environment
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Ce document se décompose en deux parties: La première énonce les valeurs et fonctions du massif forestier communes à tous les acteurs concernés par son avenir. La seconde présente les pressions et les enjeux qui pèsent sur le massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne.
-
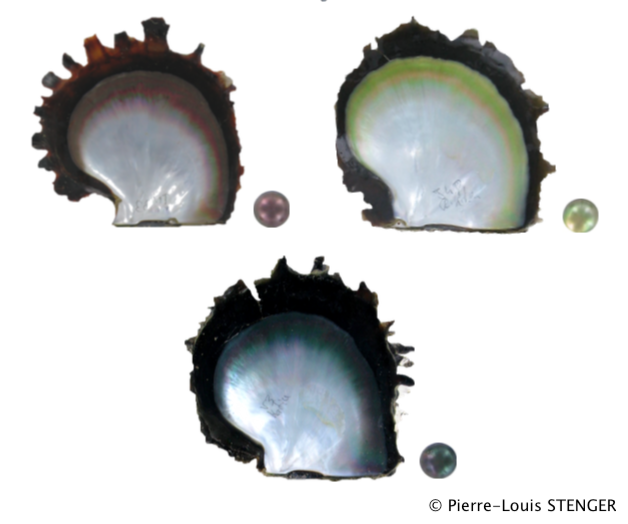

Whole genome pooled sequencing of individuals from 4 populations and 3 different color phenotype in order to uncover the genetic variants linked to color expression in the pearl oyster P. margaritifera.
-
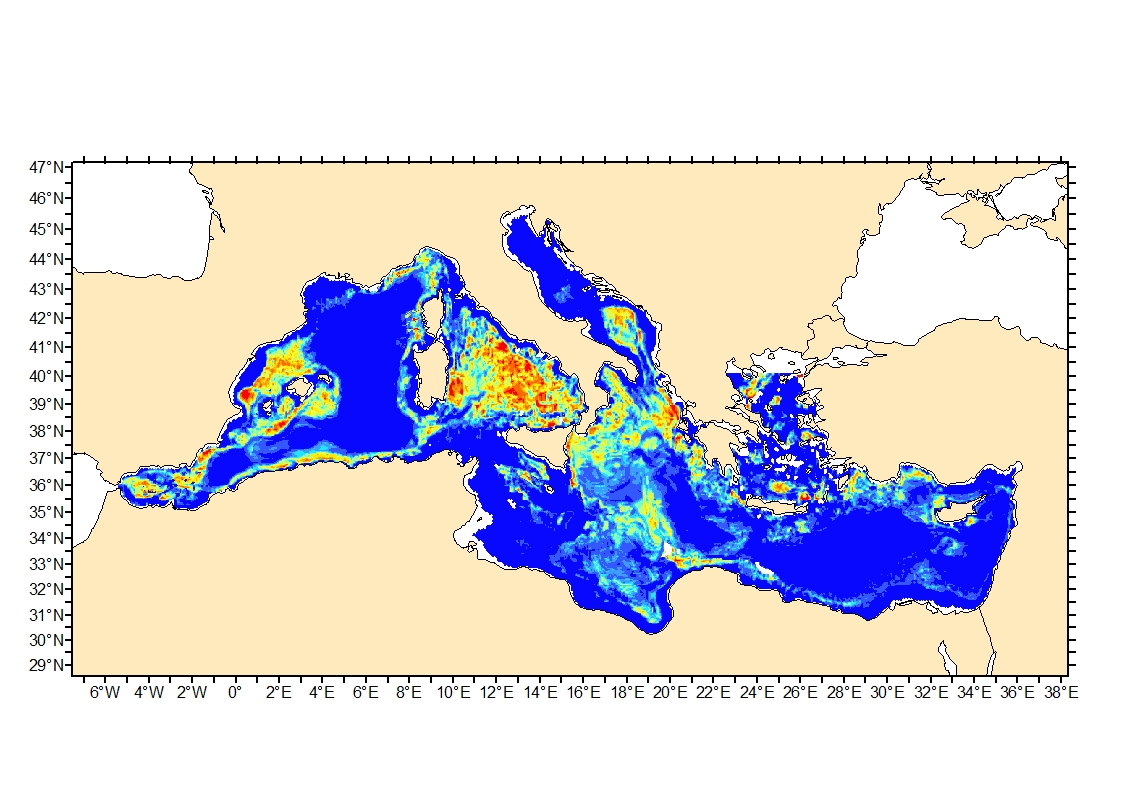
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-

The ABYSS project aims at describing deep-sea benthic biodiversity spanning several branches of the tree of life with eDNA metabarcoding tools. To accommodate both micro- and macro biologists, we designed a bioinformatic pipeline based on Illumina read correction with Dada2 allowing analysing metabarcodes from prokaryotic and eukaryotic life compartments.
-
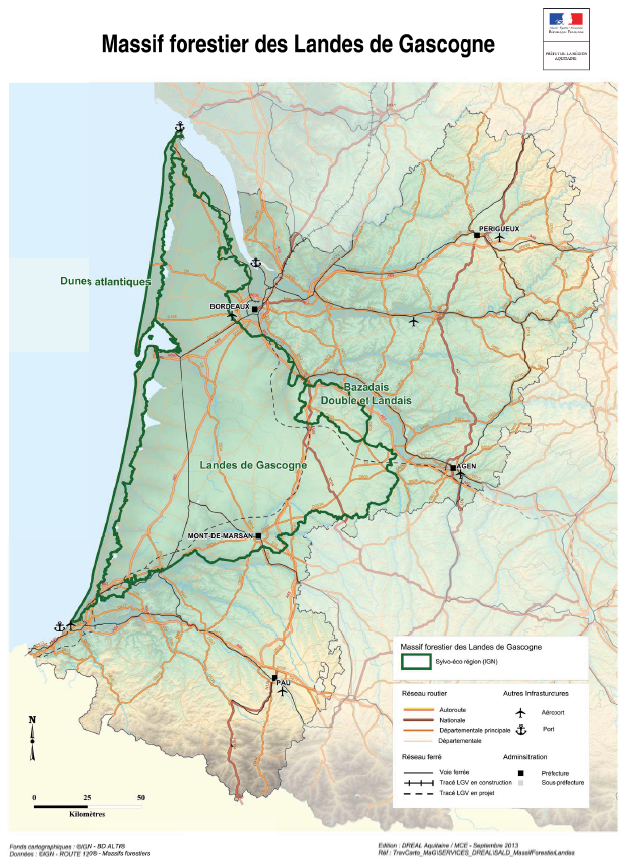
Ces travaux ont été réalisés dans le cadre de la Directive Territoriale d'Aménagement et de Développement Durable (DTADD) portée par la Préfecture de la région ex-Aquitaine. La partie I de ces travaux porte sur les valeurs du massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne. Le massif est dépositaire d’importantes valeurs et fonctions non marchandes d’intérêt général notamment : paysagères, naturalistes, hydrologiques et climatiques. Ce rapport explique également que les modes de valorisation du territoire, autres que ceux liés à la production de bois d’œuvre et d’industrie, interfèrent étroitement avec la présence même de la forêt de production : l'activité touristique, l'arrivée de nouveaux habitants et l'économie induite, ainsi que le foncier forestier.
-

Les ministères chargés de l'écologie (Meeddm) et de l'agriculture (Maap) ont confié au Gip Ecofor une mission d'expertise collective scientifique et technique à visée prospective sur « l'avenir du massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne ». Son objectif est de mobiliser la connaissance autour d'options envisageables pour assurer l'avenir du massif forestier landais et de la partager avec l'ensemble des parties intéressées. Les document disponibles sont les rapports finaux des groupes de travail et d'experts.
-

The dataset on Natura 2000 sites was created in 2014 by Cogea for the European Marine Observation and Data Network. It is entirely based on spatial data from the European Environmental Agency (EEA), plus additional info, links and selected EEA data joined to the feature attributes, as well as a calculation by Cogea of marine and coastal location of features. It is available for viewing and download on EMODnet - Human Activities web portal (www.emodnet-humanactivities.eu). Natura 2000 is an ecological network composed of sites designated under the Birds Directive (Special Protection Areas, SPAs) and the Habitats Directive (Sites of Community Importance, SCIs, and Special Areas of Conservation, SACs). The dataset covers the whole EU. Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the EU on 31 January 2020, it ceased to be part of the EEA’s institutional networks and governance. In the webmap the EEA dataset has been filtered by Cogea to show only (i) marine sites, i.e. sites with a marine area percentage higher than 0 (as calculated by the EEA) and (ii) sites that, even if not identified as marine by the EEA, intersect the EEA coastline or that are within a distance of 1 km from the coastline (using a 1 km inner buffer from the EEA coastline). In both cases the COAST_MAR field value=1. The EEA coastline dataset is available at https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/eea-coastline-for-analysis-2. Compared with the previous version, this one includes the updated dataset 'Natura 2000 End 2020', published by the EEA in July 2021. For further information (e.g. biogeographic region, directive, habitats, sites, impact, management, species and metadata) please visit the EEA's website hosting the Natura 2000 tabular data.
-

Ce projet s’attache à étudier les phénomènes Natech imputables à des inondations/tsunami en considérant deux échelles spatiales d’analyse : l’échelle du site industriel et l’échelle du territoire. Ces deux échelles permettent d’appréhender la problématique des Natechs d’une part d’un point de vue essentiellement « vulnérabilité » et d’autre part, grâce à une analyse plus globale et profonde qui fait résonner la notion de résilience territoriale. Le travail est basé sur une analyse a posteriori (au Japon) et a priori (en France) des pratiques de gestion des événements Natech auprès des parties prenantes (industriels, collectivités, services de l’état…). Pour cela, en France et au Japon, des questionnaires, des visites et des entretiens ont été réalisés sur des territoires touchés ou potentiellement concernés par le phénomène Natech inondation/tsunami. Ces données sont employées : -à l’échelle du site industriel, pour modéliser l’impact du phénomène naturel sur l’installation (par le biais notamment d’arbres de défaillances), puis produire deux outils d’aide à la décision (diagnostic de l’Etude de danger et diagnostic du Plan d’Opération Interne lors d’un événement Natech inondation) -à l’échelle du territoire pour modéliser le processus Natech, identifier 3 zones de fragilité, définir 5 scénarios de choc. Puis, en considérant que la résilience globale d’un territoire dépend notamment de la résilience des acteurs qui le constituent proposer un outil d’audit des parties prenantes du territoire afin d’estimer la résilience de chacun d’entre eux, les pistes de progrès et, in fine, améliorer la résilience du territoire qui les héberge. Mots-clefs : Natech, Science du danger, arbres de défaillance, aide à la décision, résilience territoriale.
-
L’objectif de cette étude est d’illustrer à l’aide d’indicateurs les conséquences de choix de gestion imposés par cinq scénarios socioéconomiques prospectifs appliqués à une large zone forestière pour les 60 prochaines années. Le cas d’étude choisi est la zone centrée sur la commune de Pontenx-les-Forges dans le sud-ouest de la France et couvrant 101000 hectares. Cet article présente une description de la zone d’étude et des itinéraires sylvicoles mis en œuvre par les propriétaires forestiers selon des scénarios. À l’aide d’un simulateur pilotant deux modèles de croissance, l’évolution de la zone d’étude à l’échelle de chaque parcelle est synthétisée par 9 indicateurs sur une période de 60 ans : le volume sur pied, le carbone sur pied, le volume total exploité, la valeur commerciale sur pied, le volume de l’arbre moyen, la vulnérabilité au vent et au feu, et des indices de biodiversité. Un des principaux résultats de cette étude est de montrer l’amplitude des changements pour la production et le volume sur pied : selon les scénarios les récoltes annuelles peuvent varier de 50 % dès 2030. Par conséquent, d’autres indicateurs sont impactés comme la biodiversité, la vulnérabilité au vent ou au feu. Pourtant, l’espèce dominante est maintenue et le comportement partiellement conservateur des types de propriétaires est pris en compte. En conclusion, des améliorations pour de futures simulations sont envisagées ; dans ce but, des synergies avec la télédétection sont nécessaires pour la collecte des données d’initialisation sur de larges territoires, ce qui permettra d’améliorer la précision des résultats.
-

Effets de la pollution atmosphérique industrielle sur la population de la presqu'île d'Ambès (ERS)
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA