annually
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
-

'''DEFINITION''' Ocean heat content (OHC) is defined here as the deviation from a reference period (1993-2014) and is closely proportional to the average temperature change from z1 = 0 m to z2 = 700 m depth: OHC=∫_(z_1)^(z_2)ρ_0 c_p (T_yr-T_clim )dz [1] with a reference density of = 1030 kgm-3 and a specific heat capacity of cp = 3980 J kg-1 °C-1 (e.g. von Schuckmann et al., 2009). Time series of annual mean values area averaged ocean heat content is provided for the Mediterranean Sea (30°N, 46°N; 6°W, 36°E) and is evaluated for topography deeper than 300m. '''CONTEXT''' Knowing how much and where heat energy is stored and released in the ocean is essential for understanding the contemporary Earth system state, variability and change, as the oceans shape our perspectives for the future. The quality evaluation of MEDSEA_OMI_OHC_area_averaged_anomalies is based on the “multi-product” approach as introduced in the second issue of the Ocean State Report (von Schuckmann et al., 2018), and following the MyOcean’s experience (Masina et al., 2017). Six global products and a regional (Mediterranean Sea) product have been used to build an ensemble mean, and its associated ensemble spread. The reference products are: • The Mediterranean Sea Reanalysis at 1/24 degree horizontal resolution (MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_PHY_006_004, DOI: https://doi.org/10.25423/CMCC/MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_PHY_006_004_E3R1, Escudier et al., 2020) • Four global reanalyses at 1/4 degree horizontal resolution (GLOBAL_MULTIYEAR_PHY_ENS_001_031): GLORYS, C-GLORS, ORAS5, FOAM • Two observation based products: CORA (INSITU_GLO_PHY_TS_OA_MY_013_052) and ARMOR3D (MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_TSUV_3D_MYNRT_015_012). Details on the products are delivered in the PUM and QUID of this OMI. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The ensemble mean ocean heat content anomaly time series over the Mediterranean Sea shows a continuous increase in the period 1993-2022 at rate of 1.38±0.08 W/m2 in the upper 700m. After 2005 the rate has clearly increased with respect the previous decade, in agreement with Iona et al. (2018). '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00261
-
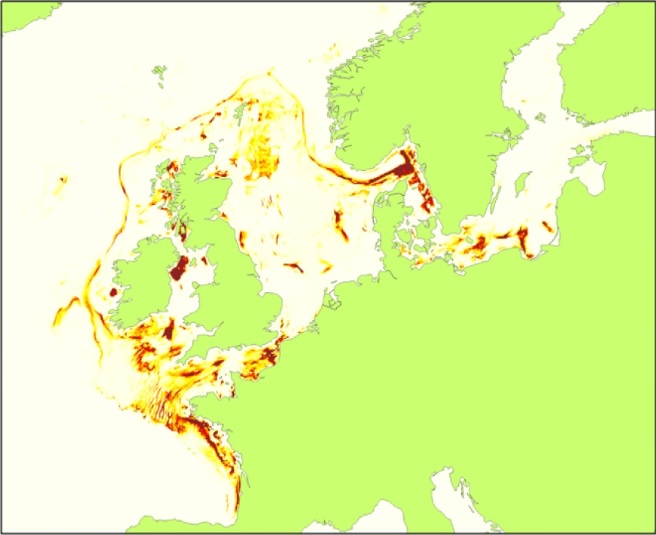
'''Short description:''' For the Global Ocean- Gridded objective analysis fields of temperature and salinity using profiles from the reprocessed in-situ global product CORA (INSITU_GLO_TS_REP_OBSERVATIONS_013_001_b) using the ISAS software. Objective analysis is based on a statistical estimation method that allows presenting a synthesis and a validation of the dataset, providing a validation source for operational models, observing seasonal cycle and inter-annual variability. Acces through CMEMS Catalogue after registration: http://marine.copernicus.eu/ '''Detailed description:''' The operational analysis system set up by the in-situ TAC Global component operated by Coriolis data centre. It produces temperature and salinity gridded fields. The system is based on a statistical estimation method (objective analysis). This system allows presenting a synthesis and a validation of the dataset, providing a validation source for operational models, observing seasonal cycle and inter-annual variability.
-

'''DEFINITION''' The temporal evolution of thermosteric sea level in an ocean layer is obtained from an integration of temperature driven ocean density variations, which are subtracted from a reference climatology to obtain the fluctuations from an average field. The products used include three global reanalyses: GLORYS, C-GLORS, ORAS5 (GLOBAL_MULTIYEAR_PHY_ENS_001_031) and two in situ based reprocessed products: CORA5.2 (INSITU_GLO_PHY_TS_OA_MY_013_052) , ARMOR-3D (MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_TSUV_3D_MYNRT_015_012). Additionally, the time series based on the method of von Schuckmann and Le Traon (2011) has been added. The regional thermosteric sea level values are then averaged from 60°S-60°N aiming to monitor interannual to long term global sea level variations caused by temperature driven ocean volume changes through thermal expansion as expressed in meters (m). '''CONTEXT''' The global mean sea level is reflecting changes in the Earth’s climate system in response to natural and anthropogenic forcing factors such as ocean warming, land ice mass loss and changes in water storage in continental river basins. Thermosteric sea-level variations result from temperature related density changes in sea water associated with volume expansion and contraction (Storto et al., 2018). Global thermosteric sea level rise caused by ocean warming is known as one of the major drivers of contemporary global mean sea level rise (Cazenave et al., 2018; Oppenheimer et al., 2019). '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' Since the year 2005 the upper (0-2000m) near-global (60°S-60°N) thermosteric sea level rises at a rate of 1.3±0.3 mm/year. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00240
-

-

'''This product has been archived''' '''DEFINITION''' The temporal evolution of thermosteric sea level in an ocean layer is obtained from an integration of temperature driven ocean density variations, which are subtracted from a reference climatology to obtain the fluctuations from an average field. The regional thermosteric sea level values are then averaged from 60°S-60°N aiming to monitor interannual to long term global sea level variations caused by temperature driven ocean volume changes through thermal expansion as expressed in meters (m). '''CONTEXT''' Most of the interannual variability and trends in regional sea level is caused by changes in steric sea level. At mid and low latitudes, the steric sea level signal is essentially due to temperature changes, i.e. the thermosteric effect (Stammer et al., 2013, Meyssignac et al., 2016). Salinity changes play only a local role. Regional trends of thermosteric sea level can be significantly larger compared to their globally averaged versions (Storto et al., 2018). Except for shallow shelf sea and high latitudes (> 60° latitude), regional thermosteric sea level variations are mostly related to ocean circulation changes, in particular in the tropics where the sea level variations and trends are the most intense over the last two decades. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' Significant (i.e. when the signal exceeds the noise) regional trends for the period 2005-2019 from the Copernicus Marine Service multi-ensemble approach show a thermosteric sea level rise at rates ranging from the global mean average up to more than 8 mm/year. There are specific regions where a negative trend is observed above noise at rates up to about -8 mm/year such as in the subpolar North Atlantic, or the western tropical Pacific. These areas are characterized by strong year-to-year variability (Dubois et al., 2018; Capotondi et al., 2020). Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00241
-

'''This product has been archived''' For operationnal and online products, please visit https://marine.copernicus.eu '''DEFINITION''' Oligotrophic subtropical gyres are regions of the ocean with low levels of nutrients required for phytoplankton growth and low levels of surface chlorophyll-a whose concentration can be quantified through satellite observations. The gyre boundary has been defined using a threshold value of 0.15 mg m-3 chlorophyll for the Atlantic gyres (Aiken et al. 2016), and 0.07 mg m-3 for the Pacific gyres (Polovina et al. 2008). The area inside the gyres for each month is computed using monthly chlorophyll data from which the monthly climatology is subtracted to compute anomalies. A gap filling algorithm has been utilized to account for missing data. Trends in the area anomaly are then calculated for the entire study period (September 1997 to December 2020). '''CONTEXT''' Oligotrophic gyres of the oceans have been referred to as ocean deserts (Polovina et al. 2008). They are vast, covering approximately 50% of the Earth’s surface (Aiken et al. 2016). Despite low productivity, these regions contribute significantly to global productivity due to their immense size (McClain et al. 2004). Even modest changes in their size can have large impacts on a variety of global biogeochemical cycles and on trends in chlorophyll (Signorini et al. 2015). Based on satellite data, Polovina et al. (2008) showed that the areas of subtropical gyres were expanding. The Ocean State Report (Sathyendranath et al. 2018) showed that the trends had reversed in the Pacific for the time segment from January 2007 to December 2016. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The trend in the North Atlantic gyre area for the 1997 Sept – 2020 December period was positive, with a 0.39% year-1 increase in area relative to 2000-01-01 values. This trend has decreased compared with the 1997-2019 trend of 0.45%, and is statistically significant (p<0.05). During the 1997 Sept – 2020 December period, the trend in chlorophyll concentration was positive (0.24% year-1) inside the North Atlantic gyre relative to 2000-01-01 values. This time series extension has resulted in a reversal in the rate of change, compared with the -0.18% trend for the 1997-209 period and is statistically significant (p<0.05). Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00226
-

-

'''DEFINITION''' The CMEMS IBI_OMI_tempsal_extreme_var_temp_mean_and_anomaly OMI indicator is based on the computation of the annual 99th percentile of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) from model data. Two different CMEMS products are used to compute the indicator: The Iberia-Biscay-Ireland Multi Year Product (IBI_MULTIYEAR_PHY_005_002) and the Analysis product (IBI_ANALYSISFORECAST_PHY_005_001). Two parameters have been considered for this OMI: • Map of the 99th mean percentile: It is obtained from the Multi Year Product, the annual 99th percentile is computed for each year of the product. The percentiles are temporally averaged over the whole period (1993-2021). • Anomaly of the 99th percentile in 2022: The 99th percentile of the year 2022 is computed from the Analysis product. The anomaly is obtained by subtracting the mean percentile from the 2022 percentile. This indicator is aimed at monitoring the extremes of sea surface temperature every year and at checking their variations in space. The use of percentiles instead of annual maxima, makes this extremes study less affected by individual data. This study of extreme variability was first applied to the sea level variable (Pérez Gómez et al 2016) and then extended to other essential variables, such as sea surface temperature and significant wave height (Pérez Gómez et al 2018 and Alvarez Fanjul et al., 2019). More details and a full scientific evaluation can be found in the CMEMS Ocean State report (Alvarez Fanjul et al., 2019). '''CONTEXT''' The Sea Surface Temperature is one of the essential ocean variables, hence the monitoring of this variable is of key importance, since its variations can affect the ocean circulation, marine ecosystems, and ocean-atmosphere exchange processes. As the oceans continuously interact with the atmosphere, trends of sea surface temperature can also have an effect on the global climate. While the global-averaged sea surface temperatures have increased since the beginning of the 20th century (Hartmann et al., 2013) in the North Atlantic, anomalous cold conditions have also been reported since 2014 (Mulet et al., 2018; Dubois et al., 2018). The IBI area is a complex dynamic region with a remarkable variety of ocean physical processes and scales involved. The Sea Surface Temperature field in the region is strongly dependent on latitude, with higher values towards the South (Locarnini et al. 2013). This latitudinal gradient is supported by the presence of the eastern part of the North Atlantic subtropical gyre that transports cool water from the northern latitudes towards the equator. Additionally, the Iberia-Biscay-Ireland region is under the influence of the Sea Level Pressure dipole established between the Icelandic low and the Bermuda high. Therefore, the interannual and interdecadal variability of the surface temperature field may be influenced by the North Atlantic Oscillation pattern (Czaja and Frankignoul, 2002; Flatau et al., 2003). Also relevant in the region are the upwelling processes taking place in the coastal margins. The most referenced one is the eastern boundary coastal upwelling system off the African and western Iberian coast (Sotillo et al., 2016), although other smaller upwelling systems have also been described in the northern coast of the Iberian Peninsula (Alvarez et al., 2011), the south-western Irish coast (Edwars et al., 1996) and the European Continental Slope (Dickson, 1980). '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' In the IBI region, the 99th mean percentile for 1993-2021 shows a north-south pattern driven by the climatological distribution of temperatures in the North Atlantic. In the coastal regions of Africa and the Iberian Peninsula, the mean values are influenced by the upwelling processes (Sotillo et al., 2016). These results are consistent with the ones presented in Álvarez Fanjul (2019) for the period 1993-2016. The analysis of the 99th percentile anomaly in the year 2023 shows that this period has been affected by a severe impact of maximum SST values. Anomalies exceeding the standard deviation affect almost the entire IBI domain, and regions impacted by thermal anomalies surpassing twice the standard deviation are also widespread below the 43ºN parallel. Extreme SST values exceeding twice the standard deviation affect not only the open ocean waters but also the easter boundary upwelling areas such as the northern half of Portugal, the Spanish Atlantic coast up to Cape Ortegal, and the African coast south of Cape Aguer. It is worth noting the impact of anomalies that exceed twice the standard deviation is widespread throughout the entire Mediterranean region included in this analysis. '''Figure caption''' Iberia-Biscay-Ireland Surface Temperature extreme variability: Map of the 99th mean percentile computed from the Multi Year Product (left panel) and anomaly of the 99th percentile in 2022 computed from the Analysis product (right panel). Transparent grey areas (if any) represent regions where anomaly exceeds the climatic standard deviation (light grey) and twice the climatic standard deviation (dark grey). '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00254
-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA