2019
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
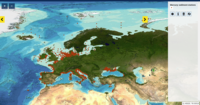
This product displays the stations present in EMODnet validated dataset where mercury levels have been measured in sediment. EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-
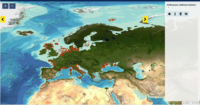
This product displays the stations present in EMODnet validated dataset where anthracene levels have been measured in sediment. EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-
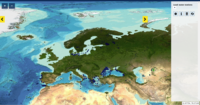
This product displays the stations present in EMODnet validated dataset where lead levels have been measured in water. EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-
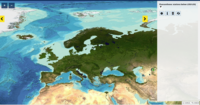
This product displays the stations where fluoranthene has been measured and the values present in EMODnet Chemistry infrastructure are always below the limit of detection or quantification (LOD/LOQ), i.e quality values found in EMODnet validated dataset can be equal to 6 or Q. It is necessary to take into account that LOD/LOQ can change with time. These products aggregate data by station, producing only one final value for each station (above, below or above/below). EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-
remontée geocatalogue mtd tag spécifique "données ouvertes"
-
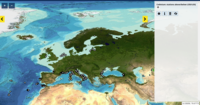
This product displays the stations where cadmium has been measured and the values present in EMODnet Chemistry infrastructure are either above or below the limit of detection or quantification (LOD/LOQ), i.e for the substance, in that station, quality values found in EMODnet validated dataset can be equal to 6, Q or 1. It is necessary to take into account that LOD/LOQ can change with time. These products aggregate data by station, producing only one final value for each station (above, below or above/below). EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-

'''This product has been archived''' For operationnal and online products, please visit https://marine.copernicus.eu '''DEFINITION''' Marine primary production corresponds to the amount of inorganic carbon which is converted into organic matter during the photosynthesis, and which feeds upper trophic layers. The daily primary production is estimated from satellite observations with the Antoine and Morel algorithm (1996). This algorithm modelized the potential growth in function of the light and temperature conditions, and with the chlorophyll concentration as a biomass index. The monthly area average is computed from monthly primary production weighted by the pixels size. The trend is computed from the deseasonalised time series (1998-2019), following the Vantrepotte and Mélin method. More details are provided in the Ocean State Reports 4 (Cossarini et al. ,2020). '''CONTEXT''' Marine primary production is at the basis of the marine food web and produce about 50% of the oxygen we breath every year (Behrenfeld et al., 2001). Study primary production is of paramount importance as ocean health and fisheries are directly linked to the primary production (Pauly and Christensen, 1995, Fee et al., 2019). Changes in primary production can have consequences on biogeochemical cycles, and specially on the carbon cycle, and impact the biological carbon pump intensity, and therefore climate (Chavez et al., 2011). Despite its importance for climate and socio-economics resources, primary production measurements are scarce and do not allow a deep investigation of the primary production evolution over decades. Satellites observations and modelling can fill this gap. However, depending of their parametrisation, models can predict an increase or a decrease in primary production by the end of the century (Laufkötter et al., 2015). Primary production from satellite observations present therefore the advantage to dispose an archive of more than two decades of global data. This archive can be assimilated in models, in addition to direct environmental analysis, to minimise models uncertainties (Gregg and Rousseaux, 2019). In the Ocean State Reports 4, primary production estimate from satellite and from modelling are compared at the scale of the Mediterranean Sea. This demonstrate the ability of such a comparison to deeply investigate physical and biogeochemical processes associated to the primary production evolution (Cossarini et al., 2020) '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The trend for the global ocean is negative over the period 1998-2019 with a decline in primary production of about 0.67 mgC.m-2.yr-1 or equivalently 0.2 %.yr-1. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00225
-
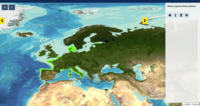
This product displays the stations present in EMODnet validated dataset where benzo[A]pyrene levels have been measured in biota. EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-

The dataset represents the introduction of non-indigenous species in European seas. Non-indigenous species are species that have been spread as a result of human activities to areas where they do not belong naturally. The main concern are the invasive species, which are defined as causing a significant negative impact on biodiversity as well as serious economic and social consequences. The dataset has been prepared first by individually mapping each aquatic invasive species that had a distinctive distribution area, which had been provided by several non-indigenous species online databases. The distribution of the species were then resampled into the EEA 10 km grid and summed together, showing the number of non-indigenous species per grid cell. The temporal reference of the dataset covers the last 30 years (1989 - 2018). This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

This metadata corresponds to the EUNIS Littoral biogenic habitat types (salt marshes), distribution based on vegetation plot data dataset. Littoral biogenic habitats (commonly known as salt marshes) are formed by animals such as worms and mussels or plants. The verified saltmarsh habitat samples used are derived from the Braun-Blanquet database (http://www.sci.muni.cz/botany/vegsci/braun_blanquet.php?lang=en) which is a centralised database of vegetation plots and comprises copies of national and regional databases using a unified taxonomic reference database. The geographic extent of the distribution data are all European countries except Armenia and Azerbaijan. The dataset is provided both in Geodatabase and Geopackage formats.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA