Habitats and biotopes
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
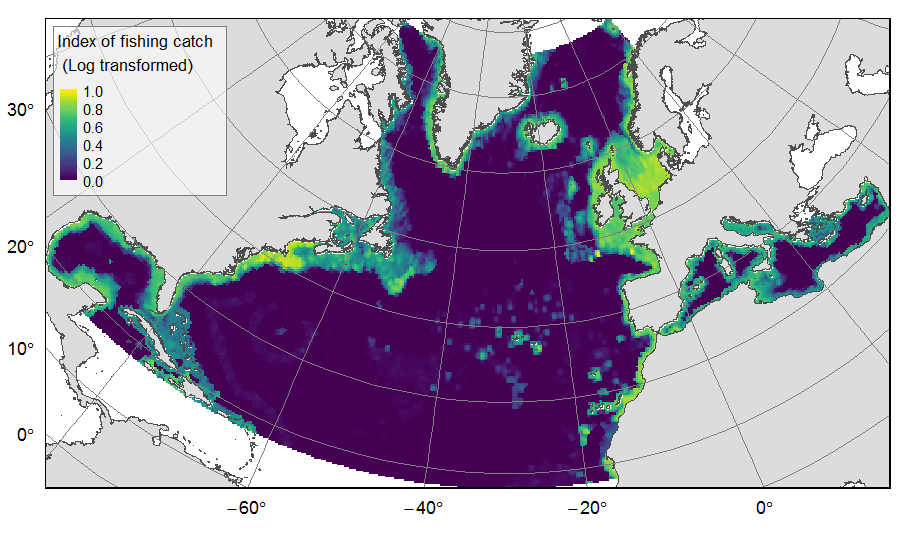
Distribution of catch from deep-sea impacting fishing on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W), for the period 2010-2015. The average of yearly fishing catch for the period 2010-2015 is displayed as an index on the ATLAS grid of 25km * 25km resolution. Source data originated from the Global Fisheries Landings V4.0 database. The dataset was filtered to select only the fishing gears that have an impact on large areas of the seafloor (dredges, bottom trawls, and Danish seines). Within each cell, all remaining catch records were summed to get the total catch rate of the considered year. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
The present data set concerne metabarcoding raw reads produced using 4 different PCR targeting polymerase or capside coding region of the genoyupe I and II of norovirus. Test samples of norovirus with serial dilutions in pure water and after a bio-accumulation in oysters. Sequencing was made after VirCapSeq-VERT approach.
-
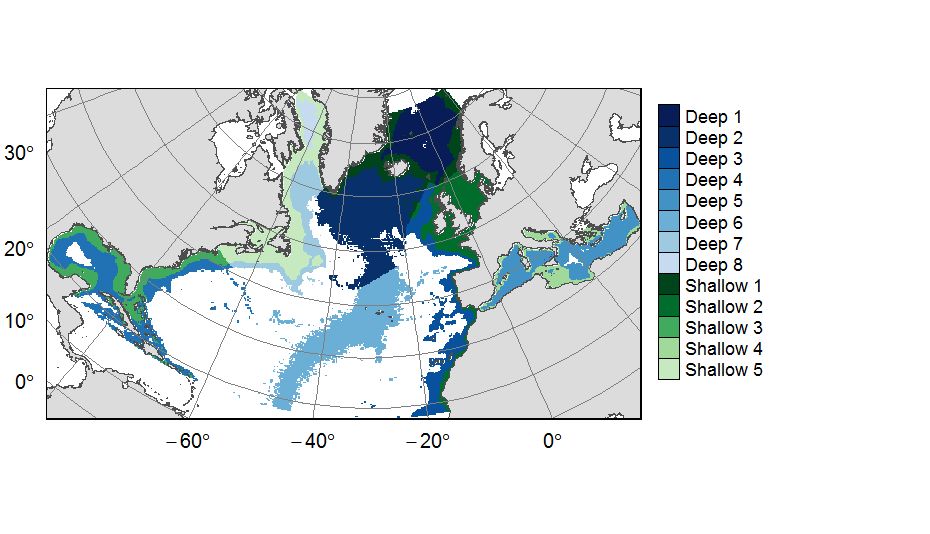
Planning units layers used for ATLAS EU prioritization scenarios on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). This raster layer is designed on a grid of 25km * 25km resolution, that served to extract all the spatial data used prioritization. The 31 518 planning units (cells with value) corresponded to areas containing depths shallower or equal to 3500m, even if they could also contain deeper areas locally. For connectivity scenarios, only the planning units matching with the extent of available connectivity data were selected. One layer allocates planning units to the 13 geographical provinces (values ranging from 1 to 13) created for the purpose of prioritization. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-

WGS for Iatlantic projet ( ) for assessing past and present connectivity
-

Raw reads for the assembly of Gambusia holbrooki genome.
-

WGS of SARS-CoV-2 by Oxford Nanopore Technology from raw wastewater samples collected in France, 2020-2021
-

Develop parentage assignment panels using genetic fingerprinting of pearl oysters for use in commercial hatcheries and research to manage pedigrees in order to limit the risks of loss of genetic variability and increased inbreeding of commercial lines.
-

This study gathers multi-year environmental sequencing datasets generated within the French ROME pilot observatory network. It includes eDNA metabarcoding and RNA-based analyses from water samples, oyster tissues, and viral fractions collected across four French estuarine ecosystems between 2020 and 2023, supporting integrated monitoring of coastal microbiomes and microbial hazards.
-

This study aims to compare different metabarcoding sequences of commercially fished shrimps collected by tree counties on the North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystem
-

Sequenced samples are city center wastewater sampled by passive samplers. Variants are identified by Illumina Miseq sequencing.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA