2025
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
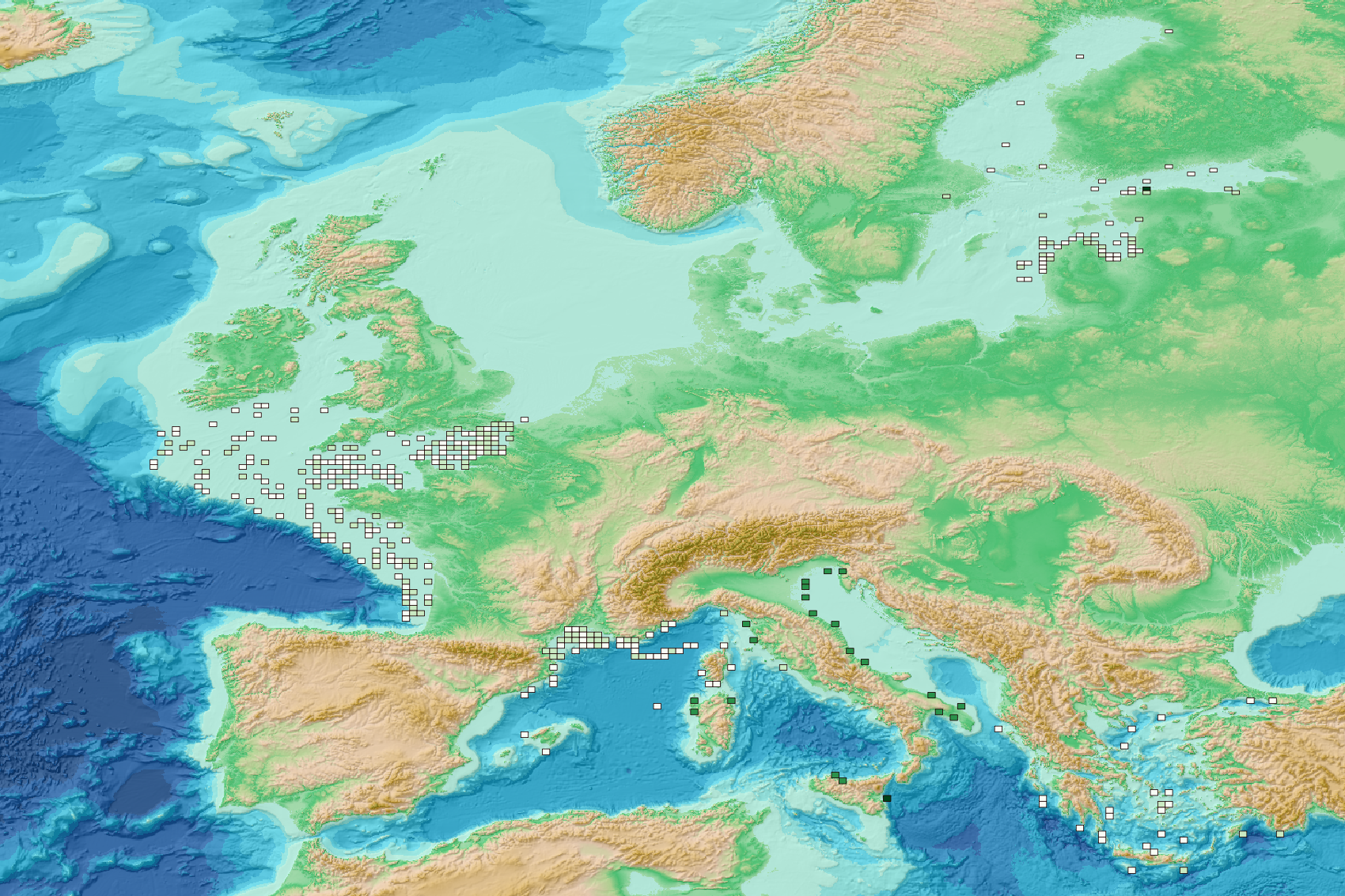
This visualization product displays the spatial distribution of the sampling effort over the six-years' period 2017-2022 from research and monitoring protocols. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Before 2021, there was no coordinated effort at the regional or European scale for micro-litter. Given this situation, EMODnet Chemistry proposed to adopt the data gathering and data management approach as generally applied for marine data, i.e., populating metadata and data in the CDI Data Discovery and Access service using dedicated SeaDataNet data transport formats. EMODnet Chemistry is currently the official EU collector of micro-litter data from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) National Monitoring activities (descriptor 10). A series of specific standard vocabularies or standard terms related to micro-litter have been added to SeaDataNet NVS (NERC Vocabulary Server) Common Vocabularies to describe the micro-litter. European micro-litter data are collected by the National Oceanographic Data Centres (NODCs). Micro-litter map products are generated from NODCs data after a test of the aggregated collection including data and data format checks and data harmonization. A filter is applied to represent only micro-litter samplings carried out according to research and monitoring protocols as MSFD monitoring. The spatial distribution was then determined by calculating the number of times each cell was sampled during the period 2017-2022. The corresponding total distance (kms) sampled in each cell is also provided in the attribute table. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that they do not exist, but that no information has been entered in the National Oceanographic Data Centre (NODC) for this area.
-

'''Short description:''' Near-Real-Time multi-mission global satellite-based spectral integral parameters. Only valid data are used, based on the L3 corresponding products. Included wave parameters are partition significant wave height, partition peak period and partition peak or principal direction. Those parameters are propagated in space and time at a 3-hour timestep and on a regular space grid, providing information of the swell propagation characteristics, from source to land. The ouput products corresponds to one file per month gathering all the swell systems at a global scale. This product is processed by the WAVE-TAC multi-mission SAR and CFOSAT/SWIM data processing system to serve in near-real time the main operational oceanography and climate forecasting centers in Europe and worldwide. It processes data from the following missions: SAR (Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B) and CFOSAT/SWIM. All the spectral parameter measurements are optimally interpolated using swell observations belonging to the same swell field. The spectral data processing system produces wave integral parameters by partition (partition significant wave height, partition peak period and partition peak or principal direction) and the associated standard deviation and density of propagated observations. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00175
-

This set of data documents the radiocarbon dates (n=19) obtained thanks to the accelerator mass spectrometry method (AMS) at the LMC14/ARTEMIS French national facility on the cores (Multicorer, Kullenberg) retrieved from the West-Gironde mud patch (WGMP) during the JERICObent-7 cruise (10-15 July 2019; NR Côtes de la Manche, https://doi.org/10.17600/18001022). The WGMP registers very high sedimentation rates since the last 600 years (≥ 0.3 cm/yr) and is thus of great interest for palaeoceanographic investigations. At present, this depocenter marks the mid-shelf of the temperate Bay of Biscay off major French rivers from the Aquitaine basin. The fine mud deposits of the WGMP are of 3 to 4 meters thick and lie on palimpsest levels rich in gravels and shells. They cover a V-shaped structure, oriented SW-NE, which is attributed to the incision(s) of a paleovalley in the Cenozoic substrate, mainly linked to the paleo-Gironde routing changes during past glacials/interglacials, and its potential past convergences with the paleo-rivers of the Antioche perthuis (Seudre, Charente paleovalleys?) at that times. Detailed information on each sample is presented with the 14C results obtained by the Artemis AMS facility at LMC14 laboratory (Dumoulin et al. 2017- https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2016.116, Beck et al. 2024- https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2023.23). Raw ages are indicated together with calibration calculations using the last two versions of the Calib software (http://calib.org/, Calib 7 and 8) to show the dispersion of ages linked to the updating of calibration curves (Marine13, Intcal13, Marine20, Intcal 20). The calibrated ages finally retained for publications (used in the related Seanoe document - https://doi.org/10.17882/104237 - and published in Eynaud et al., 2025 for the ST3c core, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2025.105039) are those obtained with the last Calib 8.1 version. Raw 14C ages were calibrated and converted to calendar ages using the IntCal20 calibration curve with a reservoir age correction of 400 years deduced from Radionuclide analyses (137Cs and 210Pb) at the top of the studied cores (see Schmidt, 2025, https://www.seanoe.org/data/00968/107979/).
-
Ensemble simulations of the ecosystem model Apecosm (https://apecosm.org) forced by the IPSL-CM6-LR climate model with the climate change scenario SSP5-8.5. The output files contain yearly mean biomass density for 3 communities (epipelagic, mesopelagic migratory and mesopelagic redidents) and 100 size classes (ranging from 0.12cm to 1.96m) The model grid file is also provided. Units are in J/m2 and can be converted in kg/m2 by dividing by 4e6. These outputs are associated with the "Assessing the time of emergence of marine ecosystems from global to local scales using IPSL-CM6A-LR/APECOSM climate-to-fish ensemble simulations" paper from the Earth's Future "Past and Future of Marine Ecosystems" Special Collection.
-
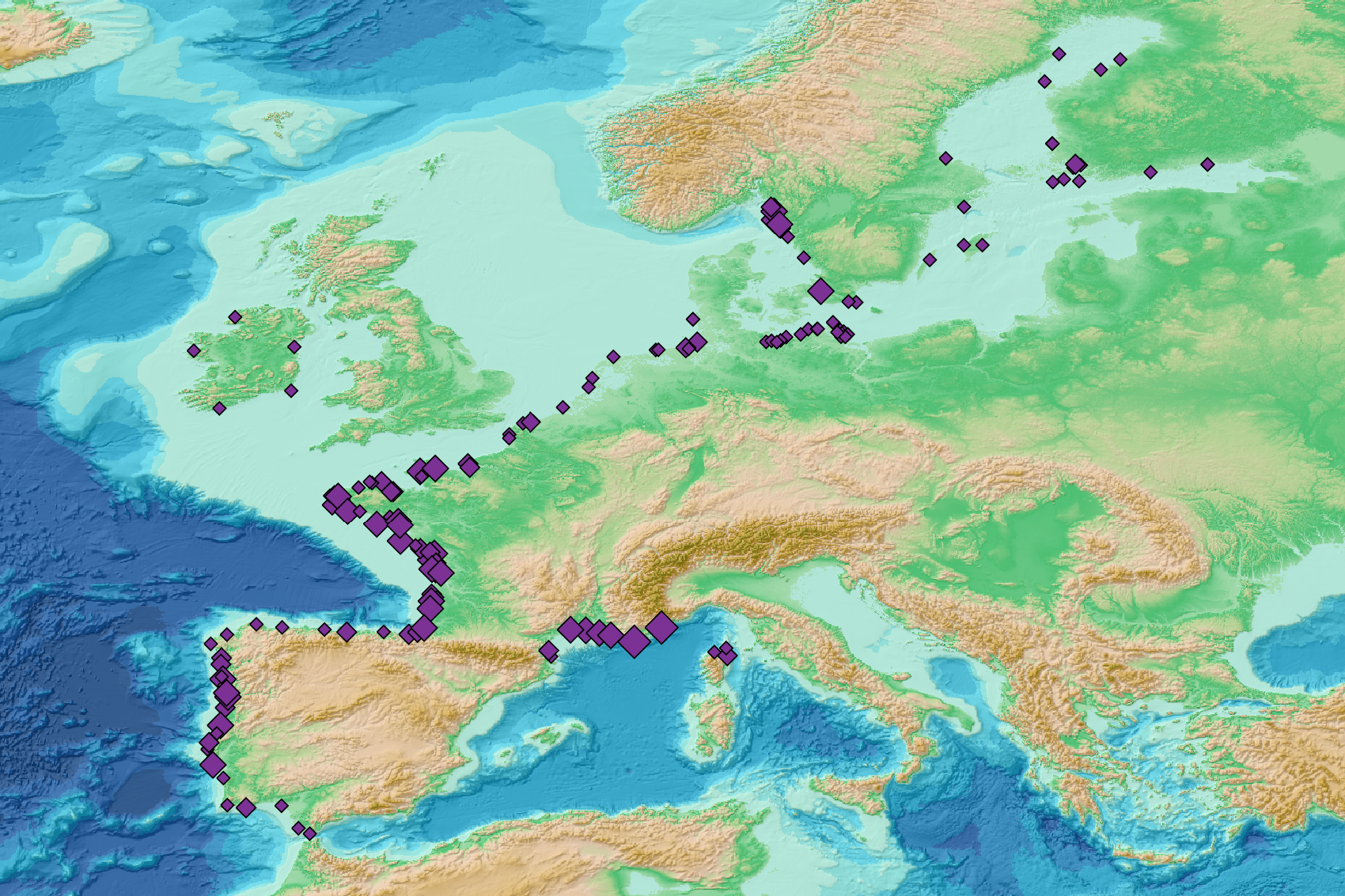
This visualization product displays the total abundance of marine macro-litter (> 2.5cm) per beach per year from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) monitoring surveys. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processings were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of MSFD surveys only (exclusion of other monitoring, cleaning and research operations); - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Some categories & some litter types like organic litter, small fragments (paraffin and wax; items > 2.5cm) and pollutants have been removed. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines, the European Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines and the Joint list of litter categories for marine macro-litter monitoring from JRC (these three documents are attached to this metadata); - Normalization of survey lengths to 100m & 1 survey / year: in some cases, the survey length was not exactly 100m, so in order to be able to compare the abundance of litter from different beaches a normalization is applied using this formula: Number of items (normalized by 100 m) = Number of litter per items x (100 / survey length) Then, this normalized number of items is summed to obtain the total normalized number of litter for each survey. Finally, the median abundance for each beach and year is calculated from these normalized abundances per survey. Sometimes the survey length was null or equal to 0. Assuming that the MSFD protocol has been applied, the length has been set at 100m in these cases. Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account MSFD data for all years. More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that it does not exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-

This dataset provides a global Look-Up Table (LUT) of physiological ratios for the real-time adjustment of chlorophyll-a fluorescence measured by biogeochemical Argo (BGC-Argo) profiling floats. The physiological ratios aim to account for the global variability in the relationship between fluorescence and chlorophyll-a concentration, as influenced by phytoplankton physiology. The LUT was developed using two different gap-filled observational Argo-based products (SOCA machine learning-based methodology ; Sauzède et al., 2016; Sauzède et al., 2024). The first product provides gap-filled chlorophyll-a data derived from fluorescence corrected for dark signal and non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) following Schmechtig et al. (2023), while the second product provides chlorophyll-a concentrations derived from light attenuation. The latter is based on the downward irradiance at 490 nm (ED490) derived from the SOCA-light method (Renosh et al., 2023). From this, the diffuse attenuation coefficient (KD490) is computed, which is subsequently used to estimate the chlorophyll-a concentration through the bio-optical relationships described by Morel et al. (2007). These two products, based on fluorescence and radiometry, enable the derivation of spatially varying correction factors, or physiological ratios. These ratios provide a validated grounded framework for adjusting real-time fluorescence observations from OneArgo floats into chlorophyll-a concentrations. The LUT is distributed in NetCDF format and is provided on a regular 1°×1° latitude–longitude grid covering the global ocean. Each grid cell contains the temporal mean, averaged over the water column (from the surface to 1.5 times the euphotic depth), of the physiological ratio. The file also includes metadata describing variable definitions, units, and other relevant information. Variables included: - physiological_ratio — fluorescence-to-radiometry-based chlorophyll correction factor (dimensionless) - physiological_ratio_sd — temporal standard deviation (over the twelve months) of the fluorescence-to-radiometry-based chlorophyll correction factor (dimensionless) - lat, lon — spatial coordinates (degrees north/east) - Global attributes — dataset description, reference citation, and contact information
-

EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry datasets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, acidity and contaminants. The importance of the selected substances and other parameters relates to the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This aggregated dataset contains all unrestricted EMODnet Chemistry data on eutrophication and acidity, and covers the Mediterranean Sea. Data were aggregated and quality controlled by the 'Hellenic Centre for Marine Research, Hellenic National Oceanographic Data Centre (HCMR/HNODC)' in Greece. ITS-90 water temperature and water body salinity variables have also been included ('as are') to complete the eutrophication and acidity data. If you use these variables for calculations, please refer to SeaDataNet for the quality flags: https://www.seadatanet.org/Products/Aggregated-datasets. Regional datasets concerning eutrophication and acidity are automatically harvested, and the resulting collections are aggregated and quality controlled using ODV Software and following a common methodology for all sea regions (https://doi.org/10.13120/8xm0-5m67 ) Parameter names are based on P35 vocabulary, which relates to EMODnet Chemistry aggregated parameter names and is available at: https://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/search_nvs/P35/. When not present in original data, water body nitrate plus nitrite was calculated by summing all nitrate and nitrite parameters. The same procedure was applied for water body dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), which was calculated by summing all nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium parameters. Concentrations per unit mass were converted to a unit volume using a constant density of 1.025 kg/L. The aggregated dataset can also be downloaded as an ODV collection and spreadsheet, which is composed of a metadata header followed by tab separated values. This spreadsheet can be imported to ODV Software for visualisation (more information can be found at: https://www.seadatanet.org/Software/ODV ).
-
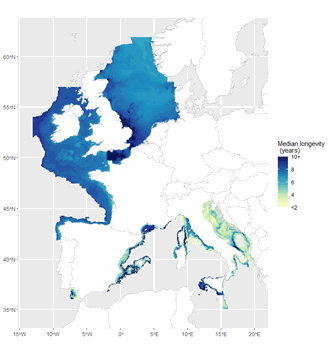
The ICES Working Group on Fisheries Benthic Impact and Trade-offs (WGFBIT) has developed an assessment framework based on the life history trait longevity, to evaluate the benthic impact of fisheries at the regional scale. In order to apply this framework to the Mediterranean sea, several Mediterranean longevity databases were merged together with existing North-East Atlantic ones to develop a common database. Longevity was fuzzy coded into four longevity classes: <1, 1-3, 3-10 and >10 years. Both benthic mega and macrofauna organisms are included in this dataset. Further details about both the purpose and the methodology may be found in ICES (2022) and Cuyvers et al. (2023). The result of the final dataset merging is one dataset containing the fuzzy coded average longevity (and standard deviation) for 2264 taxa and for each, the number of databases used.
-

EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry datasets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, acidity and contaminants. The importance of the selected substances and other parameters relates to the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This aggregated dataset contains all unrestricted EMODnet Chemistry data on potential hazardous substances, despite the fact that some data might not be related to pollution (e.g. collected by deep corer). Temperature, salinity and additional parameters are included when available. It covers the Northeast Atlantic Ocean (40W). Data were harmonised and validated by '‘IFREMER / IDM / SISMER - Scientific Information Systems for the SEA’ in France. The dataset contains water (profiles), sediment (profiles and timeseries) and biota (timeseries). The temporal coverage is 1974–2018 for water measurements, 1966–2022 for sediment measurements and 1979–2023 for biota measurements. Regional datasets concerning contaminants are automatically harvested and the resulting collections are harmonised and validated using ODV Software and following a common methodology for all sea regions ( https://doi.org/10.6092/8b52e8d7-dc92-4305-9337-7634a5cae3f4 ). Parameter names are based on P01 vocabulary, which relates to BODC Parameter Usage Vocabulary and is available at: https://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/search_nvs/P01/ . The harmonised dataset can be downloaded as as an ODV spreadsheet, which is composed of a metadata header followed by tab separated values. This spreadsheet can be imported into ODV Software for visualisation (more information can be found at: https://www.seadatanet.org/Software/ODV ). In addition, the same dataset is offered also as a txt file in a long/vertical format, in which each P01 measurement is a record line. Additionally, there are a series of columns that split P01 terms into subcomponents (substance, CAS number, matrix...).This transposed format is more adapted to worksheet applications (e.g. LibreOffice Calc).
-

As part of the European Horizon Europe FOCCUS project (https://foccus-project.eu/), the metadata inventory of European coastal platforms has been extracted. The inventory was based on the following History and Latest products, downloaded from the CMEMS website (https://marine.copernicus.eu/fr/acces-donnees) at: 1) Global Ocean-In-Situ Near-Real-Time Observation, 2) Atlantic Iberian Biscay Irish Ocean-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 3) Mediterranean Sea-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 4) Atlantic-European North West Shelf-Ocean In-Situ Near Real Time Observations. To carry out this inventory, it was decided to target only coastal platforms, located less than 200km from the coast and at a depth of less than 400m. For mobile platforms, it was also decided to focus only on the first position in the file. This data must be located within 200 km of the coast and at a depth of less than 400 m. In this inventory, FerryBox platforms have all been considered as coastal platforms. The following platforms were extracted from the products: BO (Bottles), CT (CTD), DB (Drifting Buoys), FB (Ferry Box), GL (Gliders), HF (High Frequency Radar), MO (Mooring), PF (Profiling Float), TG (Tide Gauge) and XB (XBT). Once the metadata had been extracted from the files, duplicates were removed (files with the same names). Duplicate platforms of type _TS_ and _WS_ were merged (date and parameters). Latest‘ files have been merged with ’History" files. Missing metadata have been replaced in the Excel file by ‘Missing Data’. Some old dates were also revised by hand because they had been badly extracted, as well as some institution names that included special characters. Platforms located on estuaries/rivers/lakes/ponds have also been removed by hand. This inventory identified a total of 10,479 coastal platforms.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA