GeoTIFF
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of Solitary Scleractinian fields assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image sample. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the north-east Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
-

-

The raster dataset represents fishing intensity (kilowatt per fishing hour) by pelagic towed gears in the European seas. The dataset has been derived from Automatic Identification System (AIS) based pelagic fishing intensity data received from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre - Independent experts of the Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (JRC STECF), as well as from Vessel Monitoring System (VMS) and logbook based pelagic fishing effort data from HELCOM Commission. The temporal extent varies between the data sources (between 2013 and 2015). The dataset has been transformed to a logarithmic scale (ln1). This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of Acanella arbuscula assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image sample. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the North East Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of discrete Lophelia pertusa - Desmophylum pertusum colonies assemblage in the Celtic Sea. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image samples. Modelling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the North East Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
-

This dataset is the coastal zone land surface region from Europe, derived from the coastline towards inland, as a series of 10 consecutive buffers of 1km width each. The coastline is defined by the extent of the Corine Land Cover 2018 (raster 100m) version 20 accounting layer. In this version all Corine Land Cover pixels with a value of 523, corresponding to sea and oceans, were considered as non-land surface and thus were excluded from the buffer zone.
-
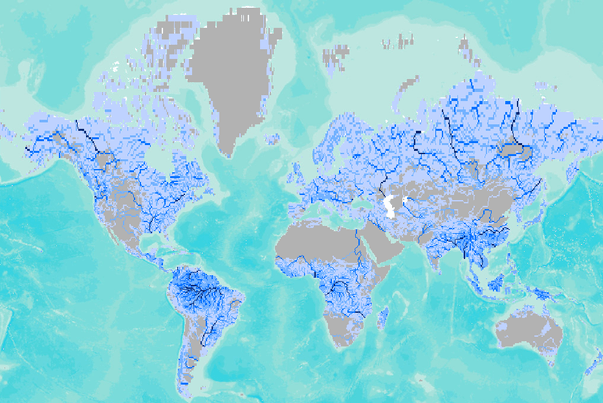
Global annual river discharge for a 0.5 degree resolution digital river network (blended, km3/yr per grid cell). Blended river flow represents a composite of observed and modeled river flow. Annual river discharge - computed as flow accumulated long term average runoff along a 30-minute resolution digital river network and blended with observed discharge data where available (km3/yr).
-
-
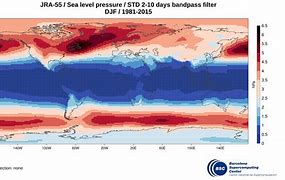
JRA55-do is a surface dataset for driving ocean-sea ice models and used in phase 2 of OMIP (OMIP-2). JRA55-do corrects the atmospheric reanalysis product JRA-55 (Kobayashi et al., 2015) using satellite and other atmospheric reanalysis products. The merits of JRA55-do are the high horizontal resolution (~55 km) and temporal interval (3 h). An assessment by Tsujino et al. (2020) implies that JRA55-do can suitably replace the current CORE/OMIP-1 dataset. This reanalysis of atmospheric variables is provided by the Japanese Meteorological Agency starting in the year 1958 and will be used to drive the coupled NEMO-ERSEM model in the hindcast configuration.
-

Species distribution models (GAM, Maxent, and Random Forest ensemble) predicting the distribution of Sea pens and burrowing megafauna assemblages in the Northeast Atlantic. This community is considered ecologically coherent according to the cluster analysis conducted by Parry et al. (2015) on image samples. Modeling its distribution complements existing work on their definition and offers a representation of the extent of the areas of the North East Atlantic where they can occur based on the best available knowledge. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA