2016
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Confidence in the full output of the 2016 EUSeaMap broad-scale predictive model, produced by EMODnet Seabed Habitats. Values are on a range from 1 (low confidence) to 3 (high confidence). Confidence is calculated by amalgamating the confidence values of the underlying applicable habitat descriptors used to generate the habitat value in the area in question. Habitat descriptors differ per region but include: Biological zone Energy class Oxygen regime Salinity regime Seabed Substrate Riverine input Confidence in habitat descriptors are driven by the confidence in the source data used to determine the descriptor, and the confidence in the threshold/margin (areas closer to a boundary between two classes will have lower confidence). Confidence values are also available for each habitat descriptor and input data layer.
-

'''Short description''' The Operational Mercator global ocean analysis and forecast system at 1/12 degree is providing 10 days of 3D global ocean forecasts updated daily. The time series is aggregated in time in order to reach a two full year’s time series sliding window. This product includes daily and monthly mean files of temperature, salinity, currents, sea level, mixed layer depth and ice parameters from the top to the bottom over the global ocean. It also includes hourly mean surface fields for sea level height, temperature and currents. The global ocean output files are displayed with a 1/12 degree horizontal resolution with regular longitude/latitude equirectangular projection. 50 vertical levels are ranging from 0 to 5500 meters. This product also delivers a special dataset for surface current which also includes wave and tidal drift called SMOC (Surface merged Ocean Current). '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016
-
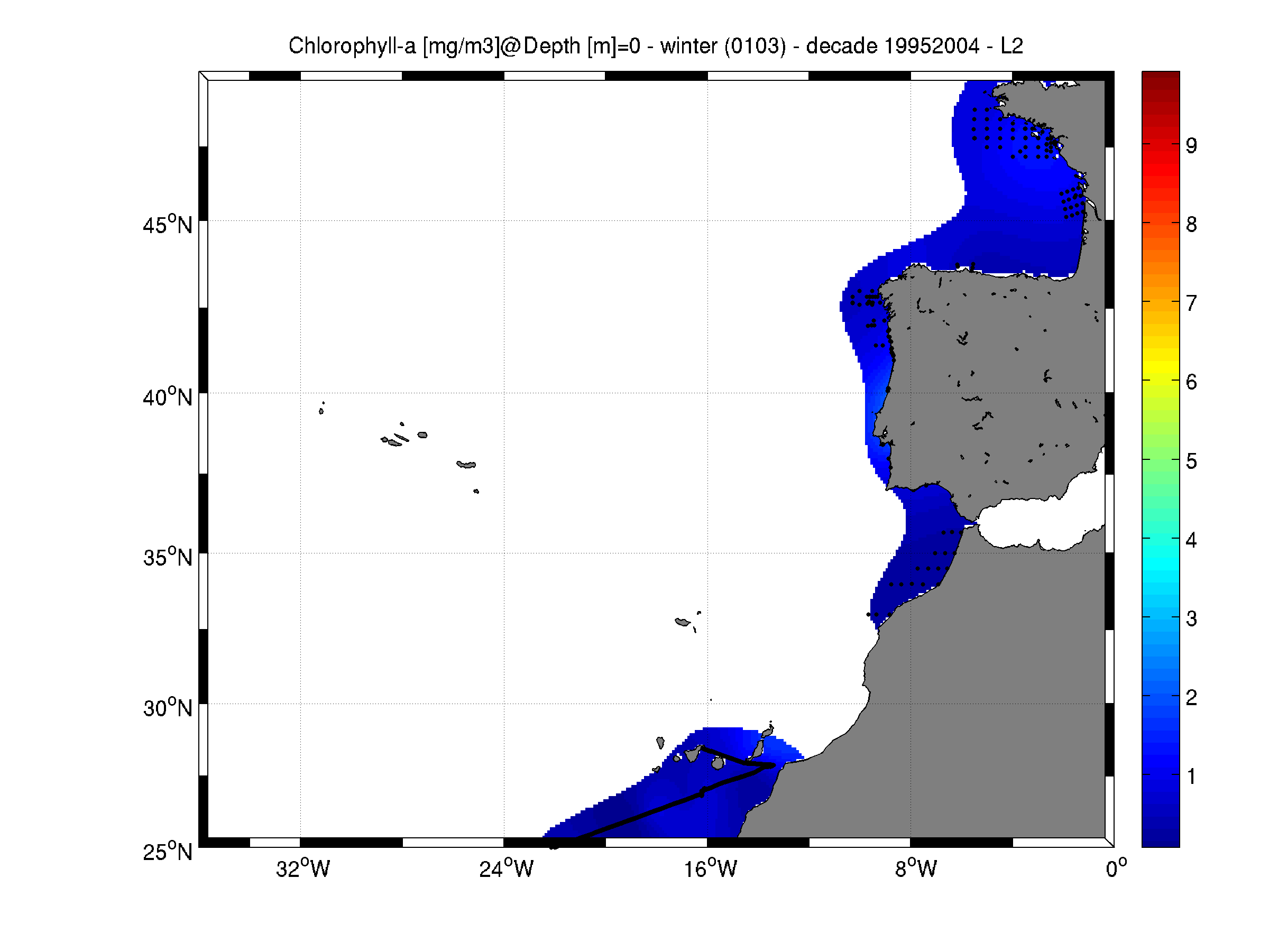
Moving 10-years analysis of Chlorophyll-a -1.0-ANA at Northeast Atlantic Ocean for each season: - winter: January-March, - spring: April-June, - summer: July-September, - autumn: October-December. Every year of the time dimension corresponds to the 10-year centred average of each season. Decades span from 1985-1994 until 2005-2014. Observational data span from 1970 to 2015. Depth range (IODE standard depths): -300.0, -250.0, -200.0, -150.0, -125.0, -100.0, -75.0, -50.0,-40.0, -30.0, -20.0, -10.0, -5.0, -0.0 Data Sources: observational data from SeaDataNet/EMODNet Chemistry Data Network. Description of DIVA analysis: Geostatistical data analysis by DIVA (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis) tool. GEBCO 1min topography is used for the contouring preparation. Analyzed filed masked using relative error threshold 0.3 and 0.5 DIVA settings. Signal to noise ratio and correlation length were optimized and filtered vertically and a seasonally-averaged profile was used. Logarithmic transformation applied to the data prior to the analysis. Background field: the data mean value is subtracted from the data. Detrending of data: no, Advection constraint applied: no. Units: mg/m^3
-
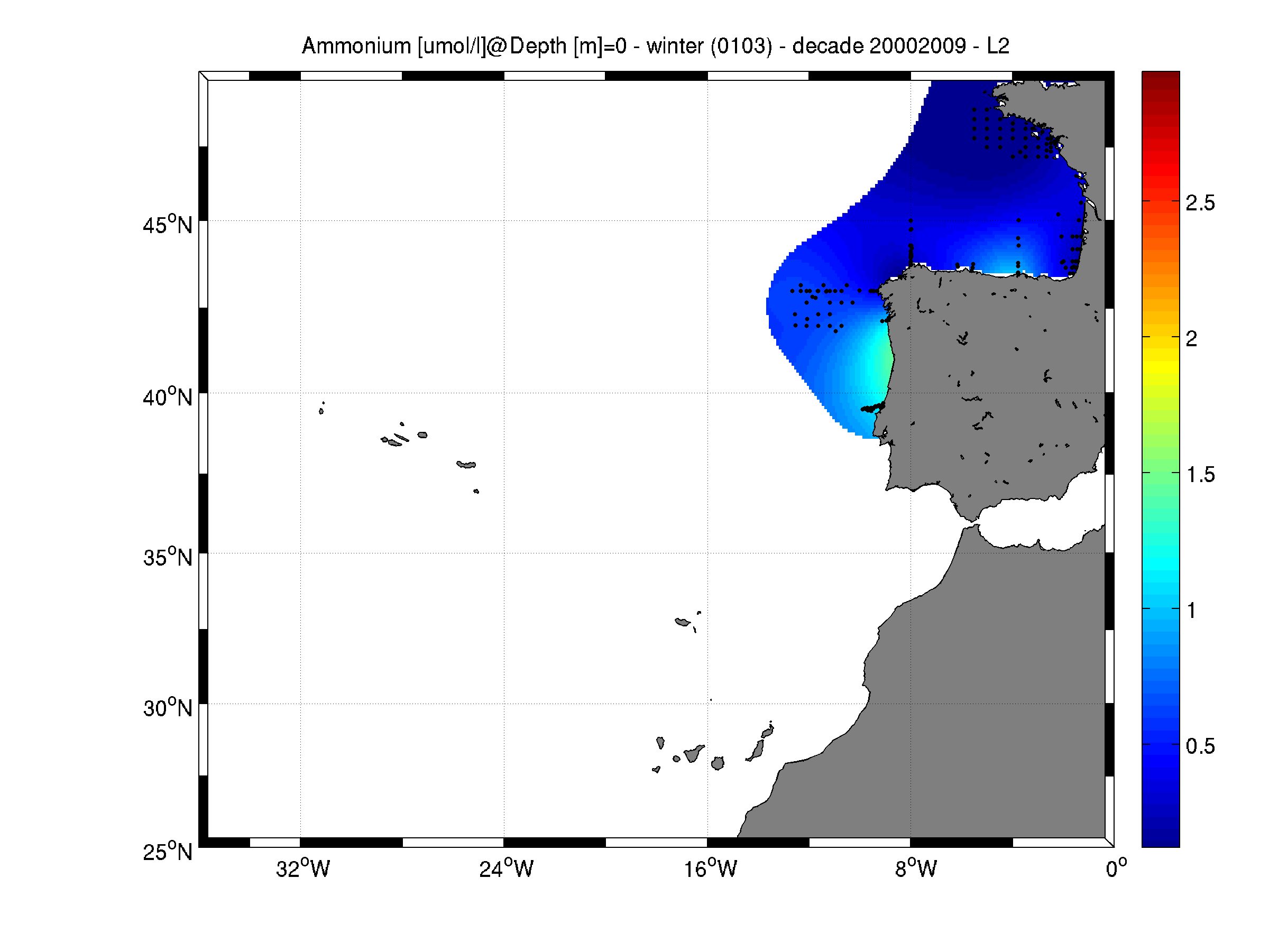
Moving 10-years analysis of Ammonium at Northeast Atlantic Ocean for each season: - winter: January-March, - spring: April-June, - summer: July-September, - autumn: October-December. Every year of the time dimension corresponds to the 10-year centred average of each season. Decades span : - from 1984-1993 until 2005-2014 (winter) - from 1980-1989 until 2005-2014 (spring) - from 1980-1989 until 2005-2014 (summer) - from 1980-1989 until 2005-2014 (autumn) Observational data span from 1962 to 2014. Depth range (IODE standard depths): -3000.0, -2500.0, -2000.0, -1750, -1500.0, -1400.0, -1300.0, -1200.0, -1100.0, -1000.0, -900.0, -800.0, -700.0, -600.0, -500.0, -400.0, -300.0, -250.0, -200.0, -150.0, -125.0, -100.0, -75.0, -50.0,-40.0, -30.0, -20.0, -10.0, -5.0, -0.0 Data Sources: observational data from SeaDataNet/EMODNet Chemistry Data Network. Description of DIVA analysis: Geostatistical data analysis by DIVA (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis) tool. GEBCO 1min topography is used for the contouring preparation. Analyzed filed masked using relative error threshold 0.3 and 0.5 DIVA settings. Signal to noise ratio and correlation length were optimized and filtered vertically and a seasonally-averaged profile was used. Logarithmic transformation applied to the data prior to the analysis. Background field: the data mean value is subtracted from the data. Detrending of data: no, Advection constraint applied: no. Units: umol/l
-
The objective of this tender is to examine the current data collection, observation and data assembly programmes in the Meditterranean Sea, identify gaps and to evaluate how they can be optimised.
-
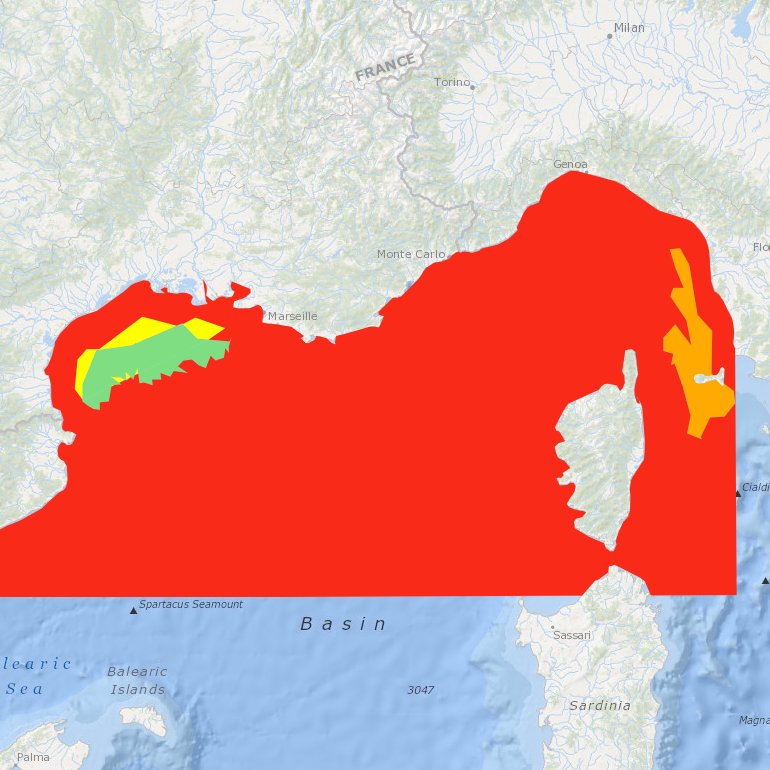
Suitability index of a wind farm in the NWMed concerning the environmental resources, the natural barriers, human activities, MPA and fisheries.
-
'''This product has been archived''' For operationnal and online products, please visit https://marine.copernicus.eu '''Short description''' The Operational Mercator global ocean analysis and forecast system at 1/12 degree is providing 10 days of 3D global ocean forecasts updated daily. The time series is aggregated in time in order to reach a two full year’s time series sliding window. This product includes daily and monthly mean files of temperature, salinity, currents, sea level, mixed layer depth and ice parameters from the top to the bottom over the global ocean. It also includes hourly mean surface fields for sea level height, temperature and currents. The global ocean output files are displayed with a 1/12 degree horizontal resolution with regular longitude/latitude equirectangular projection. 50 vertical levels are ranging from 0 to 5500 meters. This product also delivers a special dataset for surface current which also includes wave and tidal drift called SMOC (Surface merged Ocean Current). '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016
-
Specification of the desirable and recommended product attributes for generating time series of average annual sea temperature at mid-water and sea bottom for the last 10 yrs.
-
Description of de desirable and recomended attributes for generating time-series of sea surface annual average temperature for the last 10, 50 and 100 yrs for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS region along the coast.
-

Level 2 sub-skin Sea Surface Temperature derived from AVHRR on Metop, global and provided in full-resolution swath (1 km at nadir), in GHRSST compliant netCDF format. The satellite input data has successively come from Metop-A, Metop-B and Metop-C level 1 data processed at EUMETSAT. SST is retrieved from AVHRR infrared channels (3.7, 10.8 and 12.0 µm) using a multispectral algorithm and a cloud mask. Atmospheric profiles of water vapor and temperature from a numerical weather prediction model, Sea Surface Temperature from an analysis, together with a radiative transfer model, are used to correct the multispectral algorithm for regional and seasonal biases due to changing atmospheric conditions. The quality of the products is monitored regularly by daily comparison of the satellite estimates against buoy measurements.The product format is compliant with the GHRSST Data Specification (GDS) version 2. Users are advised to use data only with quality levels 3,4 and 5.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA