NC, NETCDF
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
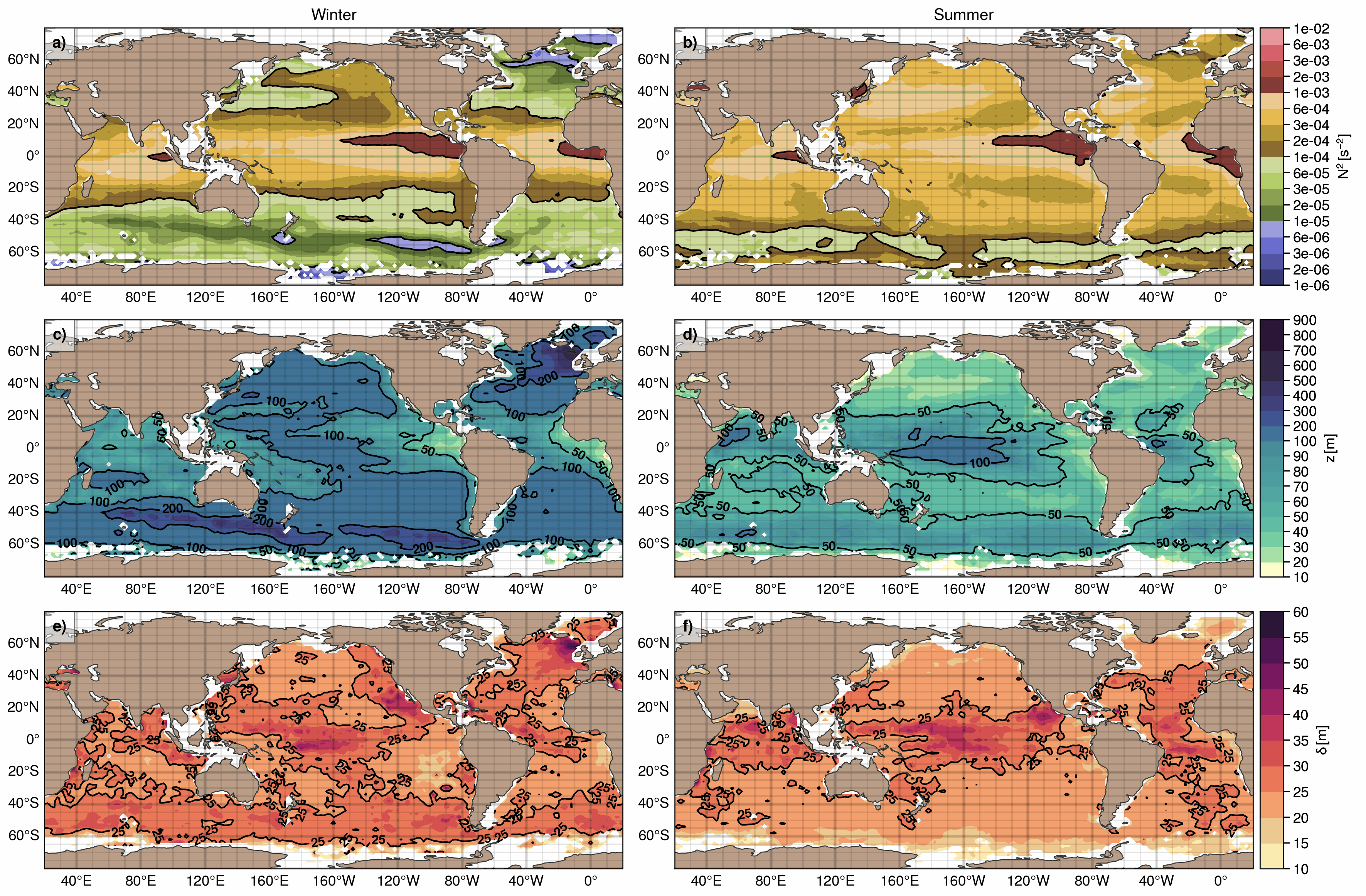
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-
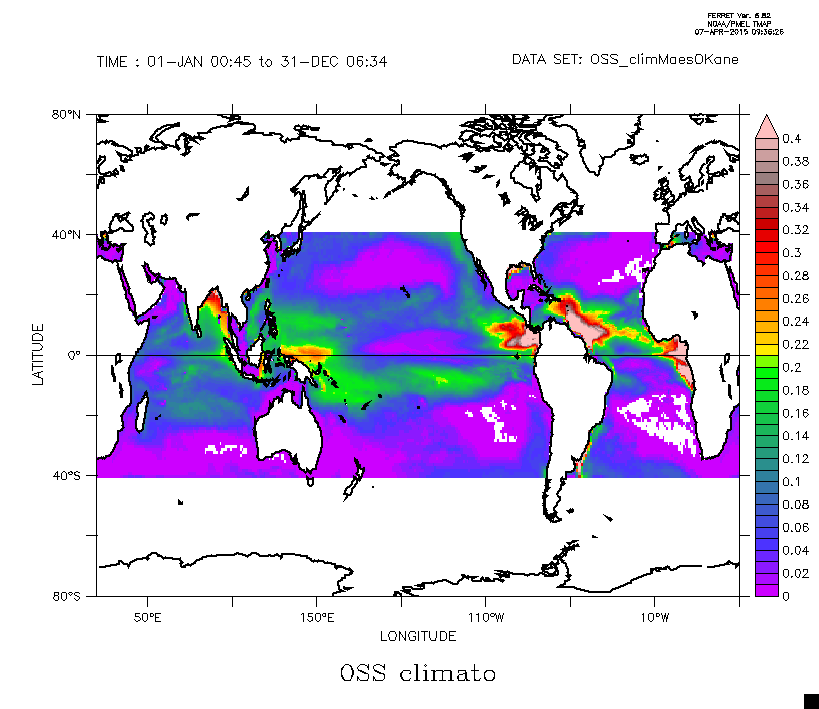
This dataset is composed by the climatological seasonal field of the Ocean Salinity Stratification as defined from the Brunt-Vaisala frequency limited to the upper 300 m depth. The details are given in Maes, C., and T. J. O’Kane (2014), Seasonal variations of the upper ocean salinity stratification in the Tropics, J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 119, 1706–1722, doi:10.1002/2013JC009366.
-
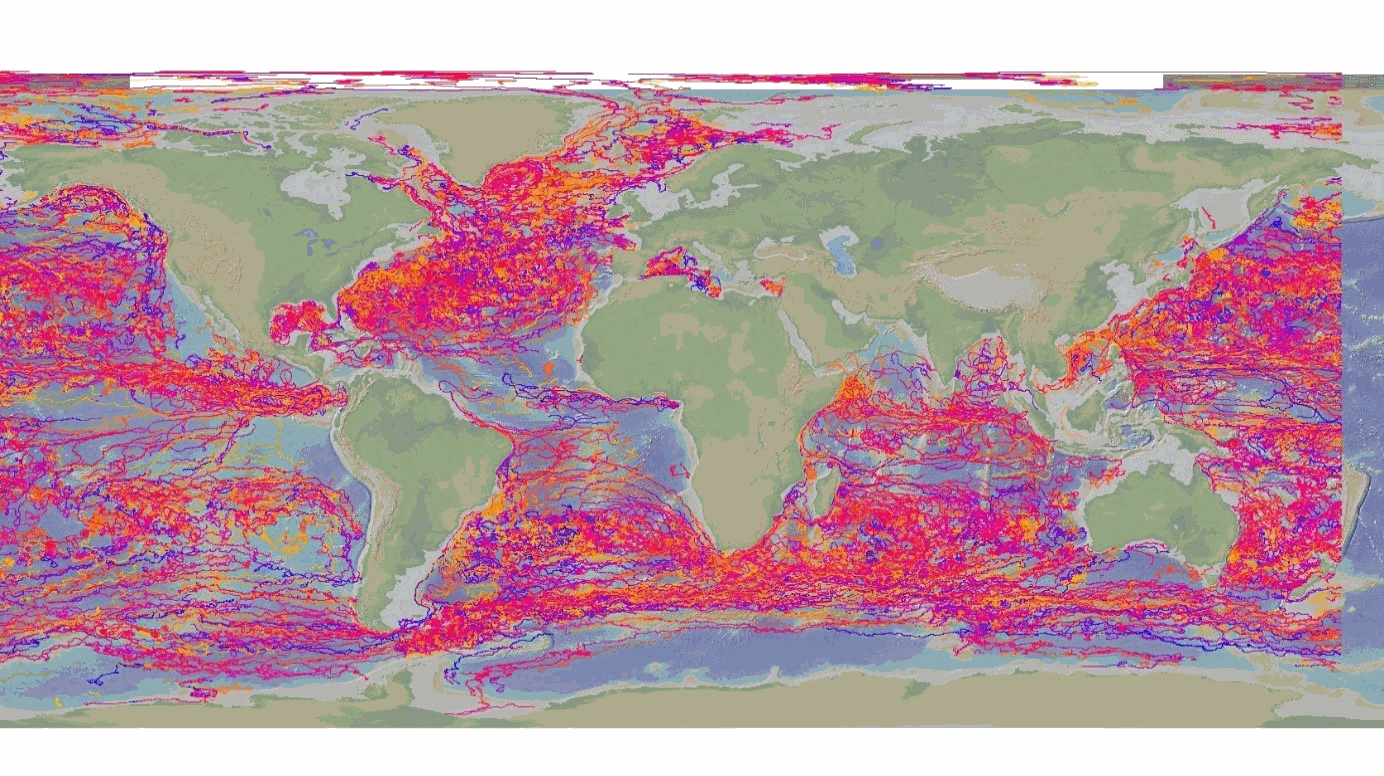
The DBCP – Data Buoy Cooperation Panel - is an international program coordinating the use of autonomous data buoys to observe atmospheric and oceanographic conditions, over ocean areas where few other measurements are taken. DBCP coordinates the global array of 1 600 active drifting buoys (August 2020) and historical observation from 14 000 drifting buoys. Data and metadata collected by drifting buoys are publically available in near real-time via the Global Data Assembly Centers (GDACs) in Coriolis-Ifremer (France) and MEDS (Canada) after an automated quality control (QC). In long term, scientifically quality controlled delayed mode data will be distributed on the GDACs. Disclaimer: the DB-GDAC is under construction. It is currently (January 2020) aggregating data from the Coriolis DAC (E-Surfmar, Canada). Additional DACs are considered. An interim provision from GTS real-time data to GDAC may be provided from Coriolis DAC.
-
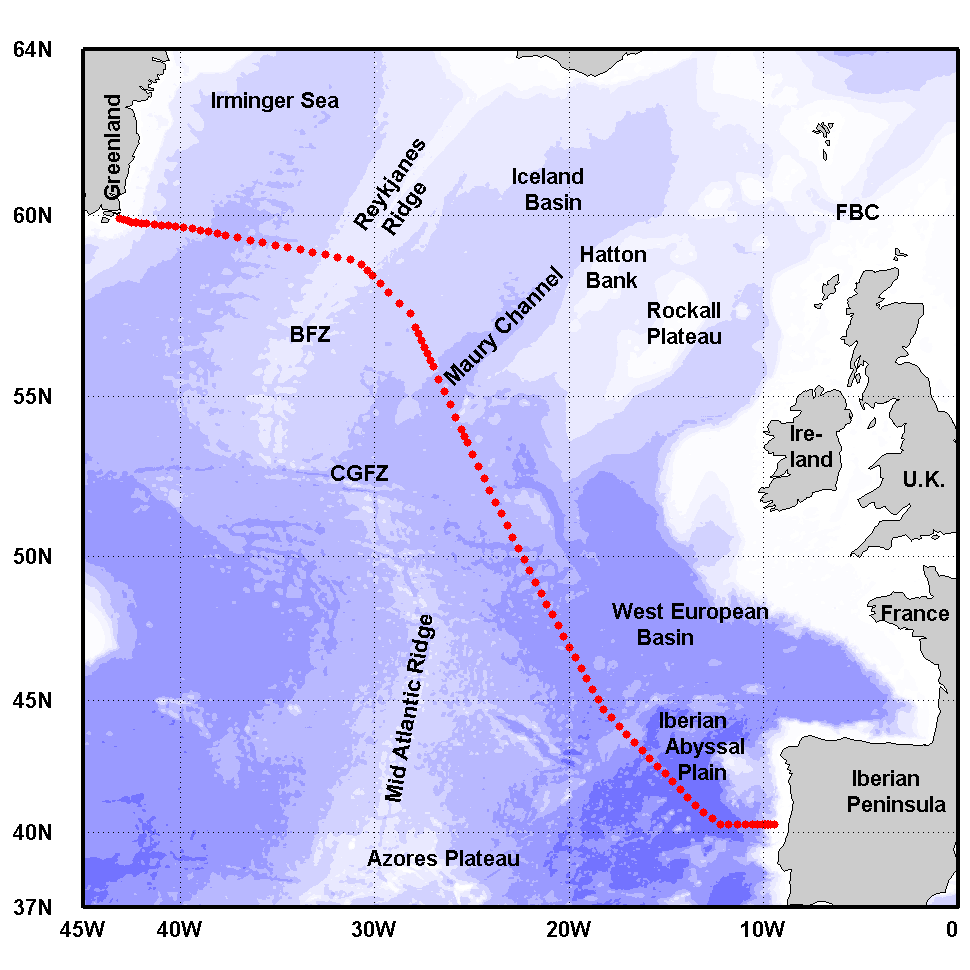
The Greenland-Portugal A25 OVIDE line is carried out biennially since 2002. The section is composed of 98 stations where hydrographic, biogeochemical and current measurements are carried out down to the bottom. OVIDE is a contribution to the international programs Go-Ship, IOCCP, and CLIVAR. This data set contains the final (adjusted) CTDO2 data.
-
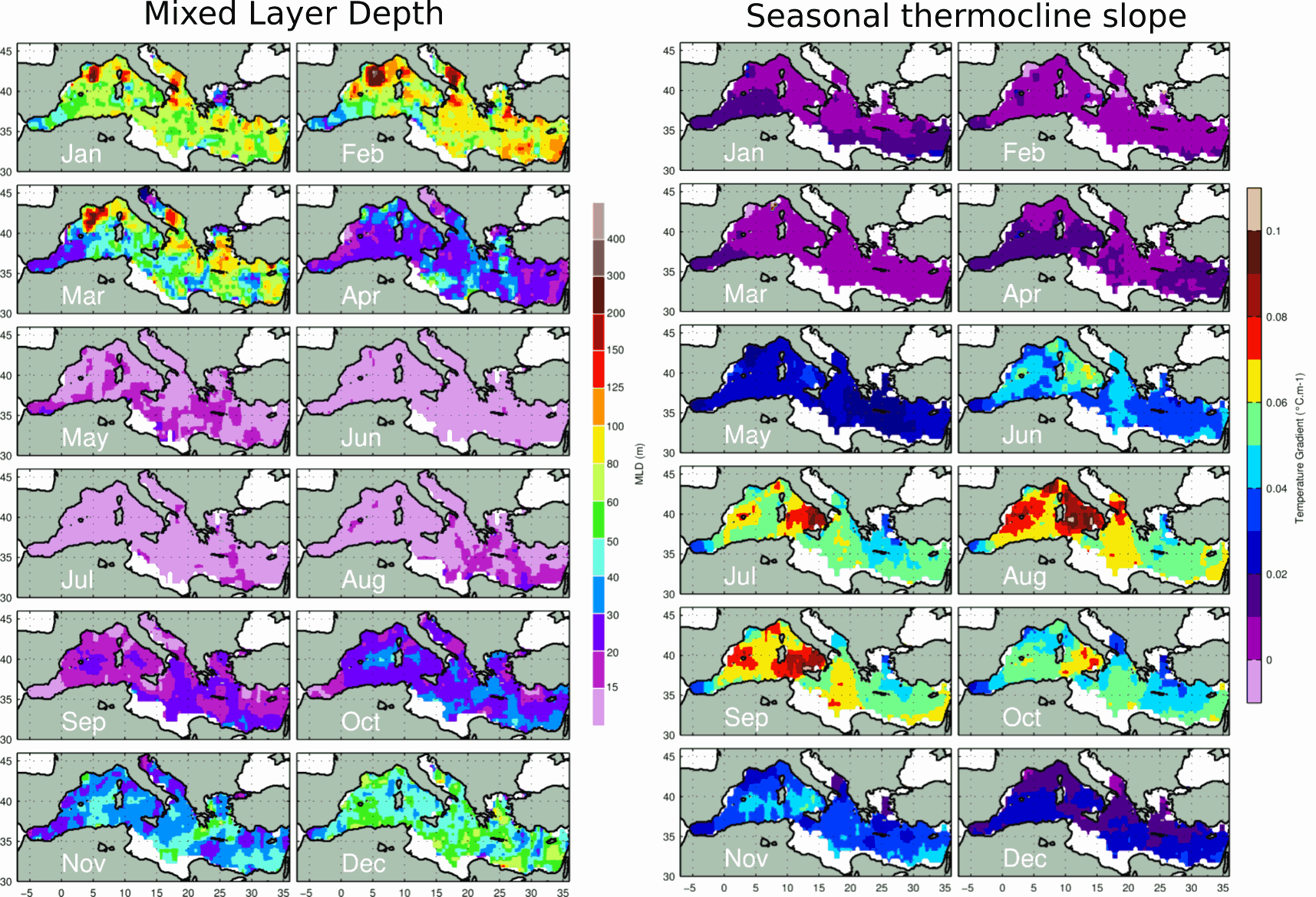
These monthly gridded climatology were produced using MBT, XBT, Profiling floats, Gliders, and ship-based CTD data from different database and carried out in the Med. between 1969 and 2013. The Mixed Layer Depth (MLD) is calculated with a delta T= 0.1 C criterion relative to 10m reference level on individual profiles. The Depth of the Bottom of the Seasonal Thermocline (DBST) is calculated on individual profiles as the maximum value from a vector composed of two elements: 1) the depth of the temperature minimum in the upper 200m; 2) the MLD. This double criterion for the calculation of DBST is necessary in areas where the mixed layer exceed 200m depth. DBST is the integration depth used in the calculation of the upper-ocean Heat Storage Rate. For more details about the data and the methods used, see: Houpert et al. 2015, Seasonal cycle of the mixed layer, the seasonal thermocline and the upper-ocean heat storage rate in the Mediterranean Sea derived from observations, Progress in Oceanography, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2014.11.004
-
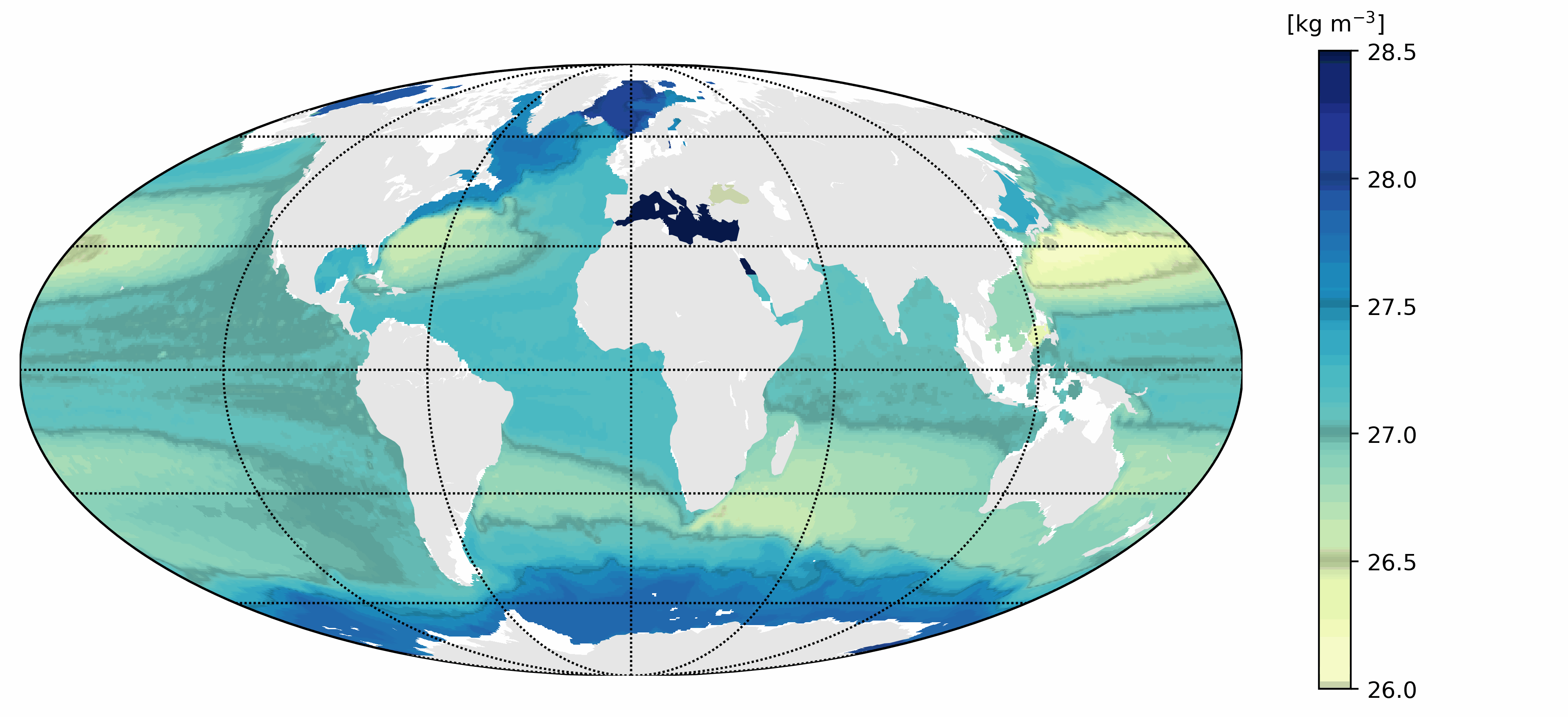
This dataset provides a World Ocean Atlas of Argo inferred statistics. The primary data are exclusively Argo profiles. The statistics are done using the whole time range covered by the Argo data, starting in July 1997. The atlas is provided with a 0.25° resolution in the horizontal and 63 depths from 0 m to 2,000 m in the vertical. The statistics include means of Conservative Temperature (CT), Absolute Salinity, compensated density, compressiblity factor and vertical isopycnal displacement (VID); standard deviations of CT, VID and the squared Brunt Vaisala frequency; skewness and kurtosis of VID; and Eddy Available Potential Energy (EAPE). The compensated density is the product of the in-situ density times the compressibility factor. It generalizes the virtual density used in Roullet et al. (2014). The compressibility factor is defined so as to remove the dependency with pressure of the in-situ density. The compensated density is used in the computation of the VID and the EAPE.
-
This In Situ delayed mode product integrates the best available version of in situ oxygen, chlorophyll / fluorescence and nutrients data. The latest version of Copernicus delayed-mode BGC (bio-geo-chemical) product is also distributed from Copernicus Marine catalogue.
-
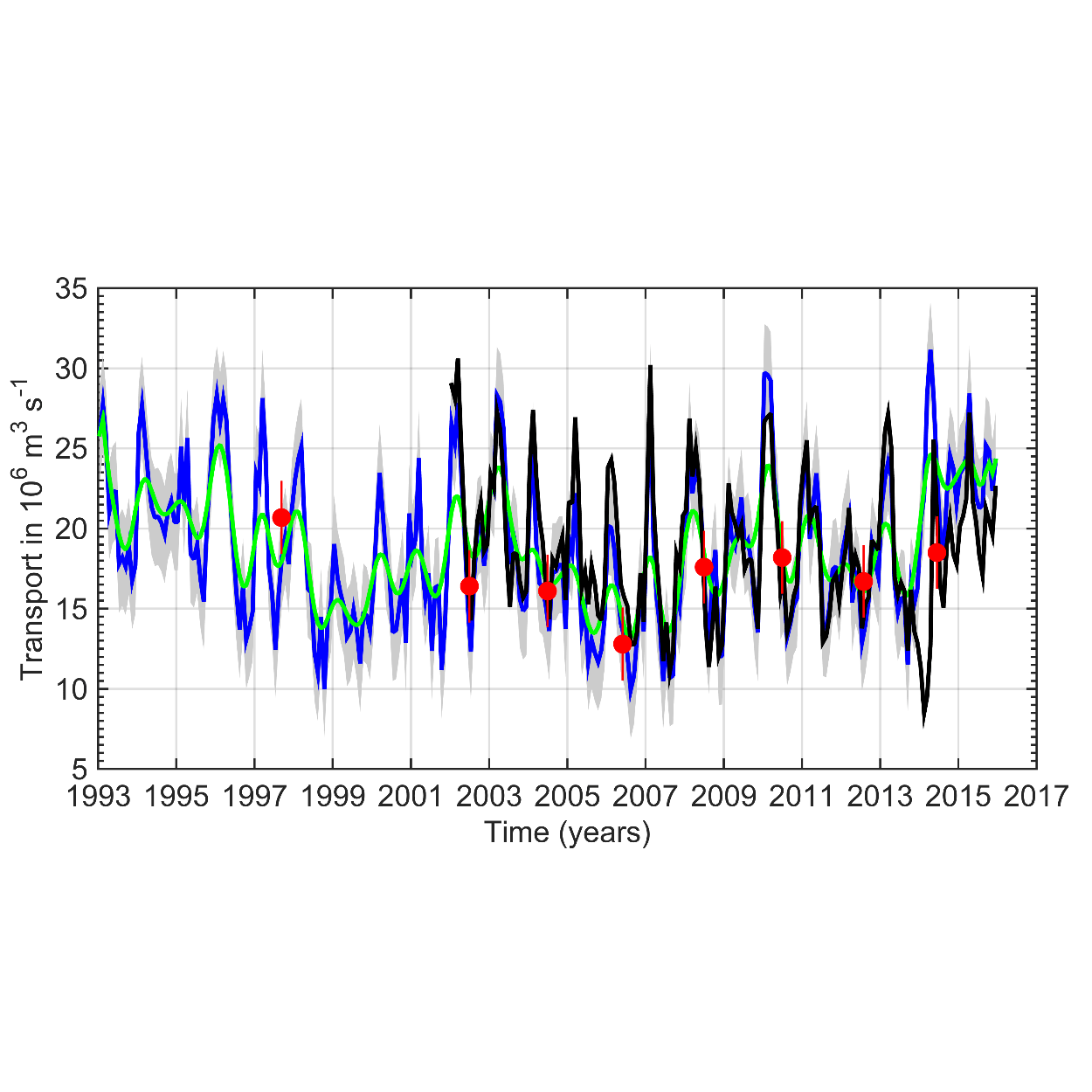
This data set provides a monthly time series of the upper limb of the Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) intensity at the A25 Greenland-Portugal OVIDE line from 1993 to 2015. The MOC was derived by combining AVISO altimetry with ISAS temperature and salinity data. The reader is referred to Mercier et al. (2015, Progress in Oceanography) for a full description of the method.
-
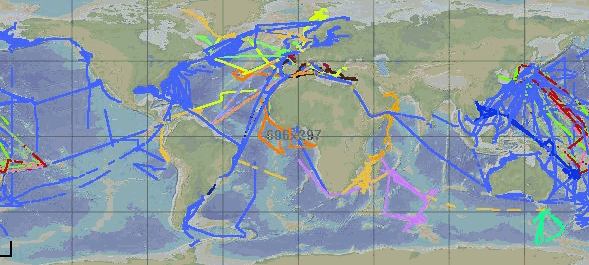
GOSUD aims at assembling in-situ observations of the world ocean surface collected by a variety of ships and at distributing quality controlled datasets. At present time the variables considered by GOSUD are temperature and salinity. The GOSUD data are mostly collected using thermosalinographs (TSG) installed on research vessels, on commercial ships and in some cases on sailing exploration ships GOSUD manages both near-real time data and delayed mode (reprocessed) data.
-
Ensemble simulations of the ecosystem model Apecosm (https://apecosm.org) forced by the IPSL-CM6-LR climate model with the climate change scenario SSP5-8.5. The output files contain yearly mean biomass density for 3 communities (epipelagic, mesopelagic migratory and mesopelagic redidents) and 100 size classes (ranging from 0.12cm to 1.96m) The model grid file is also provided. Units are in J/m2 and can be converted in kg/m2 by dividing by 4e6. These outputs are associated with the "Assessing the time of emergence of marine ecosystems from global to local scales using IPSL-CM6A-LR/APECOSM climate-to-fish ensemble simulations" paper from the Earth's Future "Past and Future of Marine Ecosystems" Special Collection.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA