CDS-IS-SISMER
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
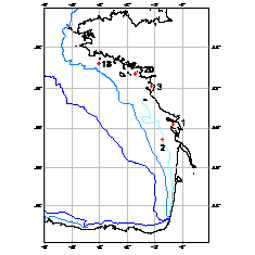
210Pb, 226Ra and 137Cs were measured by non-destructive gamma spectrometry on marine sediment cores, collected during RIKEAU 2002 cruise on board r/v Thalia, on the shelf of the Bay of Biscay
-
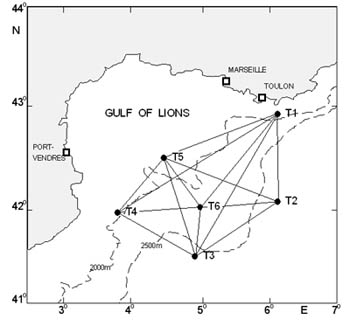
The acoustic tomography approach provides an indirect measure of the temperature of an ocean volume. The technique provides an integrated measure of temperature along the sound propagation paths. The variety of paths between a transmitter and a receiver, as well as the large number of instruments deliver information on the variability of the thermal content of the insonified volume.
-

Data were collected from the regional program LOUPE (Observation of the habitat and associated communities in the context of the fisheries of the Capbreton Canyon). It consisted in the observations of two métiers practiced around the canyon. The observations were carried out between July 2011 and April 2013 on coastal boats. Observations and interviews were made on board commercial vessels. The longlines used in the hake fishery are semi-pelagic and are deployed on the edge of the Capbreton Canyon. It is an emblematic and major métier benefiting from a particular regulation as they take advantage of a prohibition of net and trawl fishing on their fishing grounds. Between 8 and 14 costal boats practice this métier during the year and the fleet characteristics are homogeneous. Boats lay between 1,200 and 1,800 hooks per day, baited with frozen pilchard (Sardina pilchardus). Two or three men are on board these vessels. Fishing is mostly practiced in spring and summer but a small number of vessels work all year. Generally, trips last between ten and twelve hours; longline is set before sunrise and retrieved three or four hours later. Hake is the main targeted species; other targets are pollack (Pollachius pollachius), red sea bream (Pagellus bogaraveo) and conger (Conger conger). Netting is a major métier in terms of vessels involved and the number of trips. Crew composition varies and depends on boat length (from one to four men on average). This métier is practiced by 30 to 35 boats all year round, but fleet characteristics are less homogeneous than in the case of longliners . The strategy of these netters operating in the coastal area is based on the use of several types of nets (gillnets and trammel nets) targeting several species, often sold directly to consumers on the docks. Gillnets, consisting of a single mesh, target hake, sea bass and sea bream species (Diplodus spp, Sparus aurata, Litognathus mormyrus), while the trammel nets (three meshes) are used to capture benthic fish, such as common sole, monkfish (Lophius spp), turbot and brill (Scophthalmus rhombus). Generally, trips last less than twelve hours for coastal netters (less than 15 m), which predominate in the sector, and a few days for large netters. On average, the coastal vessels set 6000 to 8000 m. nets daily.
-
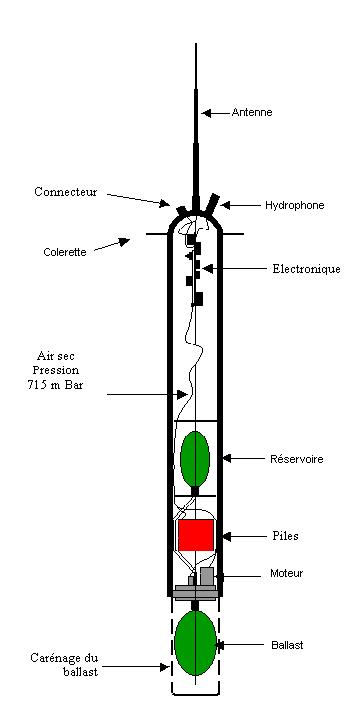
The RAFOS float technique (the reverse acronym of SOund Fixing And Ranging) is used to obtain sub-surface trajectories of floats by acoustic location. These floats are immersed at a constant depth and drift with the body of water in which they are immersed. The floats record the arrival time of the sound signals emitted by a network of fixed acoustic sources placed on moorings. They regularly come to the surface to transmit the data that they have recorded.
-
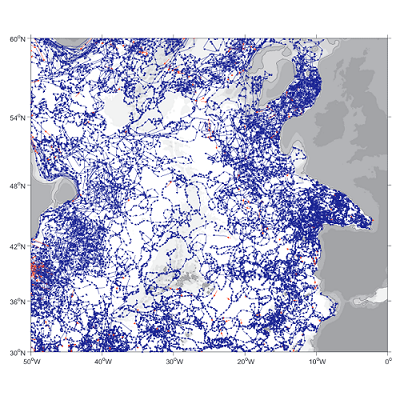
A world deep displacement dataset, named ANDRO, after a traditional dance of Brittany meaning a swirl, comprising more than 1300 000 deep displacements, has been produced from the Argo float trajectory data ('traj' files). ANDRO dataset was completed over the period 2000-2009, then was partially but yearly updated since 2010. For detailed information and status of the last released ANDRO product, please visit the dedicated Argo France web page: https://www.umr-lops.fr/SNO-Argo/Products/ANDRO-Argo-floats-displacements-Atlas One important feature of ANDRO is that the pressures measured during float drifts at depth, and suitably averaged are preserved in ANDRO. To reach this goal, it was necessary to reprocess most of the Argo raw data, because of the many different decoding versions (roughly 100) not always applied by the DACs to the displacement data because they were mainly interested in the p,t,S profiles. The result of our work was the production of comprehensive files, named DEP (for 'déplacement' in French), containing all the possibly retrievable float data.
-
Raw seismic reflexion data collected on board of the French oceanographic fleet managed by IFREMER and archived at SISMER.
-
Raw underway marine gravity data from the French civil Research vessels and archived at SISMER (IFREMER)
-
Raw underway marine magnetic data collected on board of the French civil Research vessels and archived at SISMER (IFREMER)
-
Reflectivity measurements of the multibeam echosounders of the French Research Vessels
-
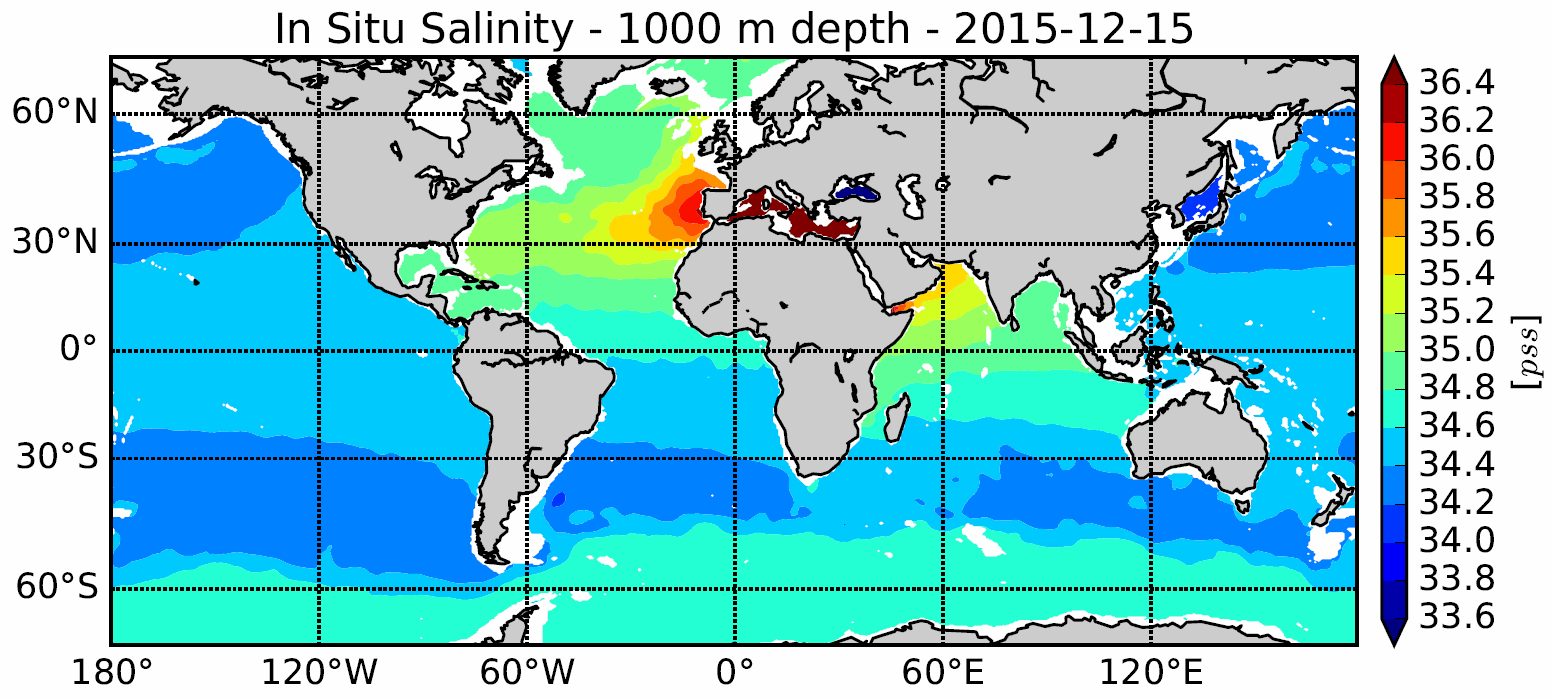
The In Situ Analysis System (ISAS) has been developed to produce temperature and salinity fields that preserve as far as possible the time and space sampling capabilities of the Argo float network. Since the first global analysis in 2009, the system has been extended to take into account all types of vertical profiles and time series, as well as new parameters such as dissolved oxygen produced by BGC Argo. ISAS gridded fields are based entirely on in situ measurements. The system aims to monitor the evolution of ocean properties as a function of time for climatological studies, and to enable easy calculation of climate indices. Delayed-time processing of the 2002-2020 dataset has been carried out using ISAS-V8 and the updating of a priori statistics. Note that ISAS-V8 has been implemented as an operational analysis tool at the Coriolis data center since June 2020.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA