2022
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
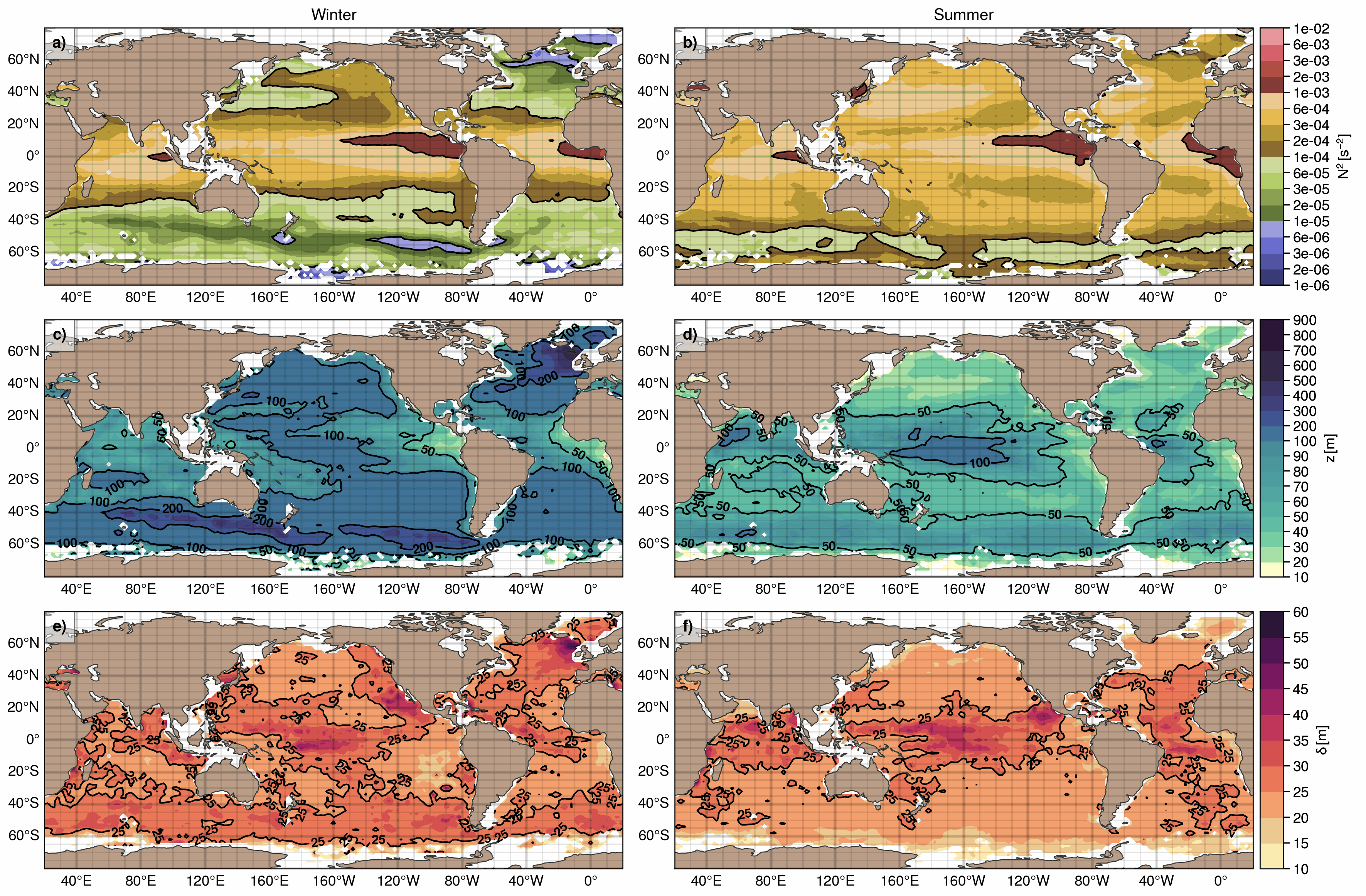
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-

WGS for Iatlantic projet ( ) for assessing past and present connectivity
-

Raw reads for the assembly of Gambusia holbrooki genome.
-
French Zostera Marina et Zostera Noltei abundance data are collected during monitoring surveys on the English Channel / Bay of Biscay coasts. Protocols are impletmented in the Water Framework Directive. Data are transmitted in a Seadatanet format (CDI + ODV) to EMODnet Biology european database. 35 ODV files have been generated from period 01/01/2004 to 31/12/2021 for Z. Marina and from 01/01/2011 to 31/12/2021 for Z. Noltei.
-
This dataset contains the pictures used for morphometric measurements, as well as the elemental compositon and production rates data, of planktonic Rhizaria. Specimens were collected in the bay of Villefranche-sur-Mer in May 2019 and during the P2107 cruise in the California Current in July-August 2021. Analyses of the data can be found at https://github.com/MnnLgt/Elemental_composition_Rhizaria.
-

The CDR-derived Wet Tropospheric Correction (WTC) Product V2 is generated from the Level-2+ along-track altimetry products version 2024 (L2P 2024) distributed by AVISO+ (www.aviso.altimetry.fr). It provides a long-term, homogenized estimation of the wet tropospheric correction based on Climate Data Records (CDRs) of atmospheric water vapour combined with high frequencies MWR data. Two independent CDRs datasets are used: - REMSS V7R2 (coverage until 2022) https://www.remss.com/measurements/atmospheric-water-vapor/tpw-1-deg-product/ - HOAPS V5 precursor CDR from EUMETSAT CM SAF (coverage until 2020) HOAPS V4/V5 data available via https://wui.cmsaf.eu Note: the HOAPS V5 precursor is not yet an official CM SAF product; full validation and public release are pending. The MWR/CDR WTC V2 estimates is derived using spatially varying but temporally constant polynomial coefficients (ai). 1. WTC V2 – Along-track L2P Product Data format: The WTC V2 product is delivered in Level-2+ (L2P) format, along the satellite ground track. Each mission is distributed as a compressed archive (.tar.gz) containing one NetCDF4 CF-1.8 file per mission cycle. Archive naming convention: <mission>_WTC_from_WV_CDR_<version>.tar.gz mission: TP (TOPEX/Poseidon), J1, J2, J3 version: product version (currently V2) File naming convention inside archives: <mission>_C<cycle>.nc cycle: 4-digit cycle index (e.g., C0001) Each NetCDF file contains: 1/ Along-track WTC estimate; 2/ Ancillary information; 3/ Space–time coordinates 2. WTC CDR Uncertainties – Gridded Product: A complementary product is provided, delivering regional trend estimates and associated uncertainties from the WTC Climate Data Record. The uncertainty product is distributed as a single NetCDF4 file: wtc_trend_uncertainties.nc . This file contains global gridded fields of WTC CDR trend and uncertainty parameters. Product content: This is the first dedicated version providing both: WTC CDR (HOAPS) linear trends, and Uncertainty estimates on these trends. Uncertainties are expressed as 1-sigma confidence intervals, and propagated using the methodology described in Section 2.3 of the Product User Manual. The product includes: - Total uncertainty on the WTC trend, propagated from all identified uncertainty sources in the WTC–TCWV regression. - Individual contributions of uncertainty sources (Uncertainties on regression coefficients: a0, a1 and their standard deviations; Uncertainties inherited from the HOAPS TCWV CDR) These fields enable users to assess the relative importance of each uncertainty component and recompute uncertainty propagation with alternative methods. Included regression input variables: To ensure transparency and reproducibility, the product provides: 1/ regression coefficients a0, a1; 2/ their associated uncertainties (std of a0, std of a1); 3/additional diagnostic fields required to recompute uncertainties if needed.
-

This dataset consists of metatranscriptomic sequencing reads corresponding to coastal micro-eukaryote communities sampled in Western Europe in 2018 and 2019.
-
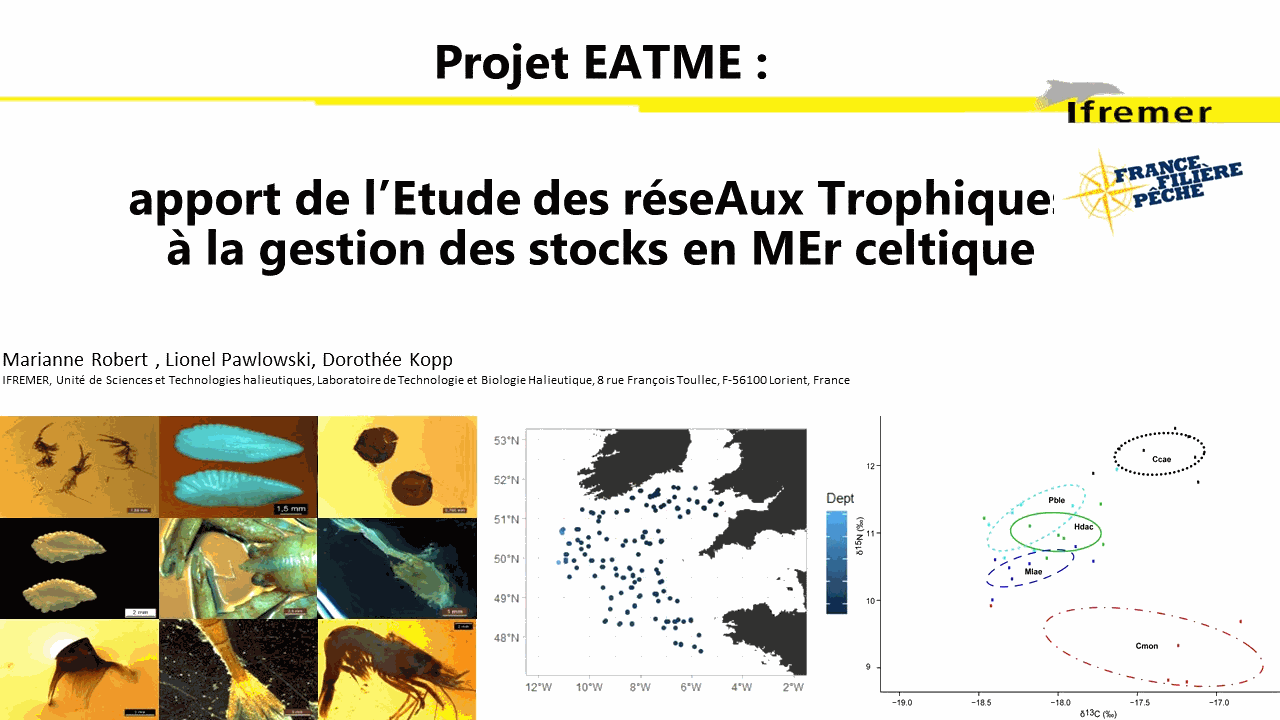
Understanding the dynamics of species interactions for food (prey-predator, competition for resources) and the functioning of trophic networks (dependence on trophic pathways, food chain flows, etc.) has become a thriving ecological research field in recent decades. This empirical knowledge is then used to develop population and ecosystem modelling approaches to support ecosystem-based management. The TrophicCS data set offers spatialized trophic information on a large spatial scale (the entire Celtic Sea continental shelf and upper slope) for a wide range of species. It combines ingested prey (gut content analysis) and a more integrated indicator of food sources (stable isotope analysis). A total of 1337 samples of large epifaunal invertebrates (bivalve mollusks and decapod crustaceans), zooplankton, fish and cephalopods, corresponding to 114 species, were collected and analyzed for stable isotope analysis of their carbon and nitrogen content. Sample size varied between taxa (from 1 to 52), with an average of 11.72 individuals sampled per species, and water depths ranged from 57 to 516 m. The gut contents of 1026 fish belonging to ten commercially important species: black anglerfish (Lophius budegassa), white anglerfish (Lophius piscatorius), blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou), cod (Gadus morhua), haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus), hake (Merluccius merluccius), megrim (Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis), plaice (Pleuronectes platessa), sole (Solea solea) and whiting (Merlangius merlangus) were analyzed. The stomach content data set contains the occurrence of prey in stomach, identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible. To consider potential ontogenetic diet changes, a large size range was sampled. The TrophicCS data set was used to improve understanding of trophic relationships and ecosystem functioning in the Celtic Sea. When you use the data in your publication, we request that you cite this data paper. If you use the present data set (TrophicCS) for the majority of the data analyzed in your study, you may wish to consider inviting at least one author of the core team of this data paper to become a collaborator /coauthor of your paper.
-
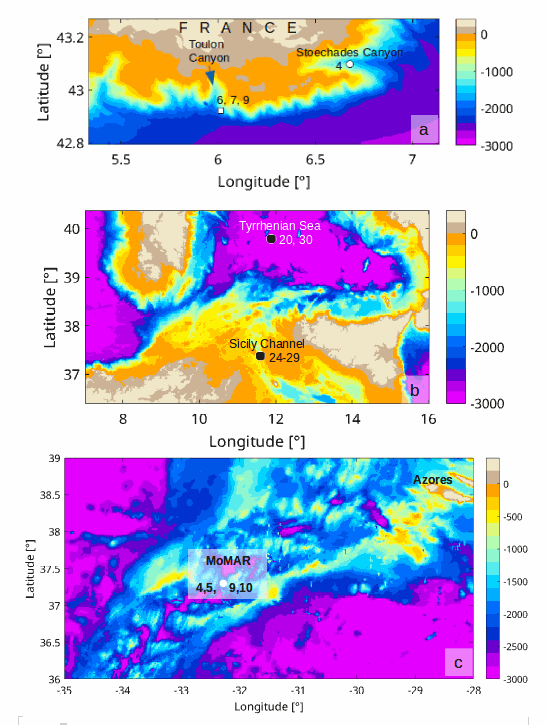
This data set is related to the article "Improving the robustness of dissipation rate estimates from microstructure shear data processing in ocean turbulence" (submitted to JTech, AMS). It provides the raw data files (with extension .p) from a vertical microstructure profiler VMP-6000 used for the published study. Raw data files are provided since the study precisely report on the data processing of raw microstructure horizontal velocity shear data to get dissipation rates of turbulent kinetic energy using the manufacturer software. The software (ODAS) can be downloaded from the manufacturer website at: https://rocklandscientific.com. The profiles were collected in the Mediterranean Sea in 2013 (French VAD cruise) and 2014 (Italian MEDOCC cruise), and in the North Atlantic Ocean in 2021 (MoMAR cruise). More details on the profiles are given in the related publication.
-
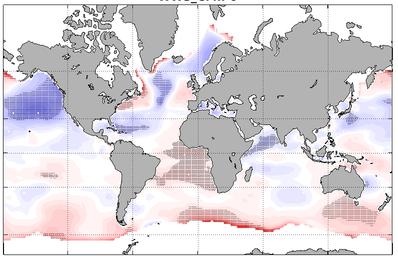
Global wave hindcast (1961-2020) at 1° resolution using CMIP6 wind and sea-ice forcings for ALL (historical), GHG (historical greenhouse-gas-only), AER (historical Anthropogenic-aerosol-only), NAT (historical natural only) scenario.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA