NC, NETCDF
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
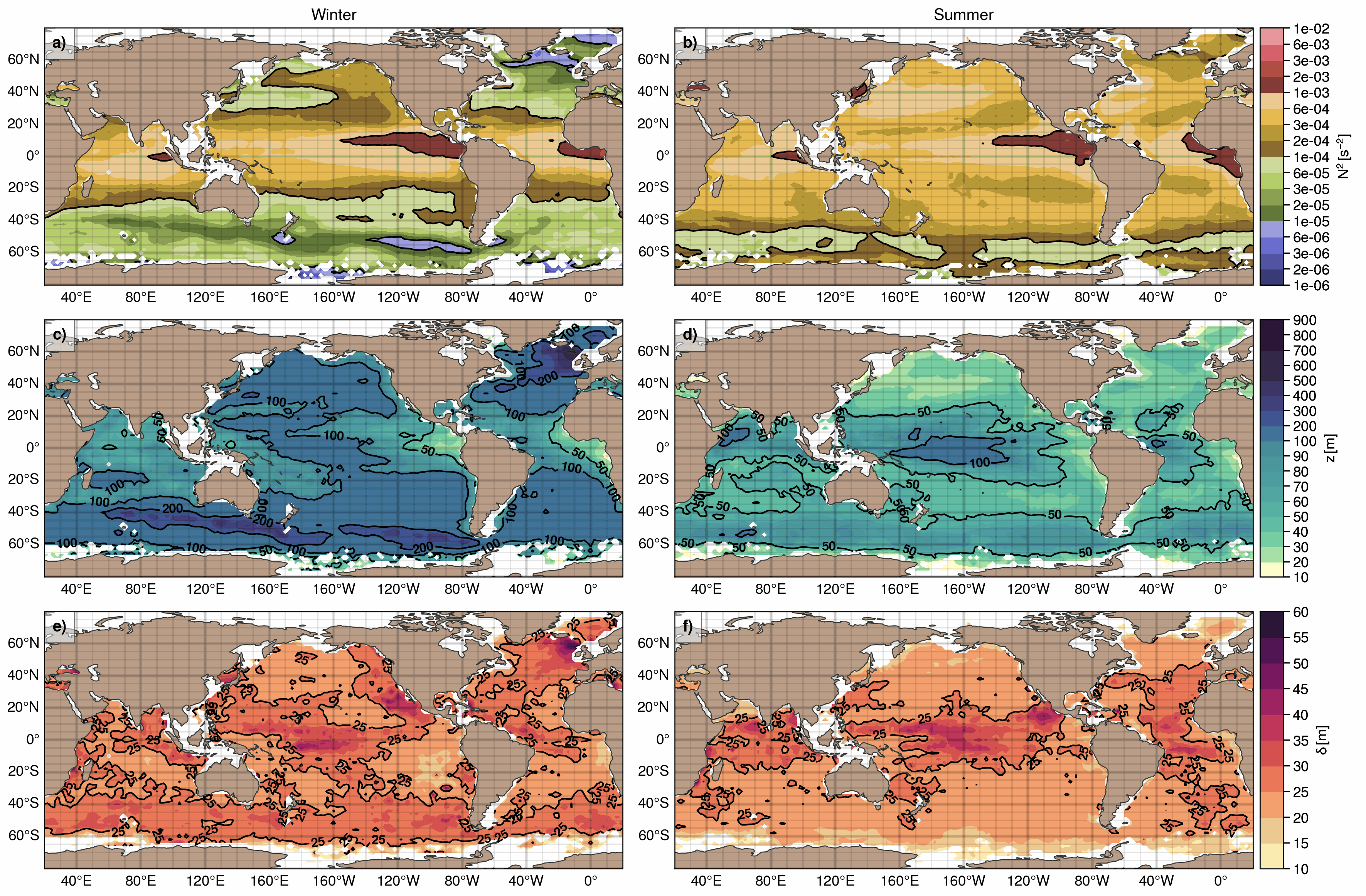
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-
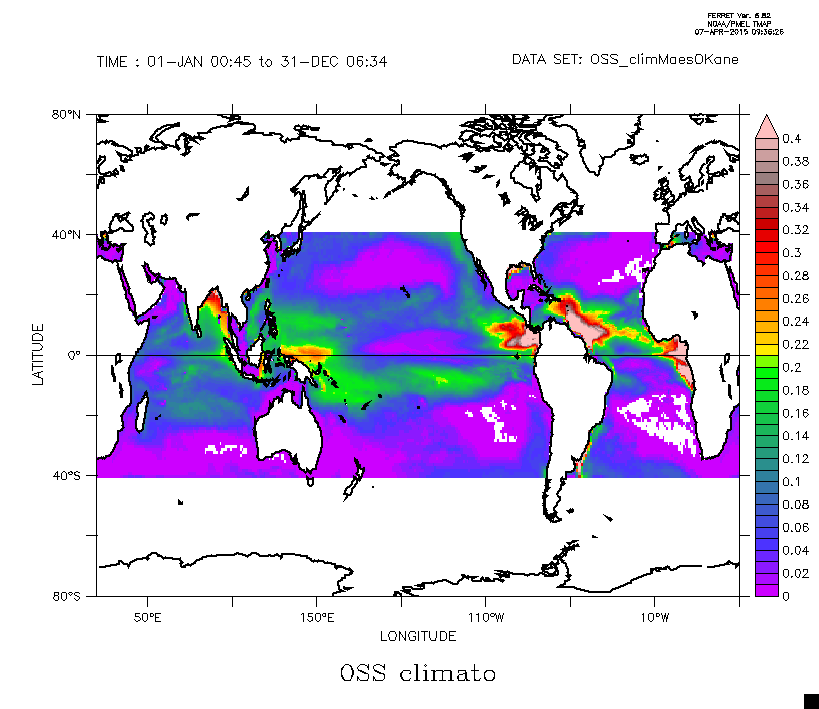
This dataset is composed by the climatological seasonal field of the Ocean Salinity Stratification as defined from the Brunt-Vaisala frequency limited to the upper 300 m depth. The details are given in Maes, C., and T. J. O’Kane (2014), Seasonal variations of the upper ocean salinity stratification in the Tropics, J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 119, 1706–1722, doi:10.1002/2013JC009366.
-
This delayed mode product designed for reanalysis purposes integrates the best available version of in situ data for ocean surface currents and current vertical profiles. It concerns three delayed time datasets dedicated to near-surface currents measurements coming from three platforms (Lagrangian surface drifters, High Frequency radars and Argo floats) and velocity profiles within the water column coming from the Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP, vessel mounted only). The latest version of Copernicus surface and sub-surface water velocity product is also distributed from Copernicus Marine catalogue.
-
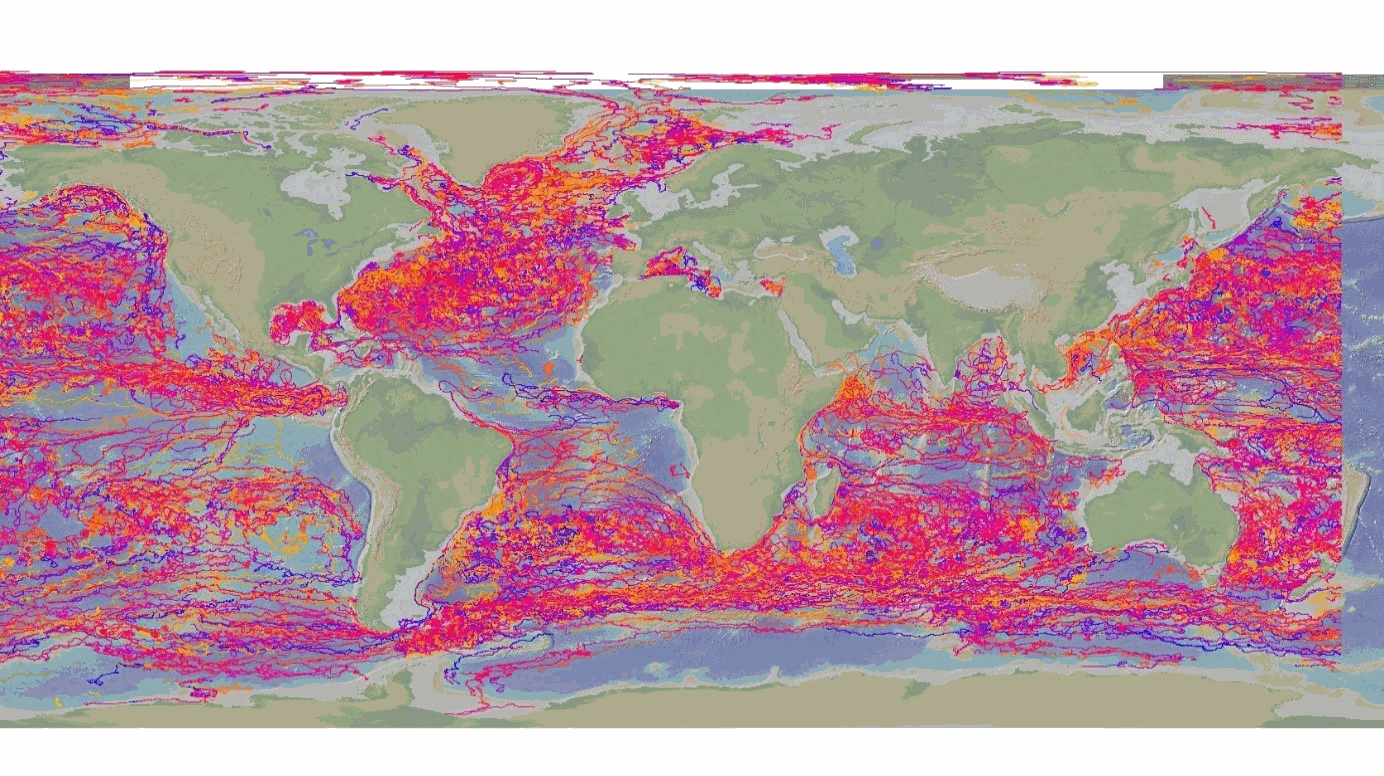
The DBCP – Data Buoy Cooperation Panel - is an international program coordinating the use of autonomous data buoys to observe atmospheric and oceanographic conditions, over ocean areas where few other measurements are taken. DBCP coordinates the global array of 1 600 active drifting buoys (August 2020) and historical observation from 14 000 drifting buoys. Data and metadata collected by drifting buoys are publically available in near real-time via the Global Data Assembly Centers (GDACs) in Coriolis-Ifremer (France) and MEDS (Canada) after an automated quality control (QC). In long term, scientifically quality controlled delayed mode data will be distributed on the GDACs. Disclaimer: the DB-GDAC is under construction. It is currently (January 2020) aggregating data from the Coriolis DAC (E-Surfmar, Canada). Additional DACs are considered. An interim provision from GTS real-time data to GDAC may be provided from Coriolis DAC.
-
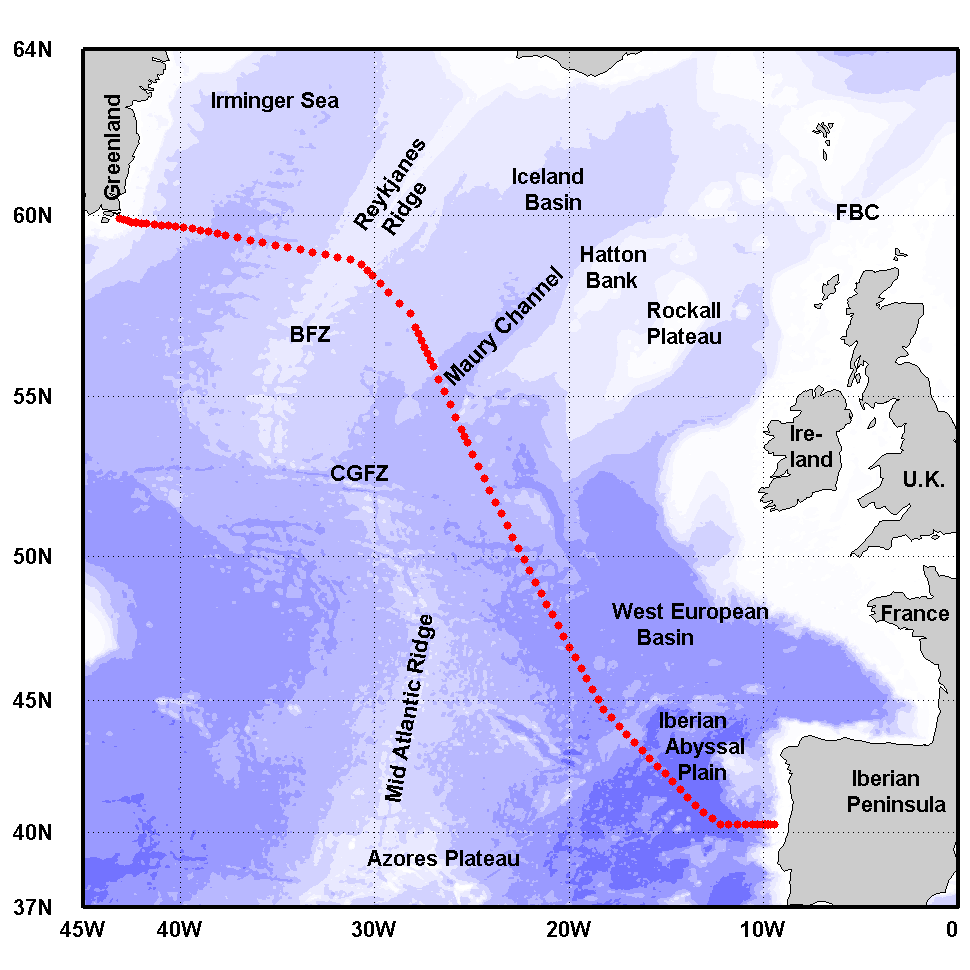
The Greenland-Portugal A25 OVIDE line is carried out biennially since 2002. The section is composed of 98 stations where hydrographic, biogeochemical and current measurements are carried out down to the bottom. OVIDE is a contribution to the international programs Go-Ship, IOCCP, and CLIVAR. This data set contains the final (adjusted) CTDO2 data.
-

The Southern Ocean plays a fundamental role in regulating the global climate. This ocean also contains a rich and highly productive ecosystem, potentially vulnerable to climate change. Very large national and international efforts are directed towards the modeling of physical oceanographic processes to predict the response of the Southern Ocean to global climate change and the role played by the large-scale ocean climate processes. However, these modeling efforts are greatly limited by the lack of in situ measurements, especially at high latitudes and during winter months. The standard data that are needed to study ocean circulation are vertical profiles of temperature and salinity, from which we can deduce the density of seawater. These are collected with CTD (Conductivity-Temperature-Depth) sensors that are usually deployed on research vessels or, more recently, on autonomous Argo profilers. The use of conventional research vessels to collect these data is very expensive, and does not guarantee access to areas where sea ice is found at the surface of the ocean during the winter months. A recent alternative is the use of autonomous Argo floats. However, this technology is not easy to use in glaciated areas. In this context, the collection of hydrographic profiles from CTDs mounted on marine mammals is very advantageous. The choice of species, gender or age can be done to selectively obtain data in particularly under-sampled areas such as under the sea ice or on continental shelves. Among marine mammals, elephant seals are particularly interesting. Indeed, they have the particularity to continuously dive to great depths (590 ± 200 m, with maxima around 2000 m) for long durations (average length of a dive 25 ± 15 min, maximum 80 min). A Conductivity-Temperature-Depth Satellite Relay Data Logger (CTD-SRDLs) has been developed in the early 2000s to sample temperature and salinity vertical profiles during marine mammal dives (Boehme et al. 2009, Fedak 2013). The CTD-SRDL is attached to the seal on land, then it records hydrographic profiles during its foraging trips, sending the data by satellite ARGOS whenever the seal goes back to the surface.While the principle intent of seal instrumentation was to improve understanding of seal foraging strategies (Biuw et al., 2007), it has also provided as a by-product a viable and cost-effective method of sampling hydrographic properties in many regions of the Southern Ocean (Charrassin et al., 2008; Roquet et al., 2013).
-
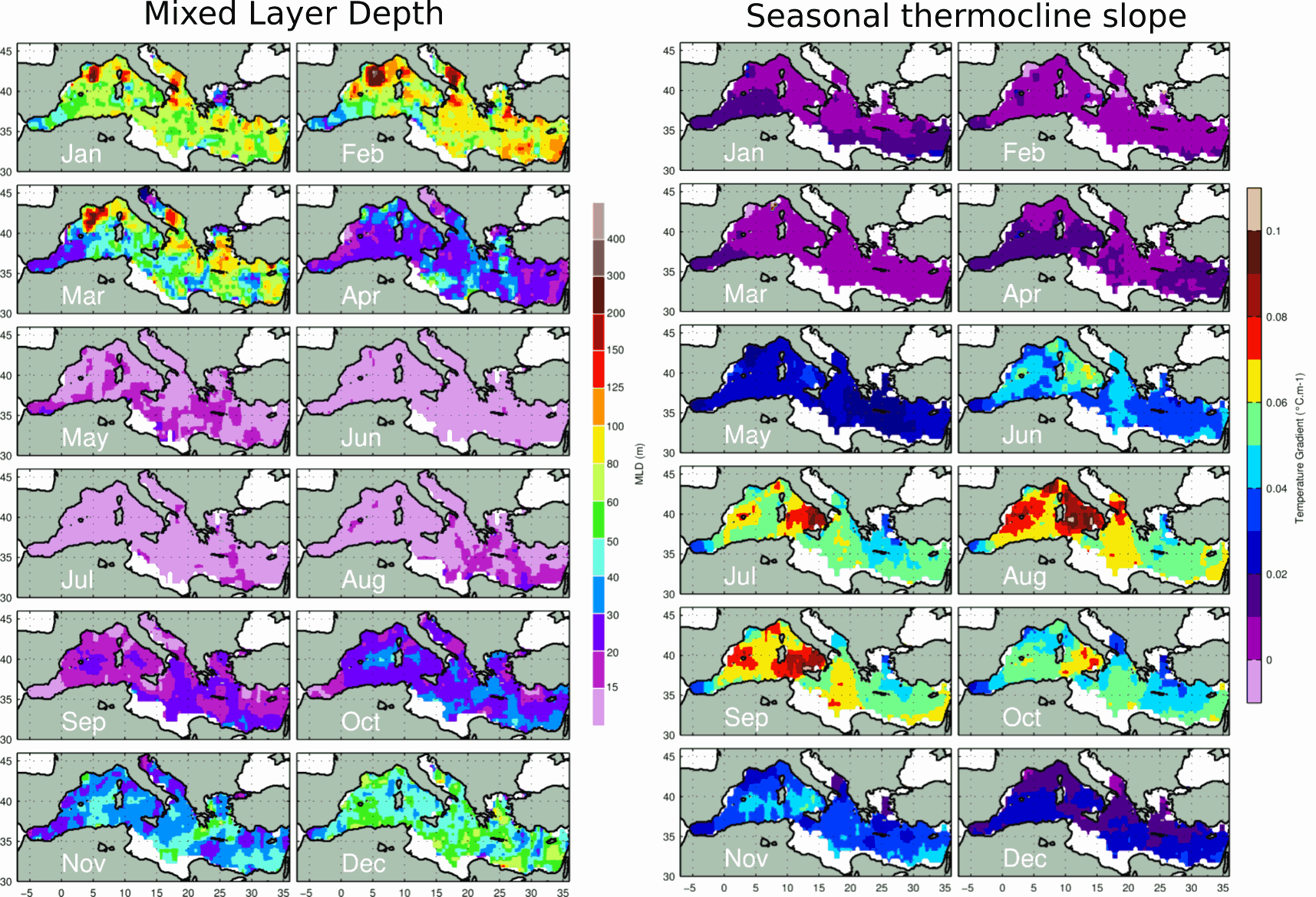
These monthly gridded climatology were produced using MBT, XBT, Profiling floats, Gliders, and ship-based CTD data from different database and carried out in the Med. between 1969 and 2013. The Mixed Layer Depth (MLD) is calculated with a delta T= 0.1 C criterion relative to 10m reference level on individual profiles. The Depth of the Bottom of the Seasonal Thermocline (DBST) is calculated on individual profiles as the maximum value from a vector composed of two elements: 1) the depth of the temperature minimum in the upper 200m; 2) the MLD. This double criterion for the calculation of DBST is necessary in areas where the mixed layer exceed 200m depth. DBST is the integration depth used in the calculation of the upper-ocean Heat Storage Rate. For more details about the data and the methods used, see: Houpert et al. 2015, Seasonal cycle of the mixed layer, the seasonal thermocline and the upper-ocean heat storage rate in the Mediterranean Sea derived from observations, Progress in Oceanography, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2014.11.004
-
The OceanGliders initiative (formerly EGO) is a gathering of several teams of oceanographers, interested in developing the use of gliders for ocean observations. OceanGliders started in Europe with members from France, Germany, Italy, Norway, Spain, and the United Kingdom. The partners of OceanGliders have been funded by both European and national agencies to operate gliders for various purposes and at different sites. Coordinated actions are being set up for these sites in order to demonstrate the capabilities of a fleet of gliders for sampling the ocean, with a given scientific and/or operational objective. Gliders were developed since the 90’s to carry out in-situ observations of the upper 1km of the ocean, filling the gaps left by the existing observing systems. Gliders look like small autonomous robotic underwater vehicles which that uses an engine to change their buoyancy. While gliding from surface to about 1000 meters, gliders provide real-time physical and biogeochemical data along their transit. They observe temperature, salinity, pressure, biogeochemical data or acoustic data. The OceanGliders GDAC handled at Ifremer/France aggregates the data and metadata from glider deployments provided by the DACs or PIs. The OceanGliders unique DOI publishes the quaterly snapshot of the whole GDAC content and preserves its successive quaterly versions (unique DOI for easy citability, preservation of quaterly versions for reproducibility). The OceanGliders unique DOI references all individual glider deployment DOIs provided by the DACs or PIs, and with data in the GDAC. DACs or PIs may use the data processing chain published at http://doi.org/10.17882/45402 to generate glider NetCDF GDAC files.
-

This dataset contains the dynamical outputs of a global ocean simulation coupling dynamics and biogeochemistry at ¼° over the year 2019. The simulation has been performed using the coupled circulation/ecosystem model NEMO/PISCES (https://www.nemo-ocean.eu/), which is here enhanced to perform an ensemble simulation with explicit simulation of modeling uncertainties in the physics and in the biogeochemistry. This dataset is one of the 40 members of the ensemble simulation. This study was part of the Horizon Europe project SEAMLESS (https://seamlessproject.org/Home.html), with the general objective of improving the analysis and forecast of ecosystem indicators. See Popov et al. (https://os.copernicus.org/articles/20/155/2024/) for more details on the study.
-
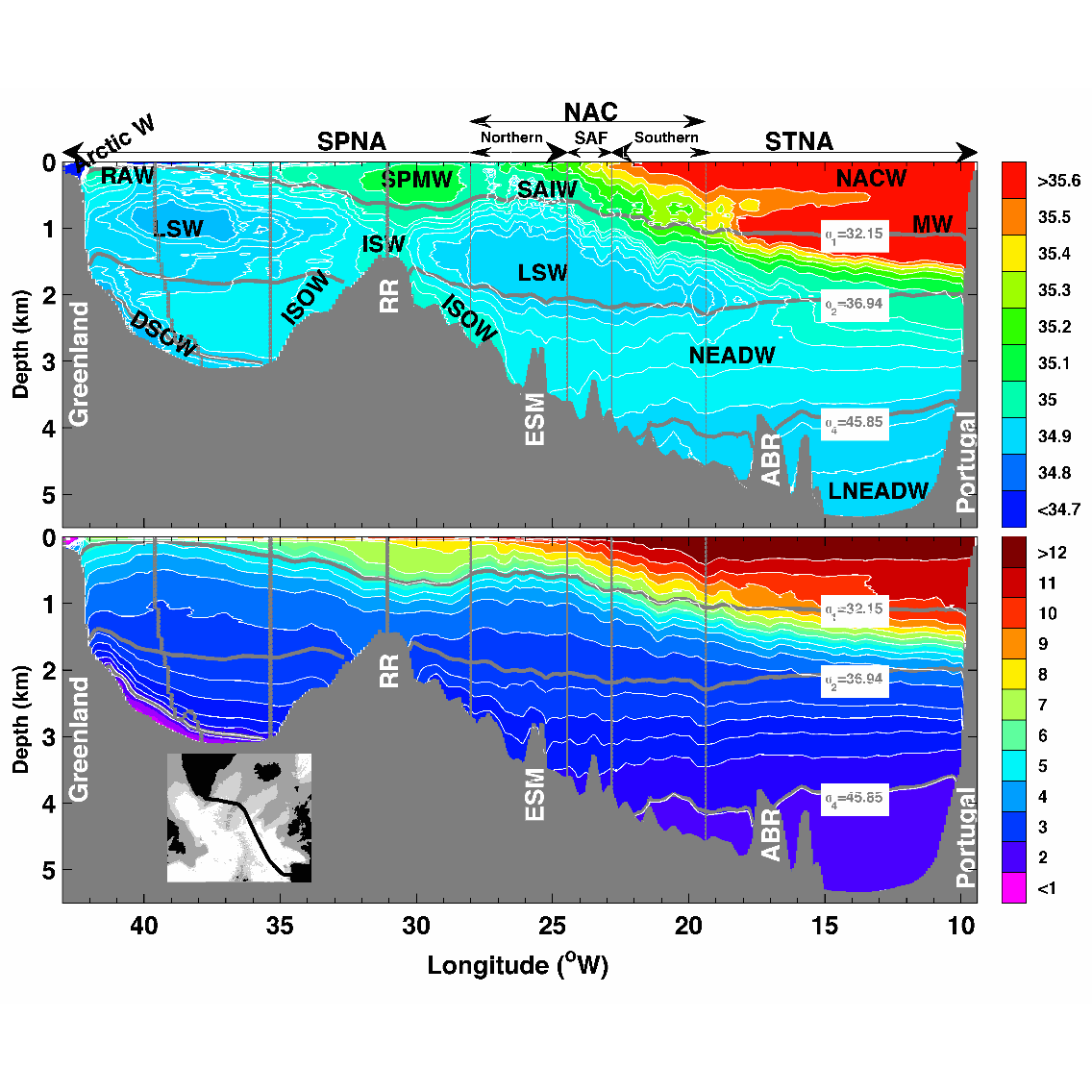
This data set contains the gridded hydrographic and transport data for the biennial Go-Ship A25 Greenland–Portugal OVIDE section from 2002 to 2012. The properties and transports are mapped on a 7km x 1m grid. Using a common grid facilitates the comparison between the different occupations of the line and the averaging. This data set was used in Daniault et al. (2016, Progress in Oceanography) to which the reader is referred for a description of the gridding method.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA