100 km
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Resolution
-

This raster dataset represents the Sea Surface Temperature (SST) anomalies, i.e. changes of sea temperatures, in the European Seas. The dataset is based on the map "Mean annual sea surface temperature trend in European seas" by Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), which depicts the linear trend in sea surface temperature (in °C/yr) for the European seas over the past 25 years (1989-2013). Since all changes of sea temperatures can be considered to have an impact on the marine environment, the pressure layer includes absolute values of SST anomalies, i.e. negative/decreasing temperature trends were changed to positive values so that they represent a pressure. The original data was in a 1° grid format but was converted to a 100 km resolution, adapted to the EEA 10 km grid and clipped with the area of interest. This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

The grid is based on proposal at the 1st European Workshop on Reference Grids in 2003 and later INSPIRE geographical grid systems. The sample grid available here is part of a set of three polygon grids in 1, 10 and 100 kilometres. The grids cover at least country borders and, where applicable, marine Exclusive Economic Zones v7.0, http://www.marineregions.org. Note that the extent of the grid into the marine area does not reflect the extent of the territorial waters.
-
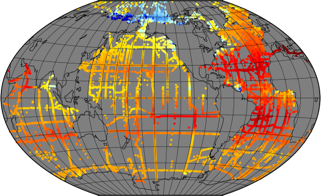
In recent years, large datasets of in situ marine carbonate system parameters (partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2), total alkalinity, dissolved inorganic carbon and pH) have been collated. These carbonate system datasets have highly variable data density in both space and time, especially in the case of pCO2, which is routinely measured at high frequency using underway measuring systems. This variation in data density can create biases when the data are used, for example for algorithm assessment, favouring datasets or regions with high data density. A common way to overcome data density issues is to bin the data into cells of equal latitude and longitude extent. This leads to bins with spatial areas that are latitude and projection dependent (eg become smaller and more elongated as the poles are approached). Additionally, as bin boundaries are defined without reference to the spatial distribution of the data or to geographical features, data clusters may be divided sub-optimally (eg a bin covering a region with a strong gradient). To overcome these problems and to provide a tool for matching in situ data with satellite, model and climatological data, which often have very different spatiotemporal scales both from the in situ data and from each other, a methodology has been created to group in situ data into ‘regions of interest’, spatiotemporal cylinders consisting of circles on the Earth’s surface extending over a period of time. These regions of interest are optimally adjusted to contain as many in situ measurements as possible. All in situ measurements of the same parameter contained in a region of interest are collated, including estimated uncertainties and regional summary statistics. The same grouping is done for each of the other datasets, producing a dataset of matchups. About 35 million in situ datapoints were then matched with data from five satellite sources and five model and re-analysis datasets to produce a global matchup dataset of carbonate system data, consisting of 287,000 regions of interest spanning 54 years from 1957 to 2020. Each region of interest is 100 km in diameter and 10 days in duration. An example application, the reparameterisation of a global total alkalinity algorithm, is shown. This matchup dataset can be updated as and when in situ and other datasets are updated, and similar datasets at finer spatiotemporal scale can be constructed, for example to enable regional studies. This dataset was funded by ESA Satellite Oceanographic Datasets for Acidification (OceanSODA) project which aims at developing the use of satellite Earth Observation for studying and monitoring marine carbonate chemistry.
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the matrices ‘water’, ‘sediment’ and ‘biota’ and indicators of ‘biological effects’, as well as an integrated classification of chemical status, combining results of all matrices. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. This is the assessment made excluding concentrations of mercury (Hg). The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Additionally, Norwegian (Barent Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Contaminants in Europe's Seas" (EEA, 2019).
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the matrices ‘water’, ‘sediment’ and ‘biota’ and indicators of ‘biological effects’, as well as an integrated classification of chemical status, combining results of all matrices. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. This is the assessment made excluding concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Additionally, Norwegian (Barent Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Contaminants in Europe's Seas" (EEA, 2019): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/contaminants-in-europes-seas.
-

The dataset presents the potential combined effects of human activities and pressures on marine species and habitats estimated using the method for assessment of cumulative effects, for the entire suite of pressures and a selected set of marine species groups and habitats by an index (Halpern et al. 2008). The spatial assessment of combined effects of multiple pressures informs of the risks of human activities on the marine ecosystem health. The methodology builds on the spatial layers of pressures and ecosystem components and on an estimate of ecosystem sensitivity through an expert questionnaire. The raster dataset consists of a division of the Europe's seas in 10km and 100 km grid cells, which values represents the combined effects index values for pressures caused by human activities. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Marine Messages" (EEA, 2020).
-

The dataset presents the potential combined effects of land-based pressures on marine species and habitats estimated using the method for assessment of cumulative effects, for the entire suite of pressures and a selected set of marine species groups and habitats by an index (Halpern et al. 2008). The spatial assessment of combined effects of multiple pressures informs of the risks of human activities on the marine ecosystem health. The methodology builds on the spatial layers of pressures and ecosystem components and on an estimate of ecosystem sensitivity through an expert questionnaire. The raster dataset consists of a division of the Europe's seas in 10km and 100 km grid cells, which values represents the combined effects index values for pressures caused by land-based human activities. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Marine Messages" (EEA, 2020).
-

This data set presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD), providing a mapping of contamination 'problem areas' and 'non-problem areas' based on measurements of biological effects. This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the of contaminant status of indicators of biological effects. The status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. Monitoring biological effects is restricted to a few indicators (e.g. imposex) and data coverage is currently limited. Biological effects have thus been addressed in only 134 assessment units, mostly in the Baltic Sea, the North Sea and the North-East Atlantic Ocean. This data set underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the EEA report “Contaminants in Europe’s seas” (No 25/2018). See the mentioned report for further information.
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of ecosystem health of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the MESH+ (Marine EcoSystem Health) tool. The MESH+ tool builds on the EEA assessment tools developed and applied in the context of assessing the degree of contamination (CHASE+), eutrophication (HEAT+) and biodiversity (BEAT+) in Europe's seas (EEA, 2018a, 2019c; Vaughan et al., 2019). MESH+ makes use of the same data sets and threshold values used in these assessments but recombines these in a new framework that addresses 'ecosystem condition'. The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the MSFD. Additionally, Norwegian (Barents Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. The spatial resolution of the assessment grid is 20 km x 20 km in coastal areas and 100 km x 100 km in offshore areas. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Marine Messages II" (EEA, 2020): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/marine-messages-2
-

The BEAT+ tool builds on the EEA assessment tools developed and applied in the context of assessing the degree of contamination (CHASE+), eutrophication (HEAT+) and biodiversity (BEAT+) in Europe's seas. BEAT+ makes use of the same data sets and threshold values used in these assessments but recombines these in a new framework that addresses 'biodiversity condition'. BEAT+ has been designed to provide an assessment of the spatial variability of a range of biodiversity components by combining existing biodiversity indicators. The tool integrates data from normalised indicators to identify worst case status measures for different biodiversity components. The results are then linked to a standard gridE based Spatial Assessment Unit (SAU) which is used both for biodiversity and for pressures assessments (Andersen et al., 2014). These grid-based SAUs not only allow alignment of indicators for biodiversity and for pressures but provide a means for combining large assessment areas (e.g. for wide‐ranging species) with point data collected from biological surveys e.g. WFD monitoring. BEAT+ tool works by calculating a Biological Quality Ratio (BQR) which is an aggregated score of indicator outcomes within a grid square. To allow objective comparison, the indicator outcomes are normalised to a scale of 0 to 1, with five status classes at equal intervals on that scale (from Bad starting at 0, Poor at 0.2, Medium at 0.4, Good at 0.6 and High at 0.8). By this means, indicators based on different biological criteria can be aggregated in a consistent way. This metadata refers to dataset providing the results of classification of biodiversity status using the BEAT+ tool. The status is evaluated in five classes, where High and Good are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and Moderate, Poor and Bad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. The dataset covers: - BQR Assessment of all marine mammals combined (mainly focused on coastal and relatively stable inshore populations of seals, dolphins and porpoises) - BQR Assessment of seabirds and wading birds - BQR Assessment of commercial fish (as these have agreed targets defined on biomass and fishing mortality) - BQR Assessment of pelagic habitats - BQR Assessment of benthic habitats - BQR Assessment of worst-performing biodiversity groups - An overall synthesis of the Biological Quality Ratios (BQR) values (showing which are the worst -lowest- BQR values in each assessment grid cell. The ‘worst’ value is used here to identify the biological group most at risk, rather than averaging over all groups to avoid over-emphasis on groups with more intensive monitoring). As reference, please consult the ETC/ICM Report 3/2019: Biodiversity in Europe's seas: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/products/biodiversity-in-europes-seas. The indicator BEAT+ Integrated Assessment Worst Case BQR has been used in the EEA report 17/2019 "Marine Messages II": https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/marine-messages-2.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA