oceans
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
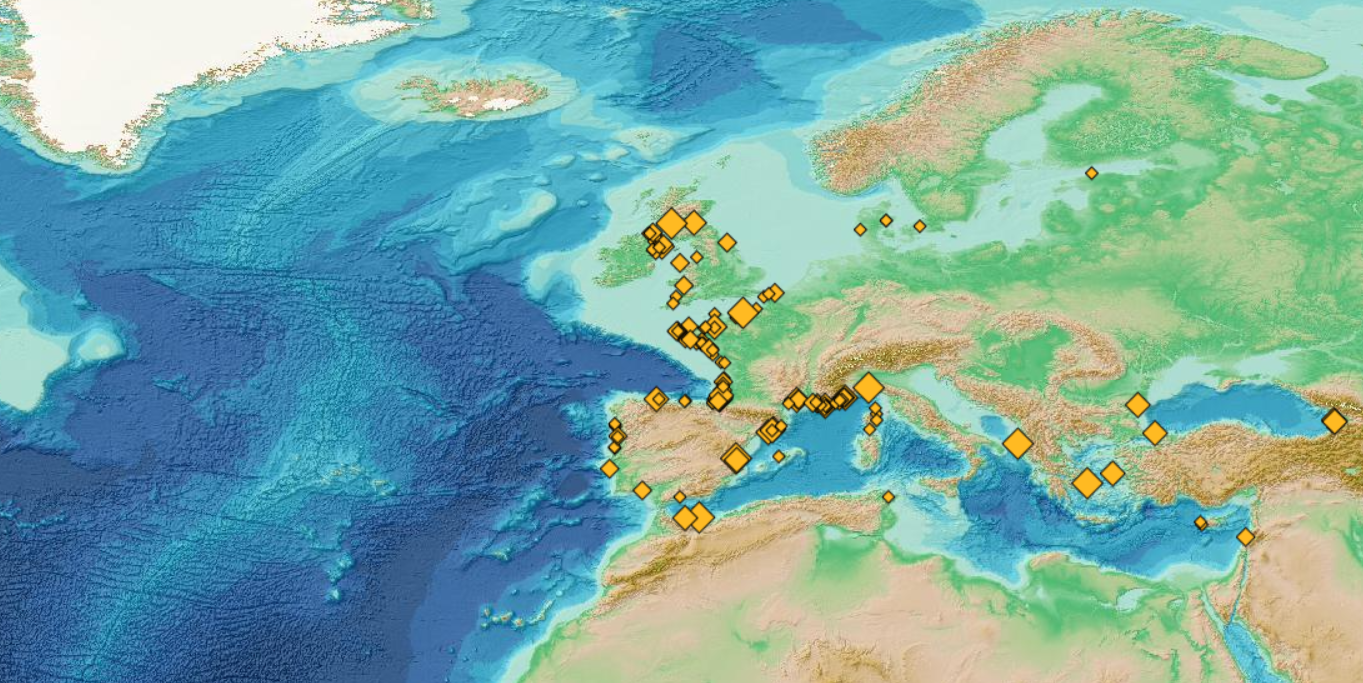
This visualization product displays the total abundance of marine macro-litter (> 2.5cm) per beach per year from non-MSFD monitoring surveys, research & cleaning operations. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of surveys from non-MSFD monitoring, cleaning and research operations; - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Some categories & some litter types like organic litter, small fragments (paraffin and wax; items > 2.5cm) and pollutants have been removed. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines and EU Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines from JRC (these two documents are attached to this metadata). - Exclusion of surveys without associated length; - Normalization of survey lengths to 100m & 1 survey / year: in some case, the survey length was not 100m, so in order to be able to compare the abundance of litter from different beaches a normalization is applied using this formula: Number of items (normalized by 100 m) = Number of litter per items x (100 / survey length) Then, this normalized number of items is summed to obtain the total normalized number of litter for each survey. Finally, the median abundance for each beach and year is calculated from these normalized abundances per survey. Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account other sources data for all years. More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map doesn't necessarily mean that they don't exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-
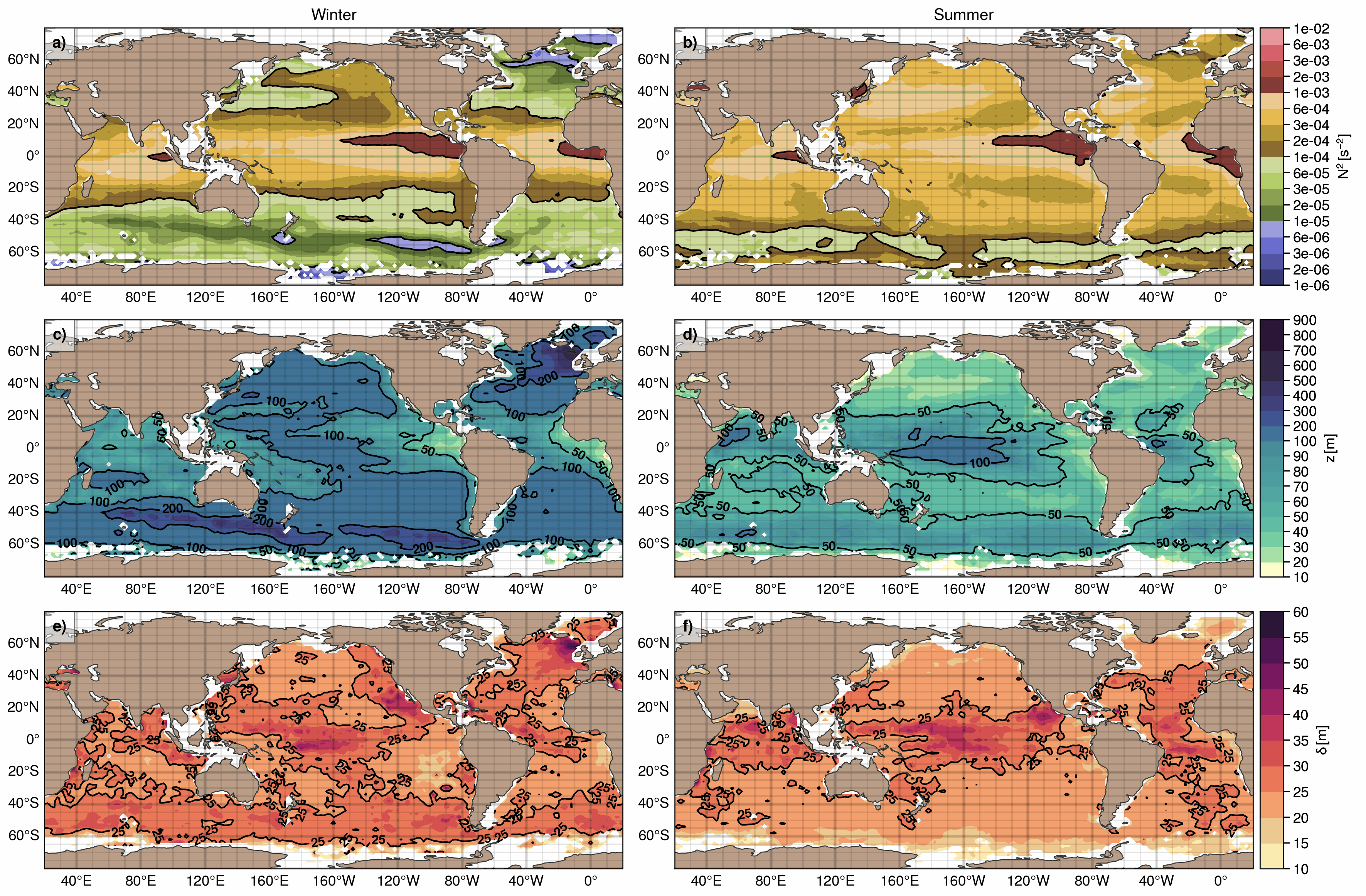
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-
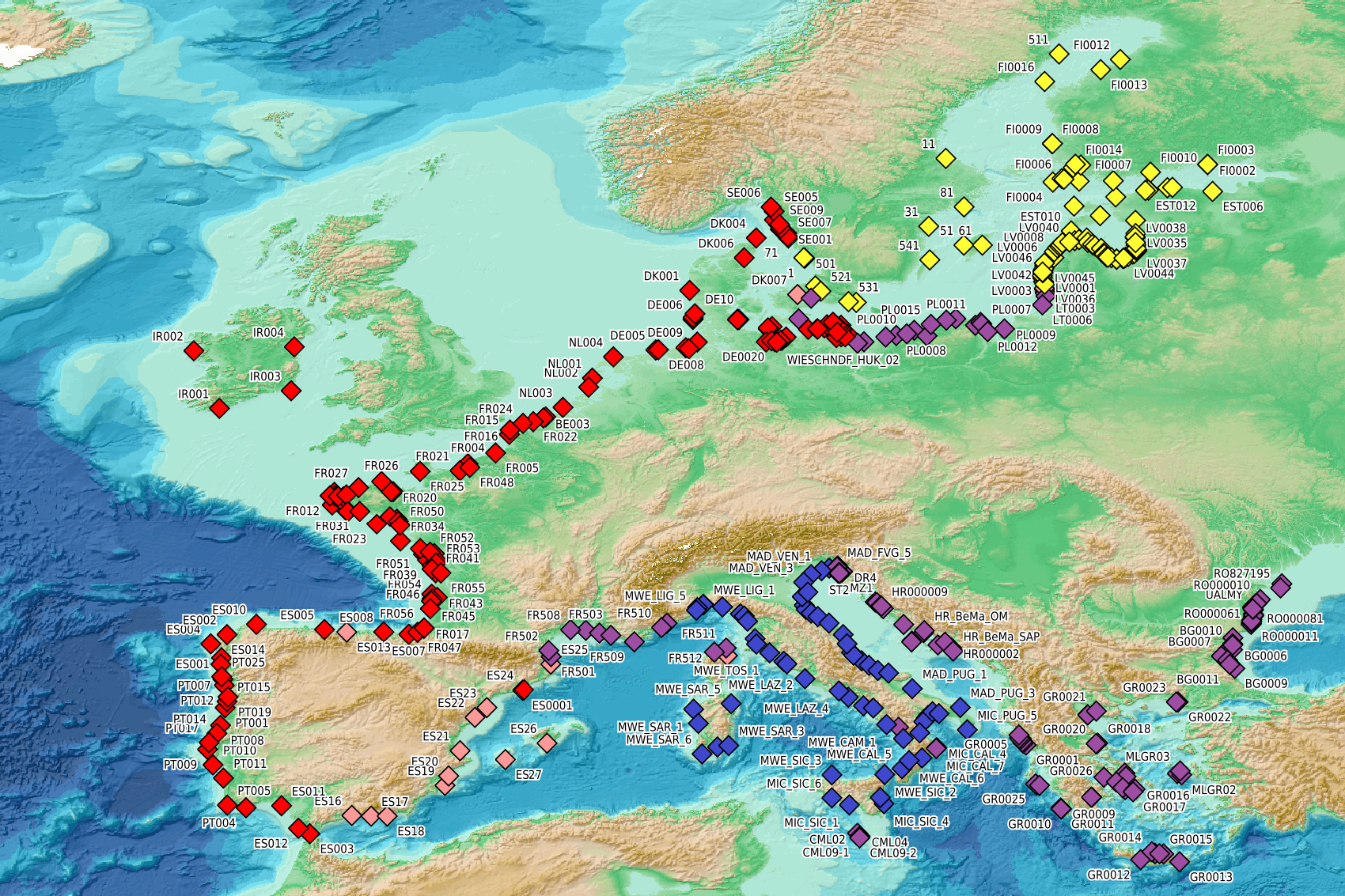
This visualization product displays beaches locations where the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) monitoring protocol has been applied to collate data on macrolitter (> 2.5 cm). Reference lists associated with these protocols have been indicated with different colors in the map. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of MSFD surveys only (exclusion of other monitoring, cleaning and research operations); - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Some categories & some litter types like organic litter, small fragments (paraffin and wax; items > 2.5cm) and pollutants have been removed. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines and EU Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines from JRC (these two documents are attached to this metadata). More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map doesn't necessarily mean that they don't exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-

'''DEFINITION''' Heat transport across lines are obtained by integrating the heat fluxes along some selected sections and from top to bottom of the ocean. The values are computed from models’ daily output. The mean value over a reference period (1993-2014) and over the last full year are provided for the ensemble product and the individual reanalysis, as well as the standard deviation for the ensemble product over the reference period (1993-2014). The values are given in PetaWatt (PW). '''CONTEXT''' The ocean transports heat and mass by vertical overturning and horizontal circulation, and is one of the fundamental dynamic components of the Earth’s energy budget (IPCC, 2013). There are spatial asymmetries in the energy budget resulting from the Earth’s orientation to the sun and the meridional variation in absorbed radiation which support a transfer of energy from the tropics towards the poles. However, there are spatial variations in the loss of heat by the ocean through sensible and latent heat fluxes, as well as differences in ocean basin geometry and current systems. These complexities support a pattern of oceanic heat transport that is not strictly from lower to high latitudes. Moreover, it is not stationary and we are only beginning to unravel its variability. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The mean transports estimated by the ensemble global reanalysis are comparable to estimates based on observations; the uncertainties on these integrated quantities are still large in all the available products. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00245
-

'''Short description:''' Le modèle biogéochimique ECO-MARS3D sur la façade Manche Atlantique (PREVIMER_B1-ECOMARS3D-MANGA4000) est un modèle 3D de résolution spatiale 4km qui fournit les concentrations de nutriments et de plancton toutes les heures sur 30 niveaux (fenêtre de prévision à 4 jours). '''Paramètres calculés :''' Les paramètres calculés sont les suivants : * SAL : sea_water_salinity * TEMP : sea_water_temperature * suspended_inorganic_particulate_matter : mass_concentration_of_suspended_matter_in_sea_water * nanopicoplankton_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * diatom_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * dinoflagellate_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * microzooplankton_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * mesozooplankton_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogen : mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_water * phaeocystis_mucus : concentration_of_phaeocystis_mucus_expressed_as_mass_in_sea_water * ammonium : mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_water * nitrate : mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_water * dissolved_silicate : mole_concentration_of_silicate_in_sea_water * dissolved_phosphate : mole_concentration_of_phosphate_in_sea_water * dissolved_oxygen : dissolved_oxygen_in_water_column * cumulative_nanoflagellate_carbon_production : cumulative_nanoflagellate_production_expressed_as_carbon_in_sea_water * cumulative_diatom_carbon_production : cumulative_diatom_production_expressed_as_carbon_in_sea_water * cumulative_dinoflagellate_carbon_production : cumulative_dinoflagellate_production_expressed_as_carbon_in_sea_water * cumulative_phaeocystis_carbon_production : cumulative_phaeocystis_production_expressed_as_carbon_in_sea_water * organic_nitrogen_benth : mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthos Les paramètres diagnostiques calculés sont les suivants : * XE : sea_surface_height_above_geoid * maximum_de_diat : maximum_diatom_mass_concentration_in_sea_water * maximum_de_dino : maximum_dinoflagellate_mass_concentration_in_sea_water * maximum_de_nano : maximum_nanoflagellate_mass_concentration_in_sea_water * grad_vert_salinite : maximum_vertical_gradient_of_sea_water_salinity * grad_vert_temp : maximum_vertical_gradient_of_sea_water_temperature * extinction_lumineuse : light_extinction_in_sea_water * prod_diat : cumulated_production_of_diatoms_in_sea_water_column_expressed_in_carbon * prod_dino : cumulated_production_of_dinoflagellates_in_sea_water_column_expressed_in_carbon * prod_nano : cumulated_production_of_nanoflagellates_in_sea_water_column_expressed_in_carbon * chlorophylle_a : chlorophyll_mass_concentration_in_sea_water * prod_cumul_chloro : cumulated_total_production_in_sea_water_column_expressed_in_carbon * maximum_de_phaeocystis : maximum_phaeocystis_mass_concentration_in_sea_water * prod_phaeocystis : cumulated_production_of_phaeocystis_in_sea_water_column_expressed_in_carbon * oxygen_saturation : oxygen_saturation * ammoniumGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * ammoniumGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * nitrateGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * nitrateGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * diatom_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * diatom_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * dinoflagellate_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * dinoflagellate_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * microzooplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * microzooplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * mesozooplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * mesozooplankton_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * detrital_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * detrital_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_sign * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterGIRON_tracer_age * organic_nitrogen_benthGIRON_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosGIRON_tracer_sign * organic_nitrogen_benthGIRON_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosGIRON_tracer_age * phytoplankton_sign_N_GIRON: nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_GIRON * phytoplankton_age_N_GIRON: age_of_nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_GIRON * ammoniumLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * ammoniumLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * nitrateLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * nitrateLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * diatom_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * diatom_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * dinoflagellate_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * dinoflagellate_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * microzooplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * microzooplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * mesozooplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * mesozooplankton_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * detrital_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * detrital_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_sign * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterLOIRE_tracer_age * organic_nitrogen_benthLOIRE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosLOIRE_tracer_sign * organic_nitrogen_benthLOIRE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosLOIRE_tracer_age * phytoplankton_sign_N_LOIRE: nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_LOIRE * phytoplankton_age_N_LOIRE: age_of_nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_LOIRE * ammoniumSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * ammoniumSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_ammonium_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * nitrateSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * nitrateSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nitrate_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * nanopicoplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_nanoplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * diatom_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * diatom_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_diatoms_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * dinoflagellate_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * dinoflagellate_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_dinoflagellates_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * microzooplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * microzooplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_microzooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * mesozooplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * mesozooplankton_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_mesozooplankton_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * detrital_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * detrital_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * colonial_phaeocystis_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_colonial_phaeocystis_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_sign * phaeocystis_cells_nitrogenSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_phaeocystis_cells_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_sea_waterSEINE_tracer_age * organic_nitrogen_benthSEINE_tracer_sign: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosSEINE_tracer_sign * organic_nitrogen_benthSEINE_tracer_age: mole_concentration_of_organic_detritus_expressed_as_nitrogen_in_benthosSEINE_tracer_age * phytoplankton_sign_N_SEINE: nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_SEINE * phytoplankton_age_N_SEINE: age_of_nitrogen_fraction_in_phytoplankton_from_source_SEINE
-
The three digital maps provided in this product aim to assess the degree of Offshore windfarm siting suitability existing over a geographical area with a focal point where waters of France and Spain meet in Biscay Bay on 500 m depth. The maps display respectively the spatial distribution of the average and lowest windfarm siting suitability scores along with the average wind speed distribution over a time period of 10 years. They are part of a process set up to assess the fit for use quality of the currently available datasets to support a preliminary selection of potential offshore sites for wind energy development. To build these maps, GIS tools were applied to several key spatial datasets from the 5 data type domains considered in the project: Air, Marine Water, Riverbed/Seabed, Biota/Biology and Human Activities, collated during the initial stages of the project. Initially, each selected dataset was formatted and clipped to the study area extent and spatially classified according to suitability scores, to define raster layers with the variables depicting levels of current anthropogenic and environmental spatial occupation of activities, seabed depth and slope, distances to shoreline, shipping intensity, mean significant wave height, and substrate type. These pre-processed layers were employed as inputs for applying a spatial multi-criteria model using a wind farming suitability classification based on a discrete 5 grades index, ranging from Very Low up to Very High suitability. In adition to suitability maps, an average wind speed spatial distribution map for a 10 years period, at 10 m height, was obtained over the study area from the raster processing of a wind speed time series of monthly means available from daily wind analysis data. The characteristics of the datasets used in this exercise underwent an appropriateness evaluation procedure based on a comparison between their measured quality and those specified for the product. All the spatial information made available in these maps and from the subsequent appropriateness analysis of the datasets, contributes to a clearer overview of the amount of public-access baseline knowledge currently existing for the North Atlantic basin area.
-
This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic, in the framework of the ATLAS H2020 project. This approach aimed to inform Marine Spatial Planning and conservation initiatives for the deep sea of the North Atlantic, by identifying conservation priority areas for the Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species and discussing the efficiency of the current spatial management context relatively to conservation stakes. This publication provides (1) the links to spatial datasets used as an input, (2) the R scripts used to run the final conservation scenarios together with associated table of targets and connectivity matrix, that can be run on the input data, and (3) the outputs of the final scenarios constructed and computed for ATLAS. Produced by IFREMER. This output reflects the authors’ views and the European Union is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains. Please note that you use these data at your own risk. No warranty is expressed or implied and no liability is accepted for any inconveniences or damages that may ensue from their use.
-

This dataset gathers results of monthly sampling with a WP2 plankton net within the Gironde plume (Bay of Biscay) in 2008 from March to August, as part of the ECLAIR suite of surveys. The sampling in May was part of the ECLAIR time-series but was performed onboard the THALASSA vessel during the PELGAS 2008 survey. Results are made of anchovy and sardine egg abundances, as well as size-fractionnated zooplankton biomass.
-

-

 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA