2022
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
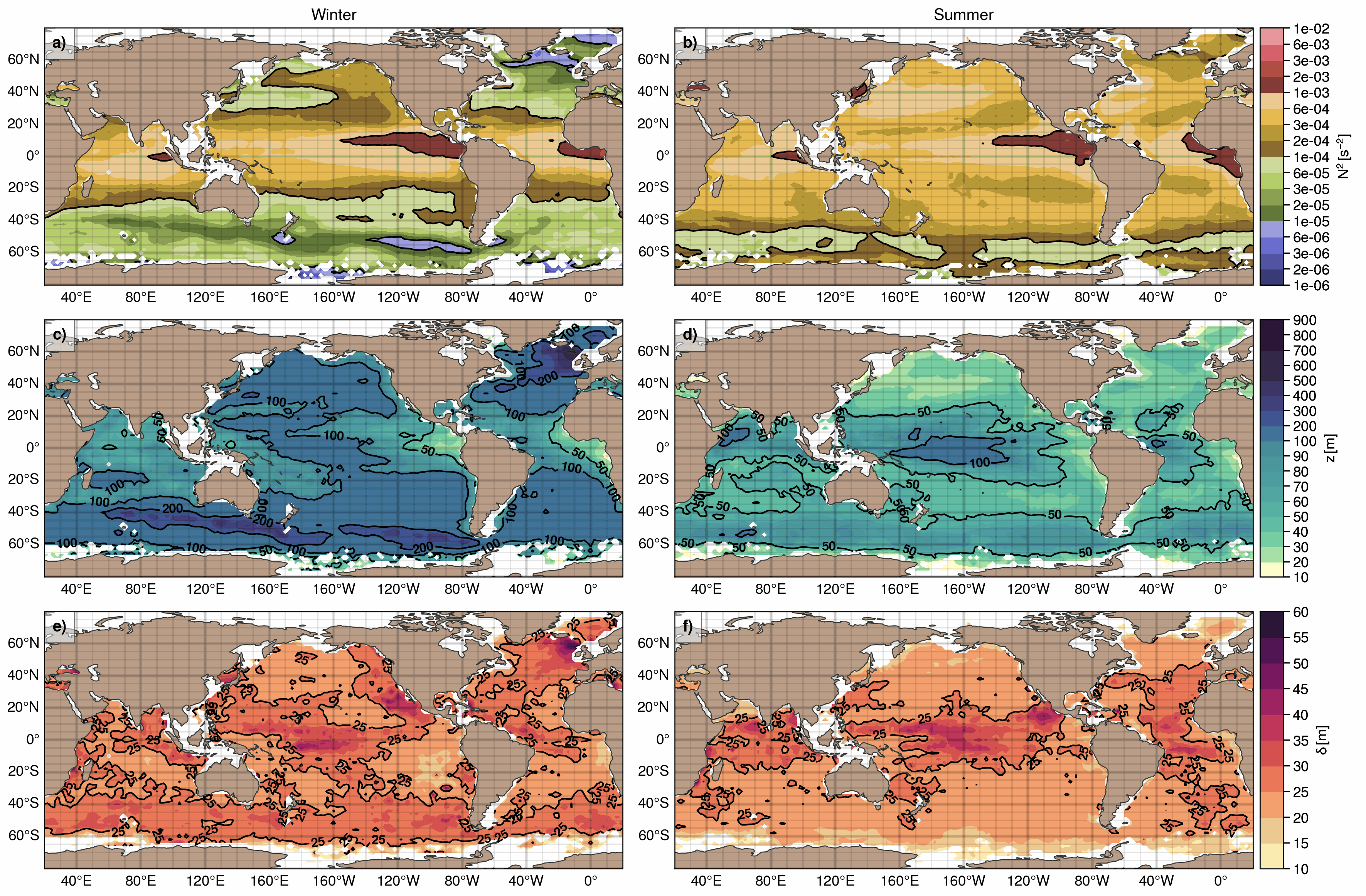
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-
French Zostera Marina et Zostera Noltei abundance data are collected during monitoring surveys on the English Channel / Bay of Biscay coasts. Protocols are impletmented in the Water Framework Directive. Data are transmitted in a Seadatanet format (CDI + ODV) to EMODnet Biology european database. 35 ODV files have been generated from period 01/01/2004 to 31/12/2021 for Z. Marina and from 01/01/2011 to 31/12/2021 for Z. Noltei.
-
This dataset contains the pictures used for morphometric measurements, as well as the elemental compositon and production rates data, of planktonic Rhizaria. Specimens were collected in the bay of Villefranche-sur-Mer in May 2019 and during the P2107 cruise in the California Current in July-August 2021. Analyses of the data can be found at https://github.com/MnnLgt/Elemental_composition_Rhizaria.
-

The CDR-derived Wet Tropospheric Correction (WTC) Product V2 is generated from the Level-2+ along-track altimetry products version 2024 (L2P 2024) distributed by AVISO+ (www.aviso.altimetry.fr). It provides a long-term, homogenized estimation of the wet tropospheric correction based on Climate Data Records (CDRs) of atmospheric water vapour combined with high frequencies MWR data. Two independent CDRs datasets are used: - REMSS V7R2 (coverage until 2022) https://www.remss.com/measurements/atmospheric-water-vapor/tpw-1-deg-product/ - HOAPS V5 precursor CDR from EUMETSAT CM SAF (coverage until 2020) HOAPS V4/V5 data available via https://wui.cmsaf.eu Note: the HOAPS V5 precursor is not yet an official CM SAF product; full validation and public release are pending. The MWR/CDR WTC V2 estimates is derived using spatially varying but temporally constant polynomial coefficients (ai). 1. WTC V2 – Along-track L2P Product Data format: The WTC V2 product is delivered in Level-2+ (L2P) format, along the satellite ground track. Each mission is distributed as a compressed archive (.tar.gz) containing one NetCDF4 CF-1.8 file per mission cycle. Archive naming convention: <mission>_WTC_from_WV_CDR_<version>.tar.gz mission: TP (TOPEX/Poseidon), J1, J2, J3 version: product version (currently V2) File naming convention inside archives: <mission>_C<cycle>.nc cycle: 4-digit cycle index (e.g., C0001) Each NetCDF file contains: 1/ Along-track WTC estimate; 2/ Ancillary information; 3/ Space–time coordinates 2. WTC CDR Uncertainties – Gridded Product: A complementary product is provided, delivering regional trend estimates and associated uncertainties from the WTC Climate Data Record. The uncertainty product is distributed as a single NetCDF4 file: wtc_trend_uncertainties.nc . This file contains global gridded fields of WTC CDR trend and uncertainty parameters. Product content: This is the first dedicated version providing both: WTC CDR (HOAPS) linear trends, and Uncertainty estimates on these trends. Uncertainties are expressed as 1-sigma confidence intervals, and propagated using the methodology described in Section 2.3 of the Product User Manual. The product includes: - Total uncertainty on the WTC trend, propagated from all identified uncertainty sources in the WTC–TCWV regression. - Individual contributions of uncertainty sources (Uncertainties on regression coefficients: a0, a1 and their standard deviations; Uncertainties inherited from the HOAPS TCWV CDR) These fields enable users to assess the relative importance of each uncertainty component and recompute uncertainty propagation with alternative methods. Included regression input variables: To ensure transparency and reproducibility, the product provides: 1/ regression coefficients a0, a1; 2/ their associated uncertainties (std of a0, std of a1); 3/additional diagnostic fields required to recompute uncertainties if needed.
-
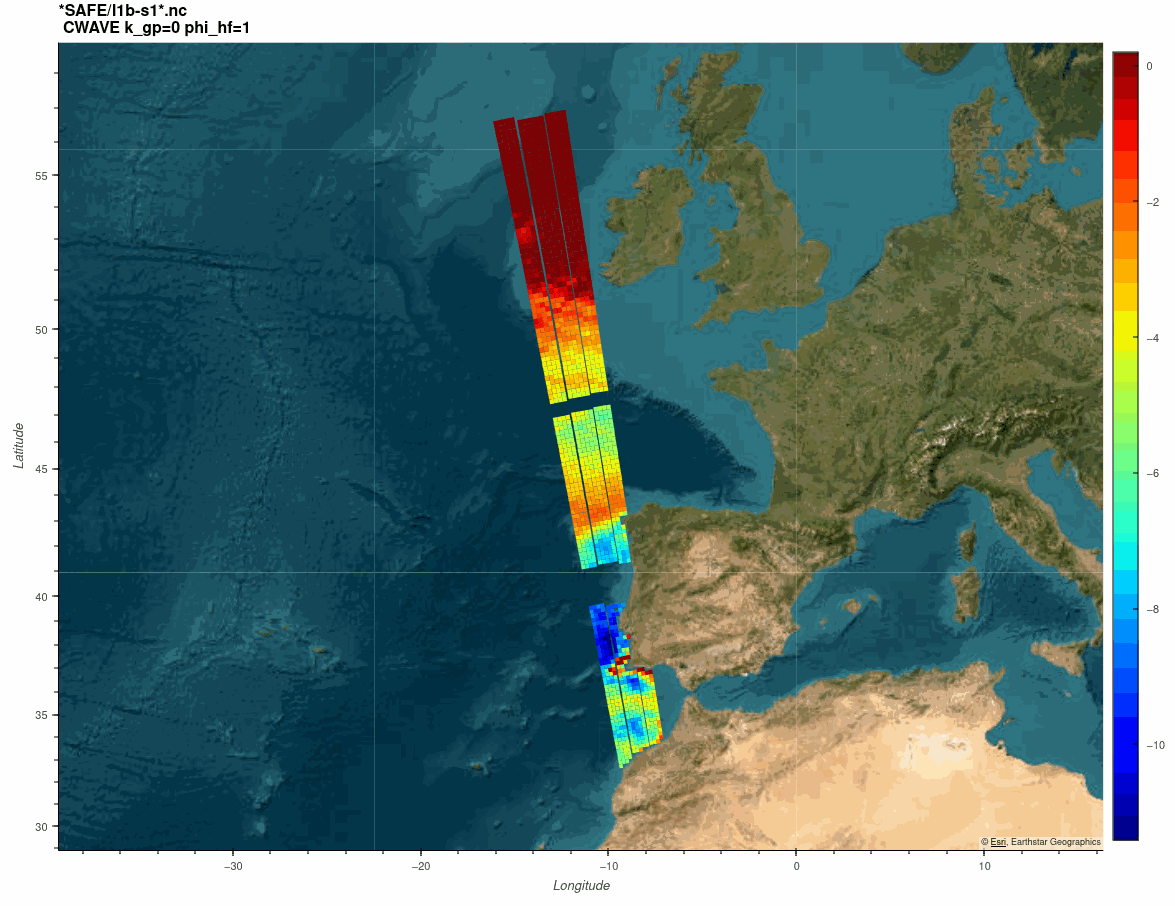
The SARWAVE project is developing a new sea state processor from SAR images to be applied over open ocean, sea ice, and coastal areas, and exploring potential synergy with other microwave and optical EO products.
-

Phenotypic plasticity, the ability of a single genotype to produce multiple phenotypes, is important for survival when species are faced with novel conditions. Theory predicts that range-edge populations will have greater phenotypic plasticity than core populations, but empirical examples from the wild are rare. The honeycomb worm, Sabellaria alveolata (L.), constructs the largest biogenic reefs in Europe, which support high biodiversity and numerous ecological functions. In order to assess the presence, causes and consequences of intraspecific variation in developmental plasticity and thermal adaptation in the honeycomb worm, we carried out common-garden experiments using the larvae of individuals sampled from along a latitudinal gradient covering the entire range of the species. We exposed larvae to three temperature treatments and measured phenotypic traits throughout development. We found phenotypic plasticity in larval growth rate but local adaptation in terms of larval period. The northern and southern range-edge populations of S. alveolata showed phenotypic plasticity for growth rate: growth rate increased as temperature treatment increased. In contrast, the core range populations showed no evidence of phenotypic plasticity. We present a rare case of range-edge plasticity at both the northern and southern range limit of species, likely caused by evolution of phenotypic plasticity during range expansion and its maintenance in highly heterogeneous environments. This dataset presents the raw image data collected for larval stages of Sabellaria alveolata from 5 populations across Europe and Northern Africa, exposed to 15, 20 and 25 C. Included are also opercular crown measurements used to estimate de size classes of individuals present in each population. All measurements made with the images collected are presented in an Excel spreadsheet, also available here.
-

Particularly suited to the purpose of measuring the sensitivity of benthic communities to trawling, a trawl disturbance indicator (de Juan and Demestre, 2012, de Juan et al. 2009) was proposed based on benthic species biological traits to evaluate the sensibility of mega- and epifaunal community to fishing pressure known to have a physical impact on the seafloor (such as dredging and bottom trawling). The selected biological traits were chosen as they determine vulnerability to trawling: mobility, fragility, position on substrata, average size and feeding mode that can easily be related to the fragility, recoverability and vulnerability ecological concepts. The five categories retained are functional traits that were selected based on the knowledge of the response of benthic taxa to trawling disturbance (de Juan et al., 2009). They reflect respectively the possibility to avoid direct gear impact, to benefit from trawling for feeding, to escape gear, to get caught by the net and to resist trawling/dredging action, each of these characteristics being either advantageous or sensitive to trawling. To expand this approach to that proposed by Certain et al. (2015), the protection status of certain species was also indicated. To enable quantitative analysis, a score was assigned to each category: from low sensitivity (0) to high sensitivity (3). Biological traits of species have been defined, from the BIOTIC database (MARLIN, 2014) and from information given by Garcia (2010), Le Pape et al. (2007) and Brind’Amour et al. (2009). For missing traits, additional information from literature has been considered. The protection status of each taxa was also scored: Atlantic species listed in OSPAR List of Threatened and/or Declining Species and Habitats (https://www.ospar.org/work-areas/bdc/species-habitats/list-of-threatened-declining-species-habitats) and Mediterranean species listed in Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (FAO, 2018 and Oceana, 2017) were scored 3 and other species were scored 1. The scores of 1085 taxa commonly found in bottom trawl by-catch in the southern North Sea, English Channel and north-western Mediterranean were described.
-
Serveur wms sur les photos anciennes
-
The ESA Sea State Climate Change Initiative (CCI) project has produced global multi-sensor time-series of along-track satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) integrated sea state parameters (ISSP) data from Sentinel-1 (referred to as SAR WV onboard Sentinel-1 Level 2P (L2P) ISSP data) with a particular focus for use in climate studies. This dataset contains the Sentinel-1 SAR Remote Sensing Integrated Sea State Parameter product (v1.0), which forms part of the ESA Sea State CCI version 3.0 release. This product provides along-track primary significant wave height measurements and secondary sea state parameters, calibrated with CMEMS model data and reference in situ measurements at 20km resolution every 100km, processed using the Pleskachevsky et. al., 2021 emprical model, separated per satellite and pass, including all measurements with flags and uncertainty estimates. These are expert products with rich content and no data loss. The SAR Wave Mode data used in the Sea State CCI SAR WV onboard Sentinel-1 Level 2P (L2P) ISSP v3 dataset come from the Sentinel-1 satellite missions spanning from 2014 to 2021 (Sentinel-1 A, Sentinel-1 B).
-

Wave impact is the primary cause of coastal structure failure. While wave impact is widely studied in controlled environments, in situ measurements of wave impact pressure are rare. The results of a campaign to measure wave impact pressure in situ are summarised here. Data were collected from 2016 to 2019 from anchored pressure gauges on the wall of the Artha breakwater in southwestern France. The acquisition frequency is 10 kHz and 10-minute bursts are recorded every hour. Two databases are published, one by burst and one by impact. The burst database summarises the main parameters describing the 10-minute record, while the impact database contains a list of parameters describing each impact.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA