CSV
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset comprises long-term time series on marine microphytoplankton, from 2003 to 2021, along the entire French metropolitan coastline. Microphytoplankton data cover microscopic taxonomic identifications and counts. The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset corresponds to a dataset extracted from the PHYTOBS network (DOI:10.17882/85178). The PHYTOBS network provides the scientific community and stakeholders with validated and qualified data on the biomass, abundance and composition of marine microphytoplankton in coastal and lagoon waters, with the aim of supporting scientific research. PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO is a dataset used as part of the Horizon Europe MARCO-BOLO project (https://marcobolo-project.eu/), in which we are currently working to understand and analyze multi-decadal trends in coastal and marine biodiversity on a European scale. The PHYTOBS-MARCOBOLO dataset gathers data from 18 sampling sites, selected from the PHYTOBS-Network dataset according to requirements of time series quality and geographical location of sampling sites established as part of the MARCO-COLO project. This dataset was also formatted according to a template imposed for the European project.
-
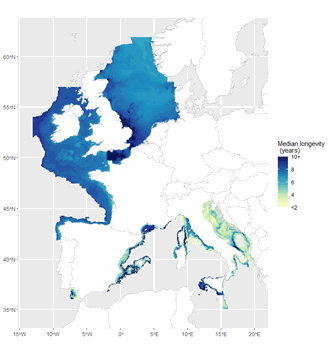
The ICES Working Group on Fisheries Benthic Impact and Trade-offs (WGFBIT) has developed an assessment framework based on the life history trait longevity, to evaluate the benthic impact of fisheries at the regional scale. In order to apply this framework to the Mediterranean sea, several Mediterranean longevity databases were merged together with existing North-East Atlantic ones to develop a common database. Longevity was fuzzy coded into four longevity classes: <1, 1-3, 3-10 and >10 years. Both benthic mega and macrofauna organisms are included in this dataset. Further details about both the purpose and the methodology may be found in ICES (2022) and Cuyvers et al. (2023). The result of the final dataset merging is one dataset containing the fuzzy coded average longevity (and standard deviation) for 2264 taxa and for each, the number of databases used.
-
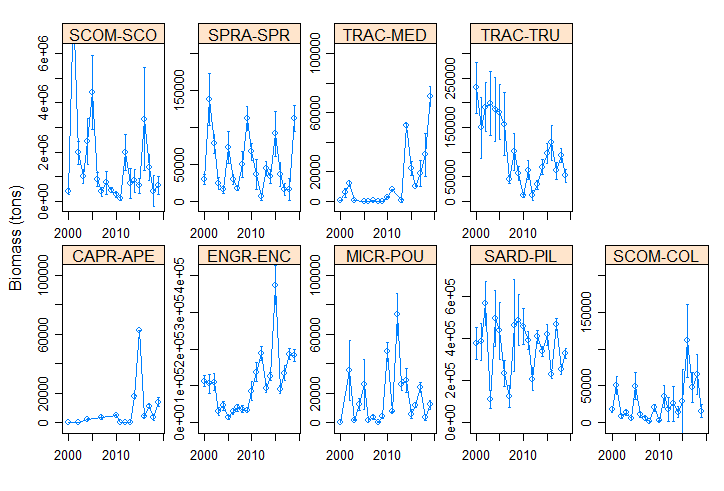
The Pélagiques Gascogne (PELGAS, Doray et al., 2000) integrated survey aims at assessing the biomass of small pelagic fish and monitoring and studying the dynamics and diversity of the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime. PELGAS has been conducted within the EU Common Fisheries Policy Data Collection Framework and Ifremer’s Fisheries Information System. Details on survey protocols and data processing methodologies can be found in Doray et al., (2014, 2018a). This dataset comprises the biomass (in metric tons) and abundance (in thousands of individuals) of small pelagic fish estimated during the PELGAS survey in the Bay of Biscay in springtime. The dataset also includes the estimation coefficient of variation, derived based on the hydroacoustic methodology described in Doray et al. (2010), and the survey area. Those estimates have been validated by the ICES WGACEGG group and provided to the ICES WGHANSA group for stock assessment purposes. Data have been used in Doray et al., 2018b.
-

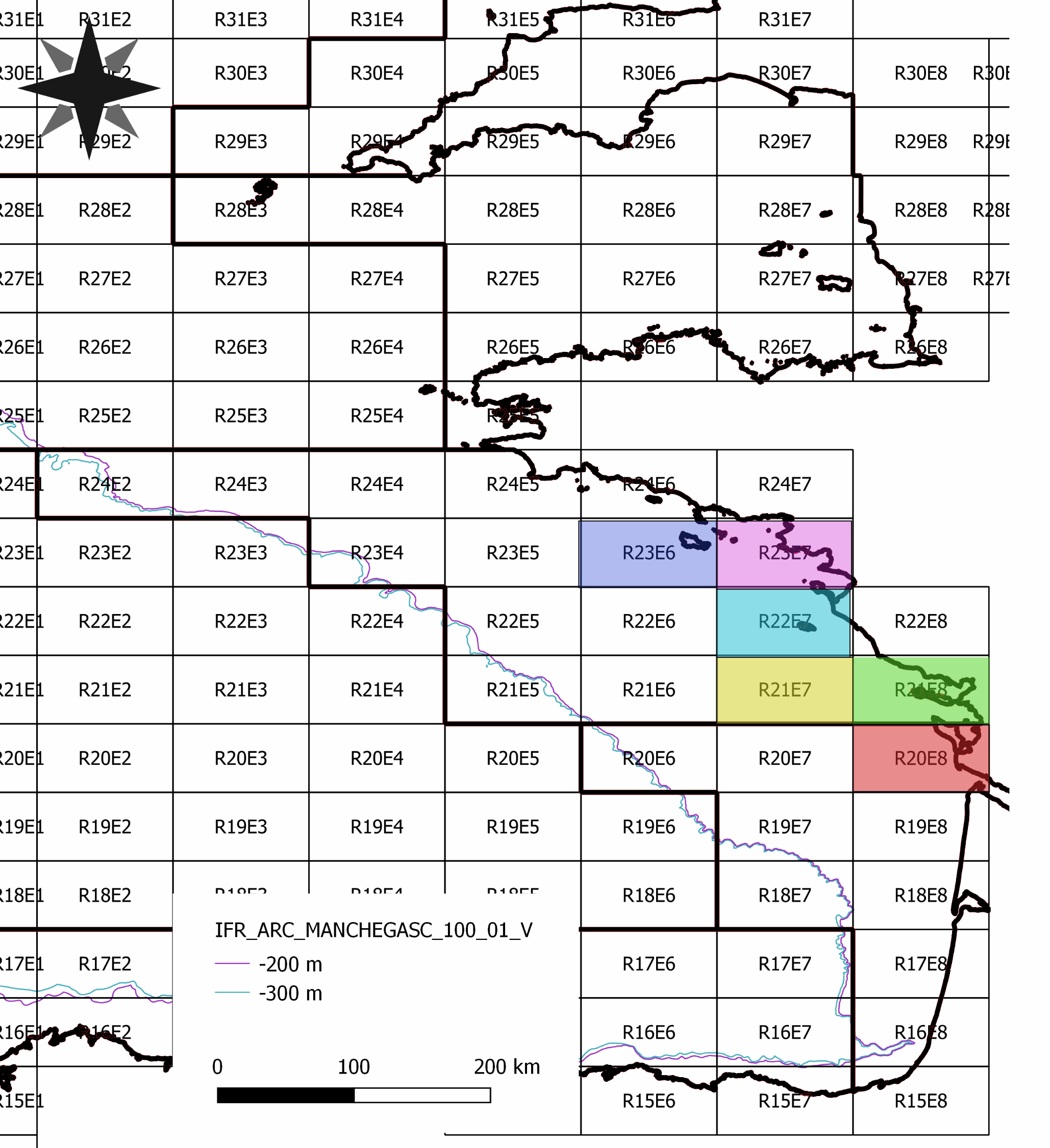
The West Gironde Mud Patch (WGMP) is a mud deposit located 25 km from the mouth of the Gironde Estuary in the Bay of Biscay. This 4-metre-thick clay-silt feature, which extends over an area of 420 km2, is found at depths between 30 and 80 meters. The main objectives of the JERICObent7 cruise, in July 2019, were to characterise the evolution of the WGMP’s benthic ecosystem in terms of its sedimentary, biogeochemical and ecological properties and to reconstruct climate variations and identify potential anthropogenic impacts over the last few centuries. To this end, a precise chronological framework was established for the sedimentary archives of the last few decades using 210Pbxs (T1/2 = 22.3 years). Interface cores were collected at stations 1, 3 and 4 along a cross-shelf transect. Twin Kullenberg cores were collected at sites 3 and 4 for geochemical (KGL) and palaeoceanographic (JB7-ST) investigations. Each interface core was carefully extruded at 0.5 cm intervals from the top of the core to 4 cm, and then at 1 cm intervals until the bottom was reached. Kullenberg cores were only collected at sites 3 and 4. Depending on their intended use, the Kullenberg cores were sampled at different resolutions, the depth of each sediment layer corresponded to the depth from the top of the core. These layers were then used to determine the dry bulk density and radioisotope activities of interest (210Pb, 226Ra, 228Th, 137Cs, 40K). Excess 210Pb was used to establish the realignment and chronological framework of the interface and Kullenberg cores.
-

The Arcachon Bay is a unique and ecologically important meso-tidal lagoon on the Atlantic coast of south-west France. The Arcachon Bay has the largest area of dwarf seagrass (Z. noltei) in Europe, the extent of which was stable in their extent between the 1950s and 1990s, but a decline in seagrass was observed in mid-2000. The decline of Zostera (seagrass) may have a significant impact on sedimentation in this coastal ecosystem rich in marine life. Interface cores were collected in September 2022 to determine sediment and mass accumulation rates (SAR, MAR) in the Arcachon Bay. Ten study areas were selected, distributed over most of the areas where seagrass meadows are actually observed. Two sites were visited each time, one with the presence of Zostera noltei in good condition (Healthy) and the other where the sediment was bare (Bare). Maximum water heights during spring tides range from 3.44 m for the deepest site (Garrèche) to 2.09 m for the shallowest site (Fontaines). A total of 20 sediment cores were sampled and carefully extruded every 1 cm from the top to the bottom of the core. The sediment layers were used to determine dry bulk density and selected radioisotope activities: DBD, 210Pb, 226Ra, 137Cs, 228Th and 40K expressed as %K).
-
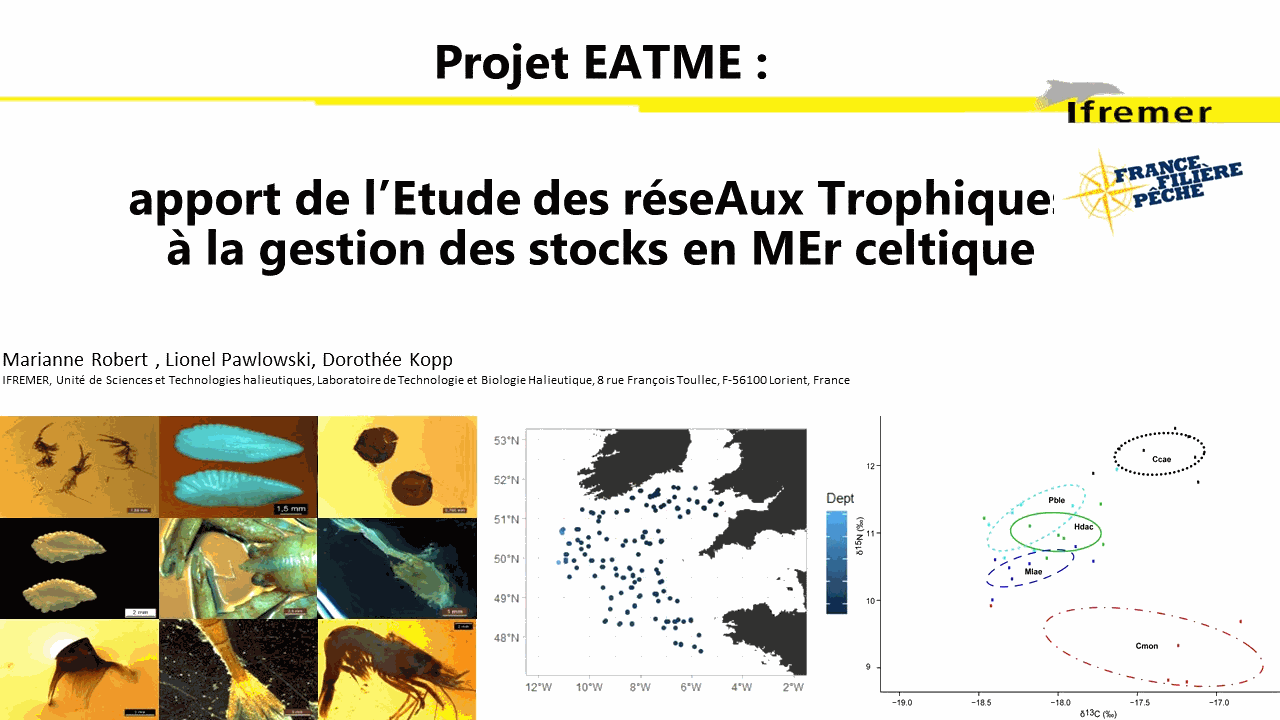
Understanding the dynamics of species interactions for food (prey-predator, competition for resources) and the functioning of trophic networks (dependence on trophic pathways, food chain flows, etc.) has become a thriving ecological research field in recent decades. This empirical knowledge is then used to develop population and ecosystem modelling approaches to support ecosystem-based management. The TrophicCS data set offers spatialized trophic information on a large spatial scale (the entire Celtic Sea continental shelf and upper slope) for a wide range of species. It combines ingested prey (gut content analysis) and a more integrated indicator of food sources (stable isotope analysis). A total of 1337 samples of large epifaunal invertebrates (bivalve mollusks and decapod crustaceans), zooplankton, fish and cephalopods, corresponding to 114 species, were collected and analyzed for stable isotope analysis of their carbon and nitrogen content. Sample size varied between taxa (from 1 to 52), with an average of 11.72 individuals sampled per species, and water depths ranged from 57 to 516 m. The gut contents of 1026 fish belonging to ten commercially important species: black anglerfish (Lophius budegassa), white anglerfish (Lophius piscatorius), blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou), cod (Gadus morhua), haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus), hake (Merluccius merluccius), megrim (Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis), plaice (Pleuronectes platessa), sole (Solea solea) and whiting (Merlangius merlangus) were analyzed. The stomach content data set contains the occurrence of prey in stomach, identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible. To consider potential ontogenetic diet changes, a large size range was sampled. The TrophicCS data set was used to improve understanding of trophic relationships and ecosystem functioning in the Celtic Sea. When you use the data in your publication, we request that you cite this data paper. If you use the present data set (TrophicCS) for the majority of the data analyzed in your study, you may wish to consider inviting at least one author of the core team of this data paper to become a collaborator /coauthor of your paper.
-
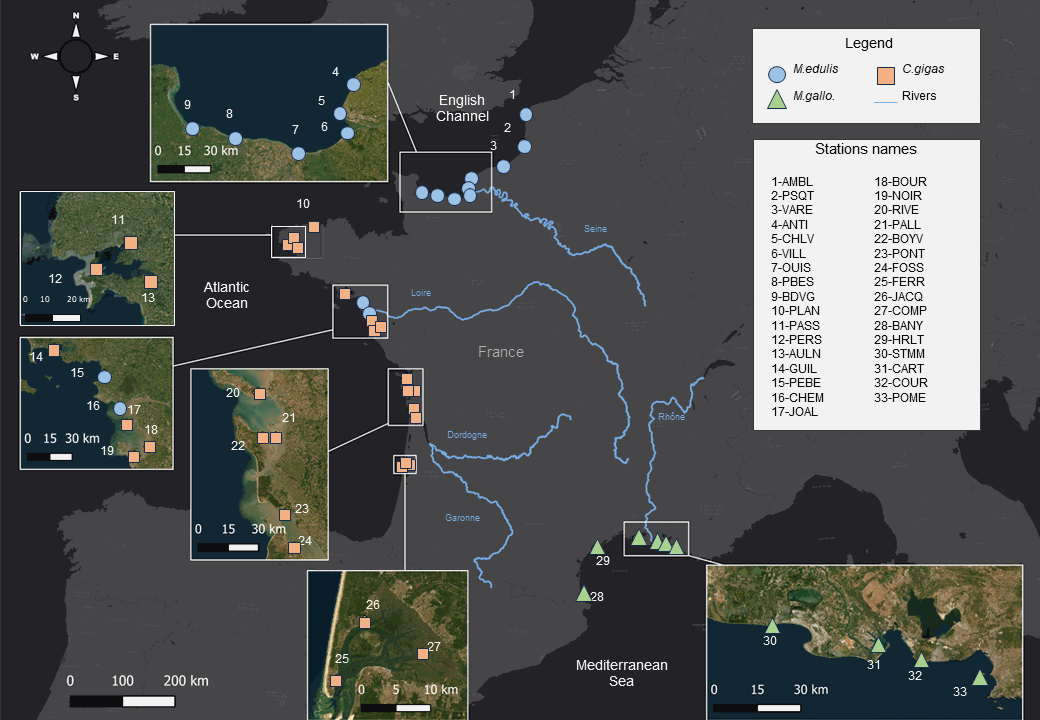
Bivalves carbon and nitrogen elemental and isotopic ratios (δ13C, δ15N, C and N%, C:N) times series (1981-2021) from 33 sites in France. Bivalve species are the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas, and the mussels Mytilus edulis and Mytilus galloprovincialis. This extensive dataset offers a comprehensive view spanning multiple decades and ecosystems, allowing to track how coastal ecosystems and marine species record changing climate, physical-chemical environments and organic matter cycles. This dataset may also be used to study bivalve physiology. Additionally, these data are crucial for establishing isotope baselines for studying food webs. Ultimately, this data set provide valuable information for more effective ecosystem conservation and management strategies in our rapidly changing world.
-
Global Fishing Watch is working across the globe to provide governments and authorities with actionable reports and capacity building to help strengthen fisheries monitoring and compliance. Our global team of experts produce analyses to inform monitoring, control and surveillance of fisheries in five key areas: - Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing - Transshipment - Port controls - Marine protected areas - Operation support Collaboration and information sharing are integral to achieving well-managed fisheries. By working with stakeholders and making analyses available to national, regional and intergovernmental partners, Global Fishing Watch is enabling fisheries agencies to make more informed and cost-efficient decisions. Topics: - Commercial fishing, Global Fishing Watch is harnessing innovative technology to turn transparent data into actionable information and drive tangible change in the way that fisheries are governed. - Transshipment, Through publicly sharing map visualisations and creating data and analysis tools, we seek to inform management and policy efforts and provide a more complete picture of transshipment at sea. - Marine protected areas, Global Fishing Watch is harnessing the data and technology revolution to support the effective design, management and monitoring of marine protected areas.
-
For the 21 years of the study, an examination of trends in chlorophyll concentration revealed a general decline throughout the Gulf over the production period. These trends, extracted from dynamic linear model, also allowed this decline to be quantified. Expressed as a percentage, a large part of the area below the 50 m bathymetric line showed a decrease of at least 10% over the period, corresponding to a value of at least 0.1 µg.l-1. However, the spatial distribution reveals some more local phenomena. In southern Brittany, from Quimper to Vannes, a particular feature appears, with an upward trend over several kilometres along the coast, followed by a pronounced gradient along the coast. This gradient includes a zone where a continuous monotonic increasing trend is observed, then a zone where the trend becomes not significant and finally, about 15 km from the coast, a new zone where a significant continuous monotonic decreasing trend is observed. The increase in chlorophyll a concentration in the very coastal part is greater than 0.1 µg.l-1 over the period. Another peculiarity concerns the central part, located at the edge of the plateau at Cap Ferrat and Pente Aquitaine, where an increase in chlorophyll a was observed, but the variations remained small, being less than 0.1 µg.l-1. About a hundred kilometres south-west of Saint Nazaire, an area of about 40 by 50 km shows a decrease in chlorophyll a of more than 20%, quantified as more than 0.1 µg.l-1 over the period.
-
############# # Data description # ############# This dataset have been constructed and used for scientific purpose, available in the paper "Detecting the effects of inter-annual and seasonal changes of environmental factors on the the striped red mullet population in the Bay of Biscay" authored by Kermorvant C., Caill-Milly N., Sous D., Paradinas I., Lissardy M. and Liquet B. and published in Journal of Sea Research. This file is an extraction from the SACROIS fisheries database created by Ifremer (for more information see https://sextant.ifremer.fr/record/3e177f76-96b0-42e2-8007-62210767dc07/) and from the Copernicus database. Biochemestry comes from the product GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_BIO_001_028 (https://resources.marine.copernicus.eu/?option=com_csw&view=details&product_id=GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_BIO_001_028). Temperature and salinity comes from GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_PHY_001_024 product (https://resources.marine.copernicus.eu/?option=com_csw&view=details&product_id=GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_PHY_001_024). As fisheries landing per unit of effort is only available per ICES rectangle and by month, environmental data have been aggregated accordingly. ############### # Colomns description # ############### rectangle - The 6 ICES statistical rectangles used in the study. time_m - Time in months, from the beginning to the end of the study. annee = year mois = month (from 1 to 12) Poids = Weight of red mullet landed valeur = Temps_peche = fishing time Nb_sequence = number of fishing sequences Moy / Med / Var / StD Quartil_1 / Quartil_3 / min / max / CV / IQR = statistical descriptors of landing by rectangle and by month log_cpue = log of Med colomn mean_surface_s = mean of surface salinity by month and by rectangle median_surface_s = median of surface salinity by month and by rectangle mean_surface_t = mean of surface temperature by month and by rectangle median_surface_t = median of surface temperature by month and by rectangle si / zeu /po4 / pyc / o2/ nppv / no3 and nh4 mean and median concentration by rectangle and by month pc3 / pc2 / pc1 - projections of previous biochemestry variables on the three first axes of a PCA
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA