CSV
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
The dataset includes age- and length-based catch per unit effort data for commercial fish species collected by the French trawl survey EVHOE.
-

In October 2019 we chose 15 sites from the 2019 EVHOE survey for environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling. The French international EVHOE bottom trawl survey is carried out annually during autumn in the BoB to monitor demersal fish resources. At each site, we sampled seawater using Niskin bottles deployed with a circular rosette. There were nine bottles on the rosette, each of them able to hold ∼5 l of water. At each site, we first cleaned the circular rosette and bottles with freshwater, then lowered the rosette (with bottles open) to 5 m above the sea bottom, and finally closed the bottles remotely from the boat. The 45 l of sampled water was transferred to four disposable and sterilized plastic bags of 11.25 l each to perform the filtration on-board in a laboratory dedicated to the processing of eDNA samples. To speed up the filtration process, we used two identical filtration devices, each composed of an Athena® peristaltic pump (Proactive Environmental Products LLC, Bradenton, Florida, USA; nominal flow of 1.0 l min–1 ), a VigiDNA 0.20 μm filtration capsule (SPYGEN, le Bourget du Lac, France), and disposable sterile tubing. Each filtration device filtered the water contained in two plastic bags (22.5 l), which represent two replicates per sampling site. We followed a rigorous protocol to avoid contamination during fieldwork, using disposable gloves and single-use filtration equipment and plastic bags to process each water sample. At the end of each filtration, we emptied the water inside the capsule that we replaced by 80 ml of CL1 conservation buffer and stored the samples at room temperature following the specifications of the manufacturer (SPYGEN, Le Bourget du Lac, France). We processed the eDNA capsules at SPYGEN, following the protocol proposed by Polanco-Fernández et al., (2020). Half of the extracted DNA was processed by Sinsoma using newly developped ddPCR assays for European seabass (Dicentrachus labrax), European hake (Merluccius merluccius) and blackspot seabream (Pagellus bogaraveo). The other half of the extracted DNA was analysed using metabarcoding with teleo primer. The raw metabarcoding data set is available at https://www.doi.org/10.16904/envidat.442 Bottom trawling using a GOV trawl was carried out before or after water sampling. The catch was sorted by species and catches in numbers and weight were recorded. No blackspot seabream individuals were caught. Data content: * ddPCR/: contains the ddPCR counts and DNA concentrations for each sample and species. * SampleInfo/: contains the filter volume for each eDNA sample. * StationInfo/: contains metadata related to the data collected in the field for each filter. * Metabarcoding/: contains metabarcoding results for teleoprimer. * Trawldata/: contains catch data in numbers and weight (kg).
-

-
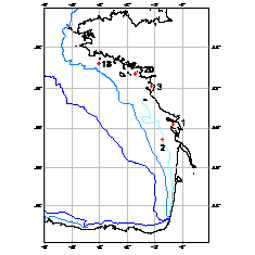
210Pb, 226Ra and 137Cs were measured by non-destructive gamma spectrometry on marine sediment cores, collected during RIKEAU 2002 cruise on board r/v Thalia, on the shelf of the Bay of Biscay
-
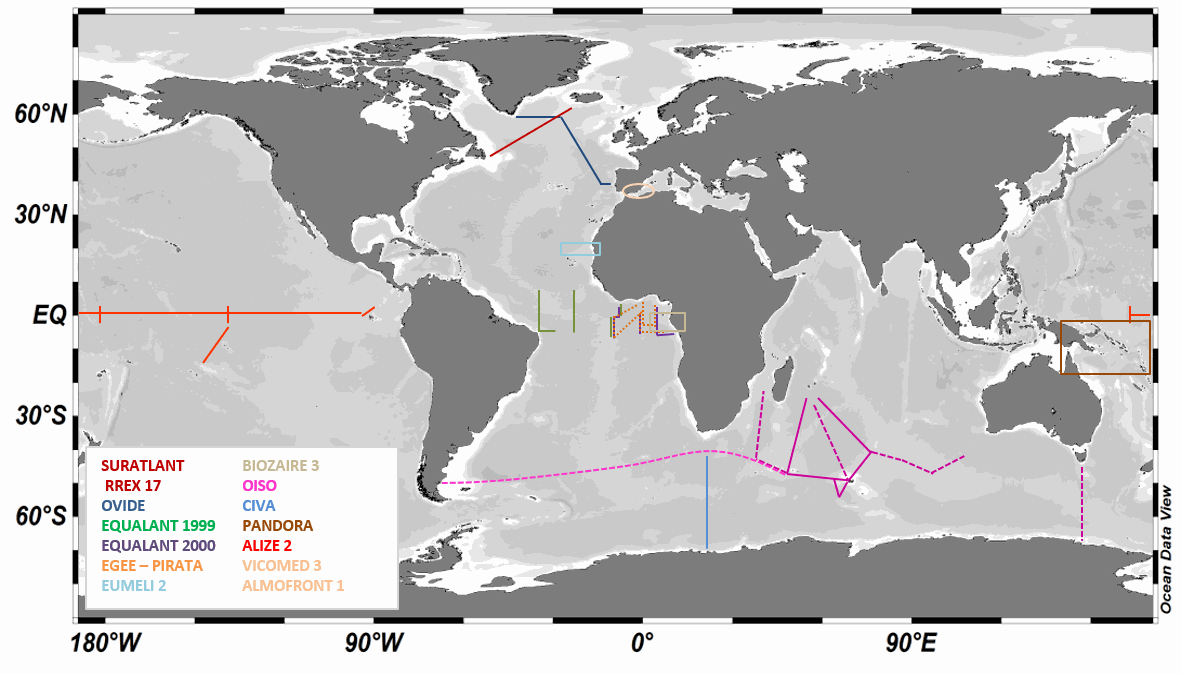
LOCEAN has been in charge of analyzing the isotopic composition of the dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in sea water collected during a series of cruises or ships of opportunity mostly in the southern Indian Ocean , the North Atlantic, and the equatorial Atlantic, but also in the Mediterranean Sea and in the equatorial Pacific. The LOCEAN sea-water samples for δ13CDIC were collected in 125/25 ml glass bottles until 2022/since then and poisoned with HgCl2 (1 ml of saturated solution) before storage in a dark room à 4°C until their measurement. The DIC was extracted from the seawater by acidification with phosphoric acid (H3PO4 85%) and CO2 gas that was produced was collected in a vacuum system following the procedure described by Kroopnick (1974). The isotopic composition of CO2 was determined using a dual inlet-isotopic ratio mass spectrometer (SIRA9-VG) by comparing the 13C/12C ratio of the sample to the 13C/12C ratio of a reference material, the Vienna-Pee Dee Belemnite (V-PDB). The isotopic composition is expressed in the δ-unit defined by Craig (1957)(method type 2). Experience showed that samples older than 3-4 years are likely to have experienced conservation issues and have been dismissed. The mass spectrometer has worked very well until 2014-2015. Afterwards, its aging as well as the aging of the preparation line resulted in more data loss, and often less accurate results. The preparation line was renovated in 2019, and analyses in 2020 were run manually, often repeating the measurement a second time for each sample. Up to 2007-2008, δ13CDIC values have a precision of±0.01 ‰ (Vangriesheim et al.,2009) and a reproducibility of±0.02 ‰. After an interlaboratory comparison exercise led by Claire Normandeau (Dalhousie University), results suggest that recent LOCEAN samples have a slightly poorer reproducibility (±0.04 ‰ ) as well as an offset of -0.13‰ (details available in Reverdin et al., ESSD 2018) that is confirmed by Becker et al. 2016 work by comparison with other cruises after removing the anthropogenic signal. Recent comparisons in early May 2021 with Orsay GEOPS facility samples suggest that the current offset is much smaller and might be +0.03‰. LOCEAN has installed in 2021 a new measurement device by coupling a Picarro G2131-I cavity ring down spectrometer (CRDS) with a CO2 extractor (Apollo SciTech) that will measure at the same time DIC (method type 3) (Leseurre, 2022). Since then, all water samples have been analyzed on this device. Part of the data set, as well as a scientific context and publications are also presented on the WEB site https://www.locean-ipsl.upmc.fr/oceans13c. Individual files correspond to regional subsets of the whole dataset. The file names are based on two letters for the region followed by (-) the cruise or project name (see below) followed by –DICisotopes, followed by either -s (surface data) or -b (subsurface data), and a version number (-V0, …): example SI-OISO-DICisotopes-s-V0; the highest version number corresponds to the latest update of the cruise/project data set, and can be directly downloaded. Earlier versions can be obtained on request, but are not recommended. The region two letters are the followings: - SI: station and surface data in the Southern Indian Ocean that include cruises : INDIGO I (1985 – stn) (https://doi.org/10.17600/85000111) CIVA I (1993 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.17600/93000870) (Archambeau et al., JMS 1998) ANTARES (1993 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.17600/93000600) OISO (*) (since 1998 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.18142/228) (Racapé et al., Tellus 2010, Leseurre, 2022) - EA: station and surface data in the Tropical Atlantic Ocean that include cruises : EQUALANT (1999 & 2000 – surf) (https://doi.org/10.18142/98) EGEE (2005 to 2007 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.18142/95) PIRATA (since 2013 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.18142/14) EUMELI 2 (1991 – stn) (https://doi.org/10.17600/91004011) (Pierre et al., JMS 1994) BIOZAIRE 3 (2003 – stn & surf ) (https://doi.org/10.17600/3010120) (Vangriesheim et al., DSRII, 2009) TARA-Microbiomes (2021 - stn & surf) - NA : station and surface data in the North Atlantic Subpolar gyre that include cruises : OVIDE (**) (since 2002 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.17882/46448) (Racapé et al., 2013) RREX (2017 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.17600/17001400) SURATLANT (since 2010 - surf) (https://doi.org/10.17882/54517) (Racapé et al., BG 2014 ; Reverdin et al., ESSD 2018, Leseurre, 2022) NUKATUKUMA (since 2017- surf) - MS: station data in the Mediterranean sea that include cruises : ALMOFRONT 1 (1991 – stn) (https://doi.org/10.17600/91004211) VICOMED 3 (1990 – stn) (https://doi.org/10.17600/90000711) - PO: tropical Pacific that include cruises : PANDORA (2012 – stn) (https://doi.org/10.17600/12010050) ALIZE2 (1991 – stn & surf) (https://doi.org/10.17600/91002711) (Laube-Lenfant and Pierre, Oceanologica Acta 1994) - SO: station and surface data in the Southern Ocean (except OISO) that include cruises: TARA-Microbiomes (2021-2022, stn & surf) AGULHASII-072022 (2022, stn) CONFLUENCE (1993-1994, stn) - AO: station and surface data in the Arctic Ocean and nearby seas that include cruises: GREENFEEDBACK (2024, stn&surf) TCA (2024, stn) REFUGE ARCTIC (2024, stn) (*) The values for cruises OISO19, 21 and 22 are doubtful (for some, too low) and will require further investigation to find whether adjusted values can be proposed. (**) Some of the OVIDE cruises are also referred to as or GEOVIDE (in 2014), and BOCATS (in 2016). CATARINA, BOCATS1 and BOCATS2 (PID2019-104279GB-C21/AEI/10.13039/501100011033) cruises were funded by the Spanish Research Agency The values of the OVIDE 2010 stations are doubtful (too low), but no particular error was found, and they have been left in the files. Data The files are in csv format reported as: - Cruise name, station id, (bottle number), day, month, year, hour, minute, longitude, latitude, pressure (db), depth (m), temperature (°C), temperature qc, salinity (pss-78), salinity qc, d13CDIC, d13CDIC qc, method type - Temperature is an in situ temperature - Salinity is a practical salinity - Method type (1) acid CO2 extraction from helium stripping technique coupled to mass spectrometer, (2) acid CO2 extraction in a vacuum system coupled to mass spectrometer,(3) CO2 extractor (Apollo SciTech) coupled to CRDS measurements. Temperature qc, salinity qc, d13CDIC qc are quality indices equal to: - 0 no quality check (but presumably good data) - 1 probably good data - 2 good data - 3 probably bad data - 4 certainly bad data - 9 missing data (and the missing data are reported with an unlikely missing value)
-

The SOMLIT-Antioche observation station, located at 5 nautical miles from Chef de Baie harbor (La Rochelle) is part of the French monitoring network SOMLIT (https://www.somlit.fr/), accredited by the INSU-CNRS as a national Earth Science Observatory (Service National d’Observation : SNO), which comprises 12 observation stations distributed throughout France in coastal locations. It aims to detect long-term changes of these ecosystems under both natural and anthropogenic forcings. SOMLIT is part of the national research infrastructure for coastal ocean observation ILICO (https://www.ir-ilico.fr/?PagePrincipale&lang=en). The SOMLIT-Antioche station (46.0842 °N, 1.30833 °W) is located in the north-eastern part of the Bay of Biscay, halfway between the islands of Ré and Oléron, at the centre of what is commonly known as the Pertuis Charentais area, which correspond to a semi-enclosed shallow basin and includes four islands (Ré, Oléron, Aix and Madame) and three Pertuis (i.e., detroit) (Breton, Antioche and Maumusson). This 40m-deep site, with muddy to sandy marine bottoms, is submitted to a macro-tidal regime and is largely open to the prevailing westerly swells. It remains under a dominant oceanic/neritic influence, even though its winter/spring hydrological context is influenced by the diluted plumes of the Charente, Gironde and Loire rivers, but not by those of too small estuaries (Lay, Seudre and Sèvre Niortaise). SOMLIT-Antioche hydrological monitoring has been carried out by the LIENSs/OASU laboratory on a fortnightly basis since June 2011. Surface water samples are collected at high-tide during intermediate tides (70 ± 10 in SHOM units) on board the research vessel ‘L’Estran’ owned by La Rochelle University. Samples are analyzed for more than 16 core parameters: temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, pH, ammonia, nitrates, nitrites, phosphates, silicates, suspended matter, particulate organic carbone, particulate organic nitrogen, chlorophyll, delta15N, delta13C; pico- and nano- plankton. Measurements are carried out in accordance with the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standard. Simultaneous monitoring of the micro-phytoplankton community (since 2013, SNO PHYTOBS: https://www.phytobs.fr/en) and monitoring of prokaryotic communities (Bacteria and Archaea) are also carried out on a monthly basis. Since 2019, seasonal observations of benthic invertebrate communities (SNO BenthObs : https://www.benthobs.fr/) have also been carried out. This monitoring is complementary to that carried out at hydrological stations in the pre-existing REPHY and DCE networks, some of which are located near marine farming areas (oyster and mussel farms).
-

The network was initiated by IFREMER from 1993 to 2009 (under the acronym REMORA) to study the rearing performance of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas at a national scale. To do so, the network monitored annually the mortality and growth of standardized batches of 18-month-old oysters. Starting in 1995, the monitoring of the rearing performance of 6-month-old oyster spat was integrated into this network. These sentinel batches were distributed simultaneously each year on 43 sites and were monitored quarterly. These sites were distributed over the main French oyster farming areas and allowed a national coverage of the multiannual evolution of oyster farming performances. Most of the sites were located on the foreshore at comparable levels of immersion. Field studies were carried out by the "Laboratoires Environnement Ressources" (LER) for the sites included in their geographical area of investigation. Following the increase in spat mortality in 2008, the network evolved in 2009 (under the acronym RESCO). From this date, the network selected 13 sites among the 43 sites previously monitored in order to increase the frequency of visits (twice a month) and the number of sentinel batches. More precisely, sentinel batches of oysters corresponding to different origins (wild or hatchery, diploid or triploid) and to two rearing age classes (spat or 18-month-old adults) were selected. The monitoring of environmental variables (temperature, salinity) associated with the 13 sites was also implemented. The actions of the network have thus contributed to disentangle the biotic and abiotic parameters involved in mortality phenomena, taking into account the different compartments (environment / host / infectious agents) likely to interact with the evolution of oyster rearing performance. Finally, since 2015, the network has merged the RESCO and VELYGER networks to adopt the acronym ECOSCOPA. The general objective of this current network is to analyze the causes of spatio-temporal variability of the main life traits (Larval stage - Recruitment - Reproduction - Growth - Survival - Cytogenetic abnormalities) of the cupped oyster in France and to follow their evolution on the long term in the context of climate change. To do this, the network proposes a regular spatio-temporal monitoring of the major proxies of the life cycle of the oyster, organized in three major thematic groups: (1) proxies related to growth, physiological tolerance and survival of experimental sentinel populations over 3 age classes: (2) proxies related to reproduction, larval phase and recruitment of the species throughout its natural range in France, and: (3) proxies related to environmental parameters essential to the species (weather conditions, temperature, salinity, pH, turbidity, chlorophyll a and phytoplankton) at daily or sub-hourly frequencies. Working in a geographical network associating several laboratories, ECOSCOPA provide these monitoring within 8 sites selected among the previous ones to ensure the continuity of the data acquisition. Today, these 8 sites are considered as ecosystems of common interest, contrasted, namely : - The Thau lagoon - The Arcachon basin - The Marennes Oléron basin - The Bourgneuf Bay - The bay of Vilaine - The bay of Brest - The bay of Mont Saint Michel - The bay of Veys The ECOSCOPA network is therefore one of the relevant monitoring tools on a national scale, allowing to objectively measure through different proxies the general state of health of cultivated and wild oyster populations, and this for the different sensitive phases of their life cycle. This network aims at allowing a better evaluation, on the long term, of the biological risks incurred by the sector but also by the ecosystems, in particular under the increasing constraint of climatic and anthropic changes. Figure : Sites monitored by the ECOSCOPA network
-
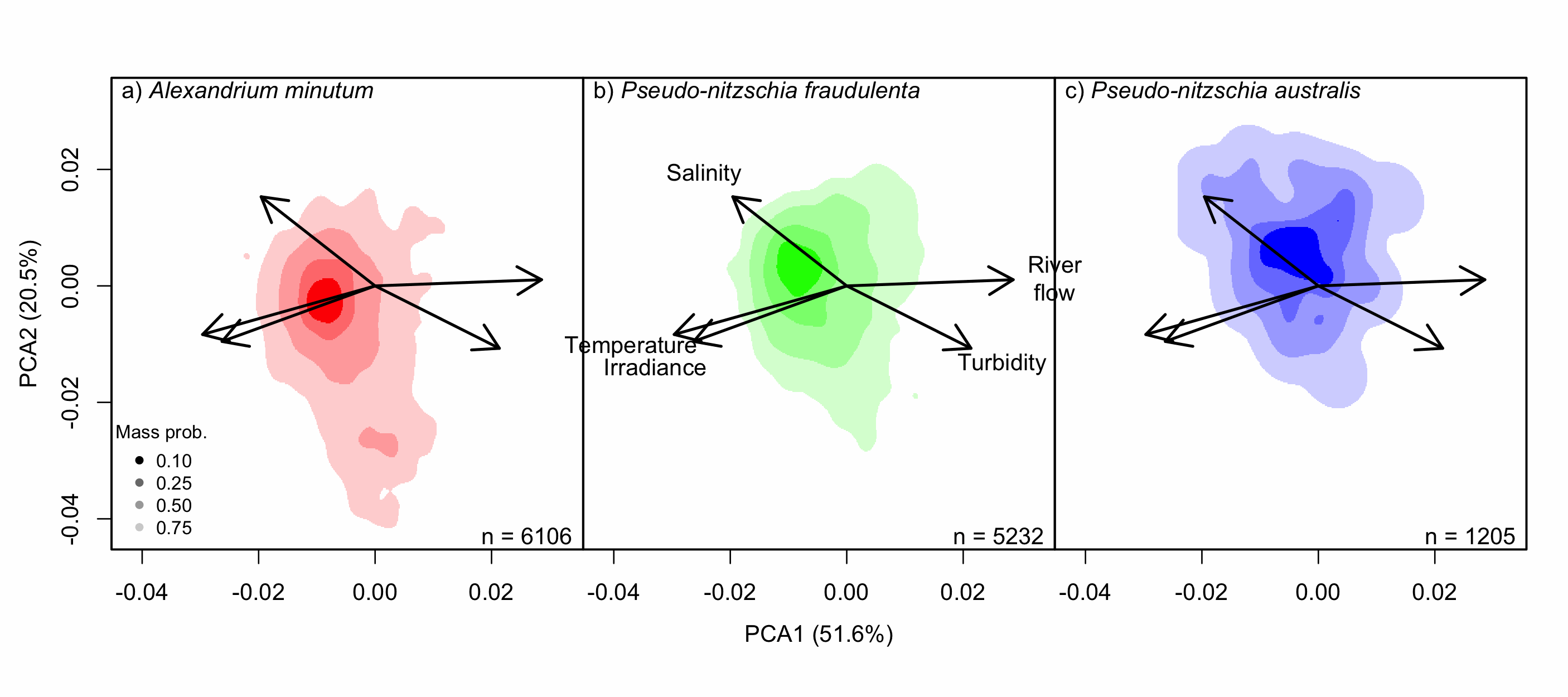
Understanding the spatial and temporal preferences of toxic phytoplankton species is of paramount importance in managing and predicting harmful events in aquatic ecosystems. In this study we address the realised niche of the species Alexandrium minutum, Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta and P. australis. We used them to highlight distribution patterns at different scales and determine possible drivers. To achieve this, we have developed original procedures coupling niche theory and habitat suitability modelling using abundance data in four consecutive steps: 1) Estimate the realised niche applying kernel functions. 2) Assess differences between the species’ niche as a whole and at the local level. 3) Develop habitat and temporal suitability models using niche overlap procedures. 4) Explore species temporal and spatial distributions to highlight possible drivers. Data used are species abundance and environmental variables collected over 27 years (1988-2014) and include 139 coastal water sampling sites along the French Atlantic coast. Results show that A. minutum and P. australis niches are very different, although both species have preference for warmer months. They both respond to decadal summer NAO but in the opposite way. P. fraudulenta realised niche lies in between the two other species niches. It also prefers warmer months but does not respond to decadal summer NAO. The Brittany peninsula is now classified as an area of prevalence for the three species. The methodology used here will allow to anticipate species distribution in the event of future environmental challenges resulting from climate change scenarios.
-

The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset comprises long-term time series on marine microphytoplankton, from 2003 to 2021, along the entire French metropolitan coastline. Microphytoplankton data cover microscopic taxonomic identifications and counts. The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset corresponds to a dataset extracted from the PHYTOBS network (DOI:10.17882/85178). The PHYTOBS network provides the scientific community and stakeholders with validated and qualified data on the biomass, abundance and composition of marine microphytoplankton in coastal and lagoon waters, with the aim of supporting scientific research. PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO is a dataset used as part of the Horizon Europe MARCO-BOLO project (https://marcobolo-project.eu/), in which we are currently working to understand and analyze multi-decadal trends in coastal and marine biodiversity on a European scale. The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset gathers data from 18 sampling sites, selected from the PHYTOBS-Network dataset according to requirements of time series quality and geographical location of sampling sites established as part of the MARCO-COLO project. This dataset was also formatted according to a template imposed for the European project.
-

Three saltmarshes, Aiguillon, Brouage, Fier d'Ars, located in the Pertuis-Charentais Sea along the south-west coast of France, were studied to evaluate their sediment and mass accumulation rates (SAR; MAR) based on 210Pb and 137Cs profiles in sediments. Coastal saltmarshes play indeed an essential role in providing services such as coastal protection and supporting biodiversity. Saltmarshes are also critical environments for the accumulation of sedimentary organic carbon (blue carbon). However, the number of studies on saltmarshes remains underrepresented compared to studies on mangroves and seagrass. This work is a contribution to the effort to document sediment and mass accumulation rates of saltmarshes.A total of 16 1m sediment cores were collected in the three saltmarshes (Aiguillon, Brouage, Fier d'Ars) in 2021 and 2022 using an Eijkelkamp stainless steel peat sampler. Each sediment core was sampled every 1 cm from the top to the bottom of the core. The sediment layers were used to determine dry bulk density and selected radioisotope activities (210Pb, 226Ra, 137Cs, 228Th, 137Cs). Combining excess 210Pb and 137Cs has allowed to establish a reliable chronology of sediment deposition on a multidecadal timescale.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA