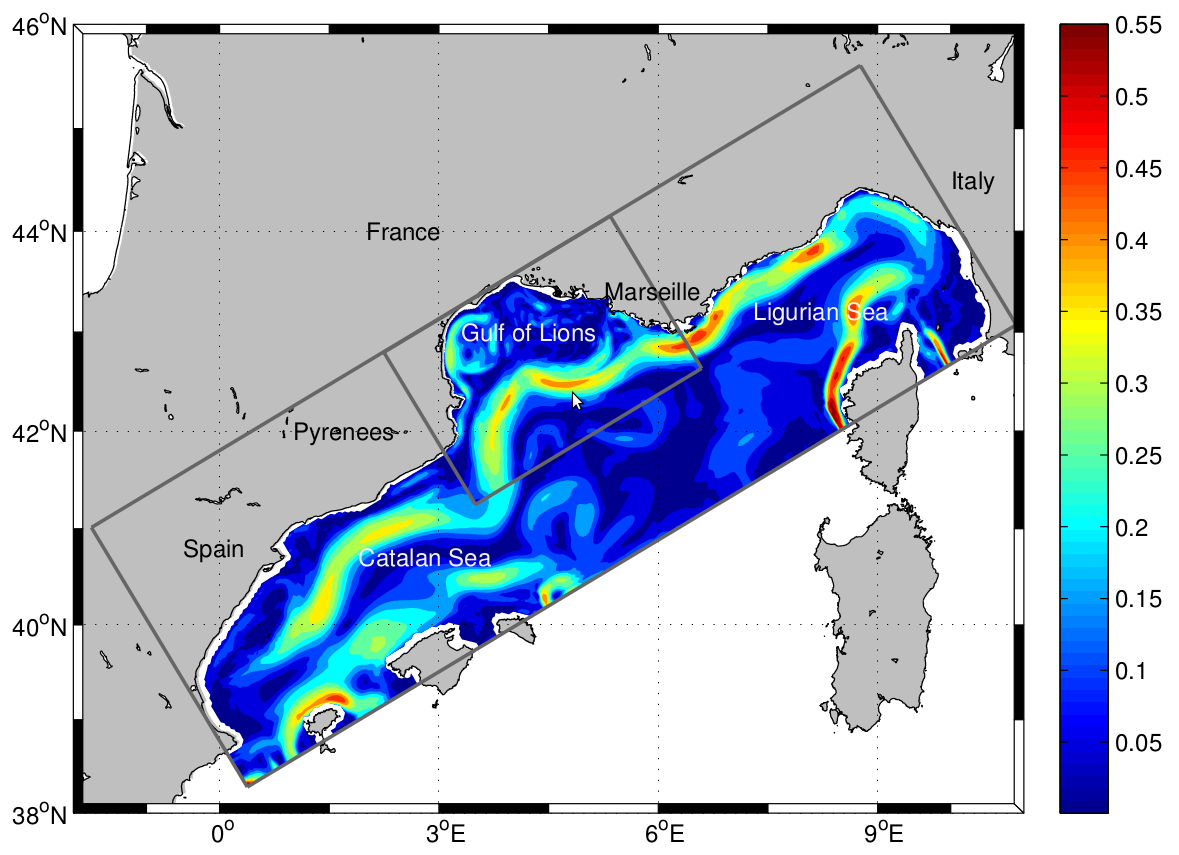
The LAgrangian Transport EXperiment (LATEX) project (2008-2011) is designed to study the mechanisms of formation of anticyclonic eddies and their influence on cross-shelf exchanges in the western part of the GoL. The dynamics of mesoscale eddies is particularly important in this part of the GoL since it represents a key region for regulating the outflow from the continental shelf. The eddy dynamics is investigated using Symphonie, a 3-dimensional, primitive equation model, with a free sea surface, hybrid sigma coordinates, based on Boussinesq and hydrostatic approximations [Marsaleix et al., 2006, 2008]. We use the upwind-type advection-diffusion scheme adapted by Hu et al. [2009] to improve the ability of the model to reproduce coastal mesoscale eddies in the western part of the GoL. In the present study, the model is implemented over the whole GoL with an horizontal resolution of 1 km × 1 km (Figure 1). The vertical discretization consists of 40-hybrid vertical levels. The vertical resolution varies from 1 m in the upper ocean to 40 m near the bottom. "For a complete review of the LATEX projet, see : - Petrenko, A., A., Doglioli, A.M., Nencioli, F., Kersalé, M., Hu, Z., d'Ovidio, F. (2017). A review of the LATEX project: mesoscale to submesoscale processes in a coastal environment. Ocean Dynam., 67:513 - doi: 10.1007/s10236-017-1040-9 - https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-017-1040-9 ----- Le projet LAgrangian Transport EXperiment (LATEX) (2008-2011) est conçu pour étudier les mécanismes de formation des tourbillons anticycloniques et leur influence sur les échanges entre plateaux dans la partie occidentale du GdL. La dynamique des tourbillons à méso-échelle est particulièrement importante dans cette partie du GdL, car elle représente une région clé pour la régulation du flux sortant du plateau continental. La dynamique des tourbillons est étudiée à l'aide de Symphonie, un modèle d'équation primitive tridimensionnel, avec une surface de mer libre, des coordonnées sigma hybrides, basé sur Boussinesq et des approximations hydrostatiques [Marsaleix et al., 2006, 2008]. Nous utilisons le schéma d'advection-diffusion de type vent debout adapté par Hu et al [2009] pour améliorer la capacité du modèle à reproduire les tourbillons côtiers à méso-échelle dans la partie occidentale du GdL. Dans la présente étude, le modèle est mis en œuvre sur l'ensemble du GdL avec une résolution horizontale de 1 km × 1 km (Figure 1). La discrétisation verticale est constituée de 40 niveaux verticaux hybrides. La résolution verticale varie de 1 m dans la partie supérieure de l'océan à 40 m près du fond. Pour plus d'information sur le projet LATEX : - Petrenko, A., A., Doglioli, A.M., Nencioli, F., Kersalé, M., Hu, Z., d'Ovidio, F. (2017). A review of the LATEX project: mesoscale to submesoscale processes in a coastal environment. Ocean Dynam., 67:513 - doi:10.1007/s10236-017-1040-9 - https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-017-1040-9
-
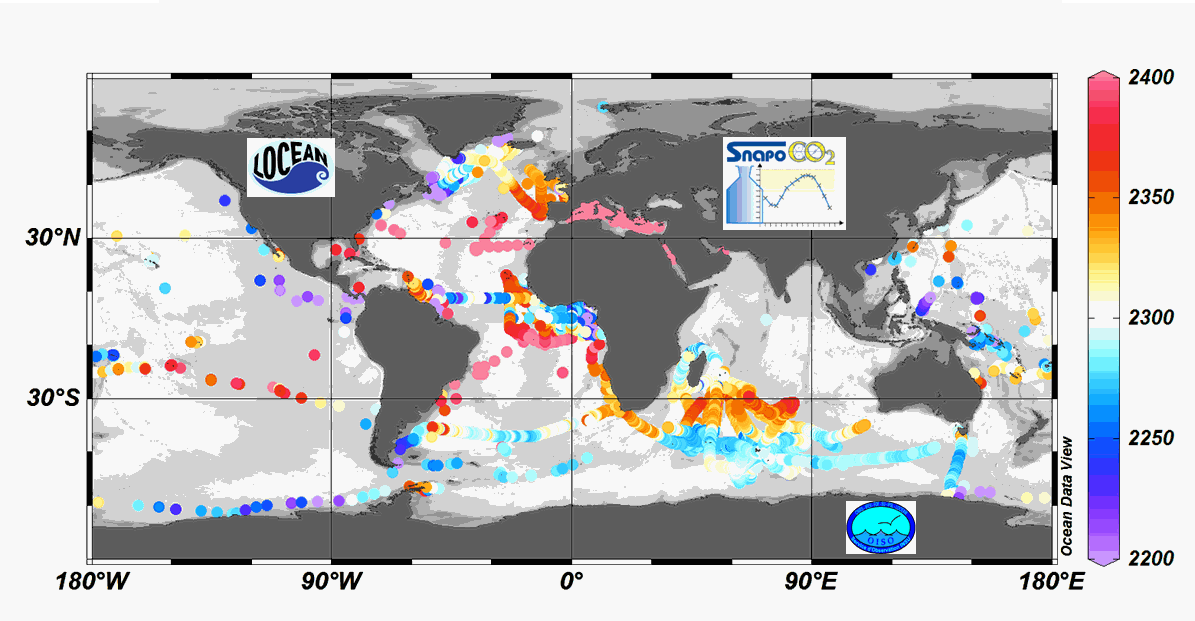
Since 2004, the Service facility SNAPO-CO2 (Service National d’Analyse des Paramètres Océaniques du CO2) housed by the LOCEAN laboratory (Paris, France) has been in charge for the analysis of Total Alkalinity (AT) and Total dissolved inorganic carbon (CT) of seawater samples on a series of cruises or ships of opportunity conducted in different regions in the frame of French projects. More than 44000 observations are synthetized in this work. Sampling was performed either from CTD-Rosette casts (Niskin bottles) or collected from the ship’s seawater supply (intake at about 5m depth). After completion of each cruise, discrete samples were returned back at LOCEAN laboratory and stored in a dark room at 4 °C before analysis generally within 2-3 months after sampling (sometimes within a week). AT and CT were analyzed simultaneously by potentiometric titration using a closed cell (Edmond, 1970). Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) provided by Pr. A. Dickson (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, San Diego, USA) were used to calibrate the measurements. The same instrumentation was used for underway measurements during OISO cruises (https://doi.org/10.18142/228) and OISO AT-CT data for 1998-2018 in the South Indian Ocean added in this synthesis. The synthesis is organized in two files (one for Global ocean and the Coastal Zones, one for the Mediterranean Sea) with the same format: Cruise name, Ship name, day, month, year, hour, minute, second, latitude, longitude, depth, AT (µmol/kg), Flag-AT, CT (µmol/kg), Flag-CT, Temperature (°C), Flag-Temp, Salinity (PSU), Flag-Salinity, nsample/cruise, nsample on file, sampling method.
-
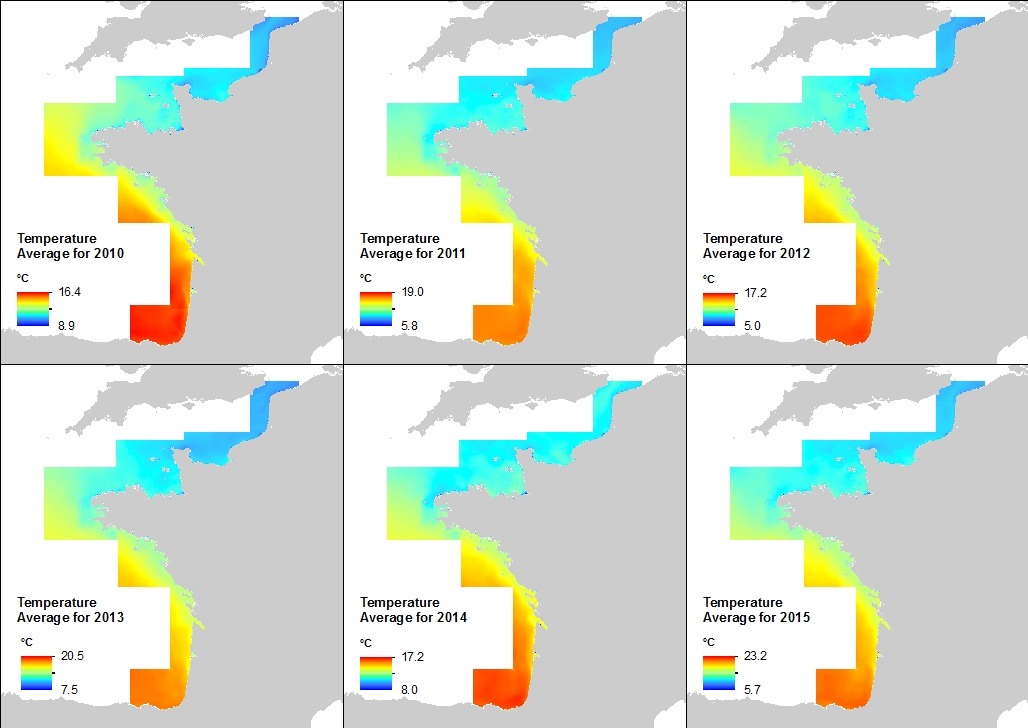
This annual statistics at 500m horizontal resolution was produced from the archived time series of MARS 3D physics model hindcast runs along French Atlantic Coast. The variable that is available here is the Temperature. Values are expressed in Celcius degrees. The vertical level is the seabed.
-
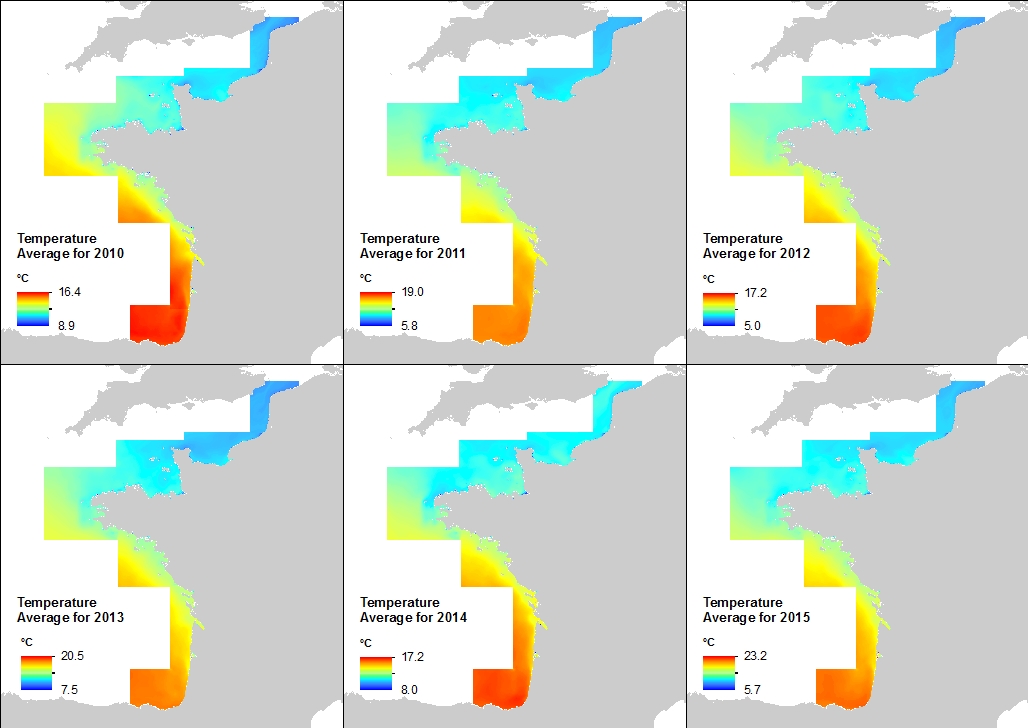
This annual statistics at 500m horizontal resolution was produced from the archived time series of MARS 3D physics model hindcast runs along French Atlantic Coast. The variable that is available here is Temperature. Values are expressed in Celsius degrees. In each pixel the value is an average of the values of the 40 vertical levels that are considered in the model.
-
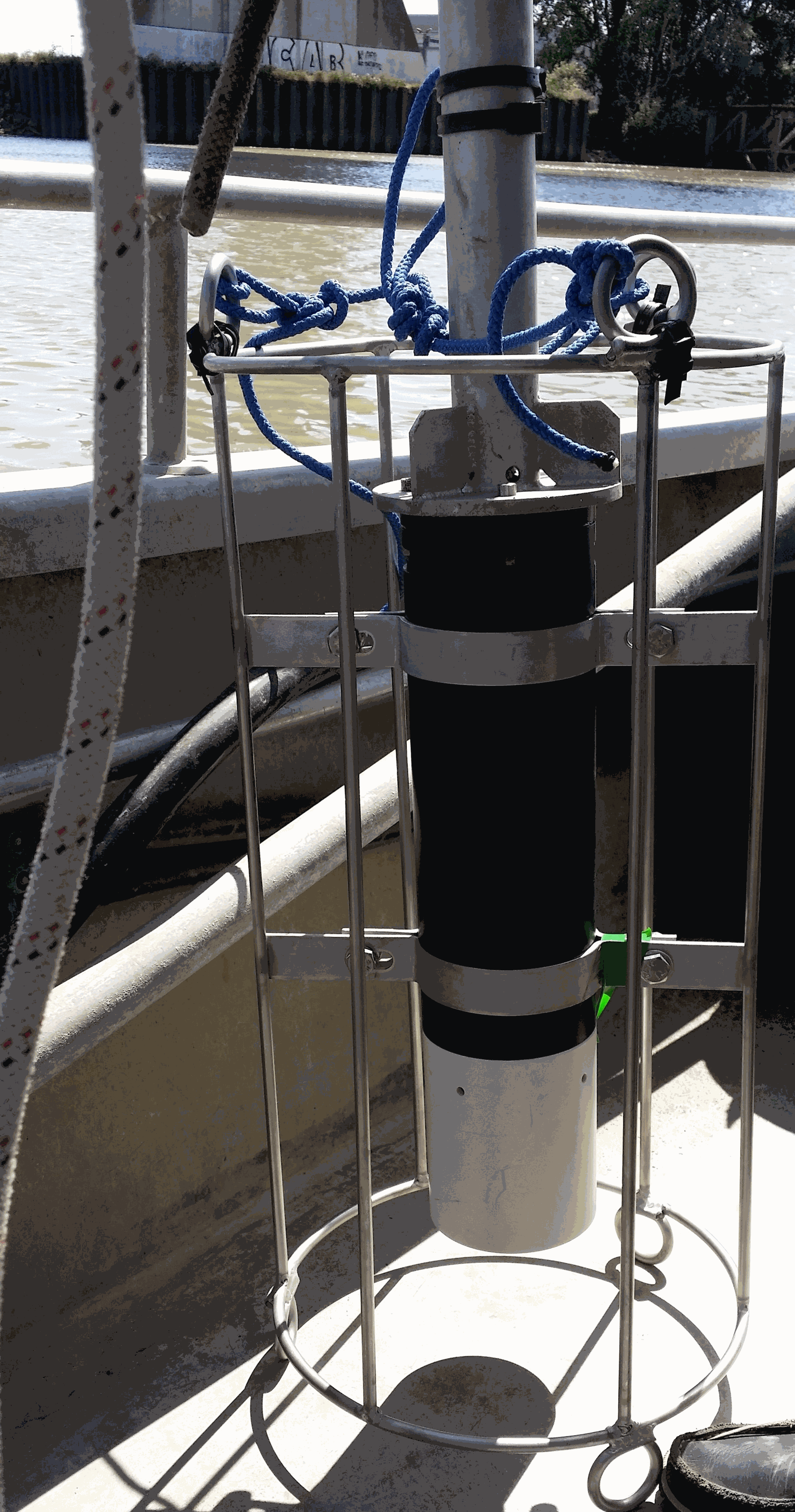
Key physico-chemical parameters (salinity, temperature, turbidity and dissolved oxygen) were measured in surface water during longitudinal transects in the Loire and Gironde estuaries in summers 2017 and 2018. This objective of this work was to determine the distribution of the dissolved oxygen and to detect potential severe desoxygenation. The transects were scheduled in order to begin the measurements at high tide from a site located upstream of an area where severe deoxygenation have been already been reported. Then, the transect was realised by sailing at low speed downstream with a multiparameter probe SAMBAT, maintained at 0.5 m below the surface, that collected a measurement every 2 minutes.
-

Phenotypic plasticity, the ability of a single genotype to produce multiple phenotypes, is important for survival when species are faced with novel conditions. Theory predicts that range-edge populations will have greater phenotypic plasticity than core populations, but empirical examples from the wild are rare. The honeycomb worm, Sabellaria alveolata (L.), constructs the largest biogenic reefs in Europe, which support high biodiversity and numerous ecological functions. In order to assess the presence, causes and consequences of intraspecific variation in developmental plasticity and thermal adaptation in the honeycomb worm, we carried out common-garden experiments using the larvae of individuals sampled from along a latitudinal gradient covering the entire range of the species. We exposed larvae to three temperature treatments and measured phenotypic traits throughout development. We found phenotypic plasticity in larval growth rate but local adaptation in terms of larval period. The northern and southern range-edge populations of S. alveolata showed phenotypic plasticity for growth rate: growth rate increased as temperature treatment increased. In contrast, the core range populations showed no evidence of phenotypic plasticity. We present a rare case of range-edge plasticity at both the northern and southern range limit of species, likely caused by evolution of phenotypic plasticity during range expansion and its maintenance in highly heterogeneous environments. This dataset presents the raw image data collected for larval stages of Sabellaria alveolata from 5 populations across Europe and Northern Africa, exposed to 15, 20 and 25 C. Included are also opercular crown measurements used to estimate de size classes of individuals present in each population. All measurements made with the images collected are presented in an Excel spreadsheet, also available here.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA