XLS, XLSX
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
Key physico-chemical parameters (salinity, temperature, turbidity and dissolved oxygen) were measured in surface water during longitudinal transects in the Loire and Gironde estuaries in summers 2017 and 2018. This objective of this work was to determine the distribution of the dissolved oxygen and to detect potential severe desoxygenation. The transects were scheduled in order to begin the measurements at high tide from a site located upstream of an area where severe deoxygenation have been already been reported. Then, the transect was realised by sailing at low speed downstream with a multiparameter probe SAMBAT, maintained at 0.5 m below the surface, that collected a measurement every 2 minutes.
-
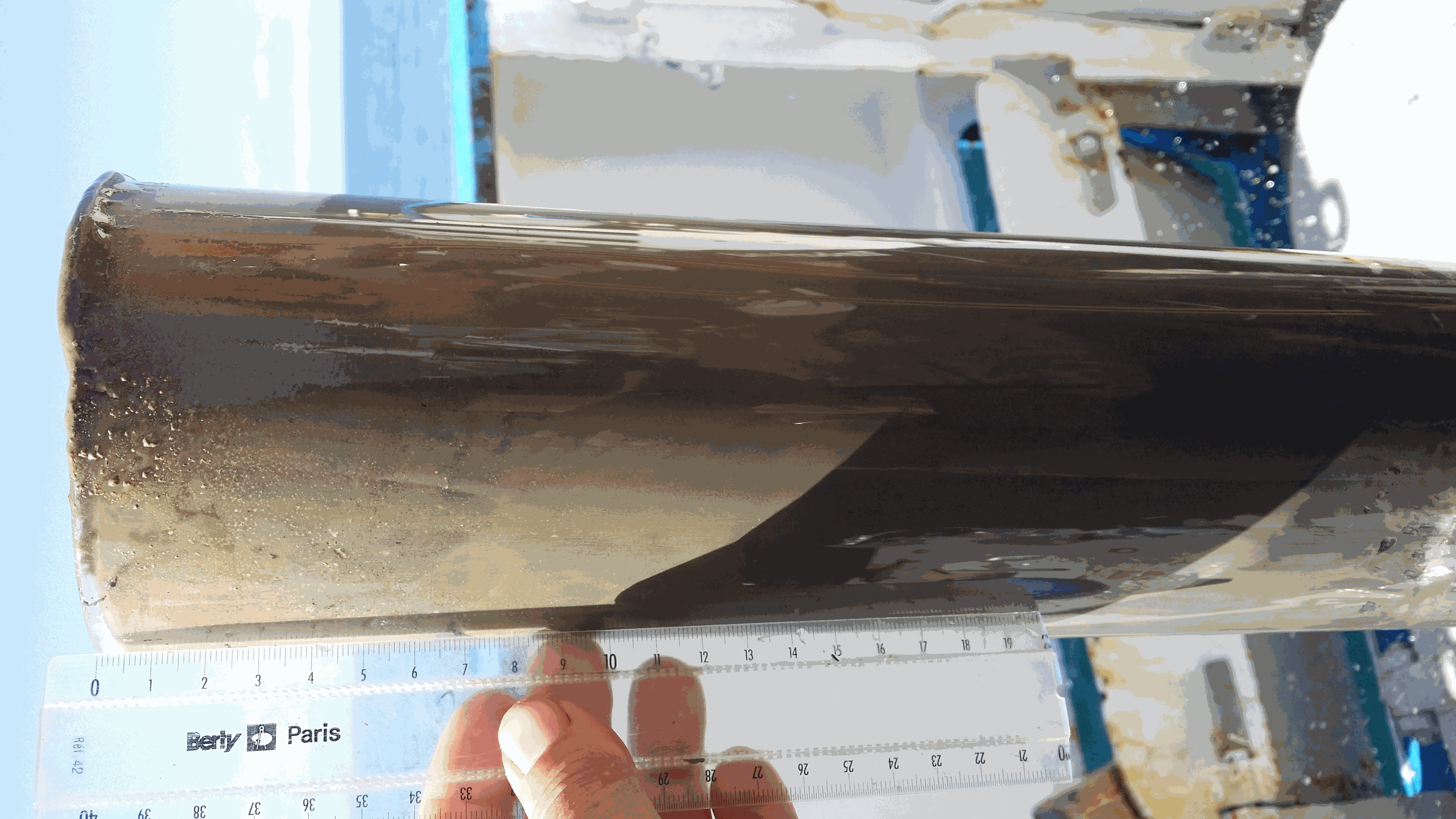
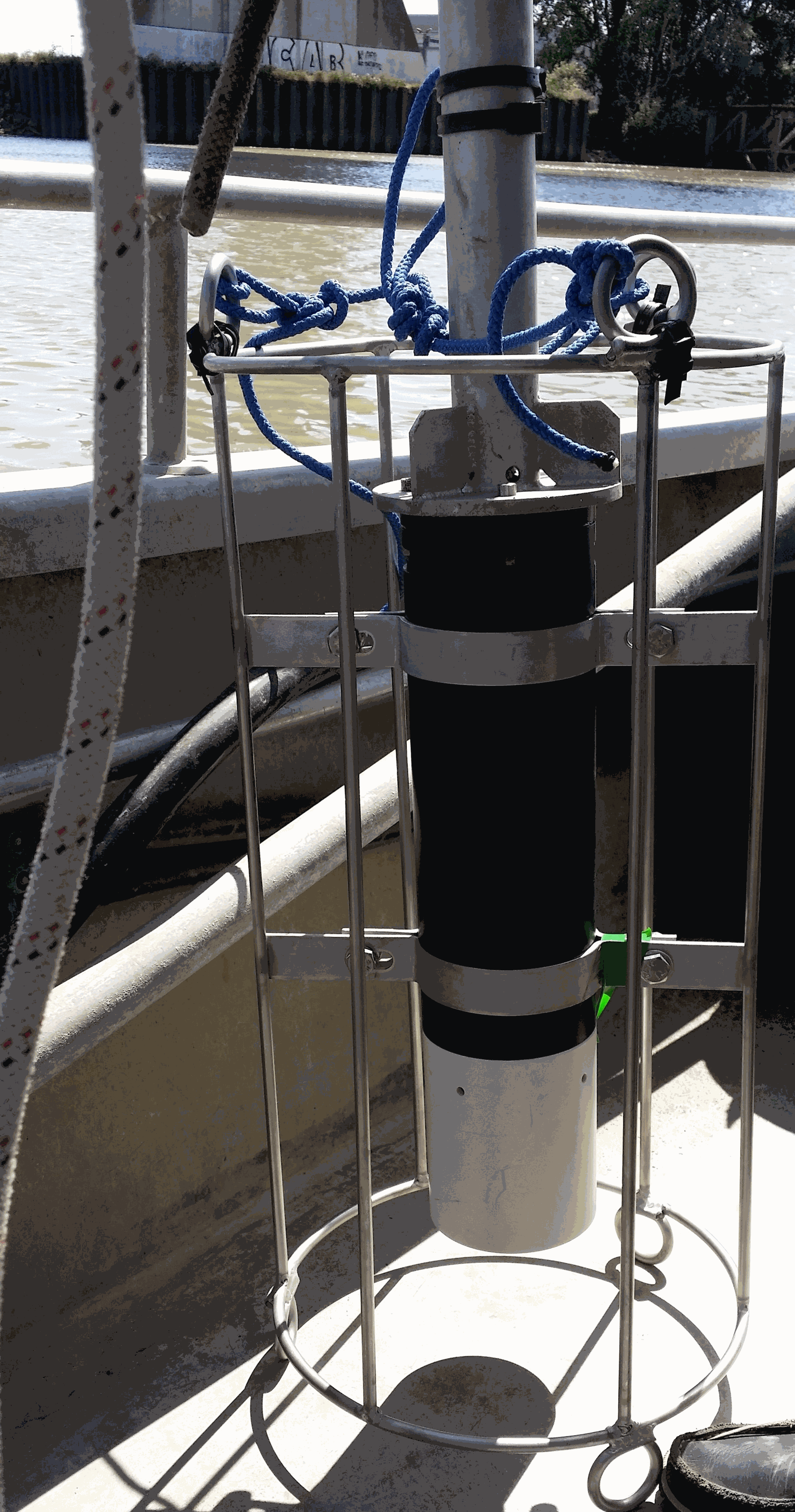
The West Gironde Mud Patch (WGMP) is a 420-km2 mud belt in the Bay of Biscay, located 25 km off the mouth of the Gironde estuary. This clay-silt feature of 4 m in thickness extends between 30 and 75m water depth, surrounded by the sands and gravels that cover the North Aquitaine continental shelf. Interface cores were collected during JERICOBent-1 cruise (October 2016; Deflandre (2016) doi.org/10.17600/16010400) along two cross-shelf transects for a total of 9 sites. Each sediment core was carefully extruded every 0.5 cm from the top core to 4 cm and every 1 cm below until the core bottom. The sediment layers were used to determine dry bulk density, grain size and selected radioisotope activities (210Pb, 226Ra, 137Cs, 228Th, K).
-

This set of data documents the radiocarbon dates (n=19) obtained thanks to the accelerator mass spectrometry method (AMS) at the LMC14/ARTEMIS French national facility on the cores (Multicorer, Kullenberg) retrieved from the West-Gironde mud patch (WGMP) during the JERICObent-7 cruise (10-15 July 2019; NR Côtes de la Manche, https://doi.org/10.17600/18001022). The WGMP registers very high sedimentation rates since the last 600 years (≥ 0.3 cm/yr) and is thus of great interest for palaeoceanographic investigations. At present, this depocenter marks the mid-shelf of the temperate Bay of Biscay off major French rivers from the Aquitaine basin. The fine mud deposits of the WGMP are of 3 to 4 meters thick and lie on palimpsest levels rich in gravels and shells. They cover a V-shaped structure, oriented SW-NE, which is attributed to the incision(s) of a paleovalley in the Cenozoic substrate, mainly linked to the paleo-Gironde routing changes during past glacials/interglacials, and its potential past convergences with the paleo-rivers of the Antioche perthuis (Seudre, Charente paleovalleys?) at that times. Detailed information on each sample is presented with the 14C results obtained by the Artemis AMS facility at LMC14 laboratory (Dumoulin et al. 2017- https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2016.116, Beck et al. 2024- https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2023.23). Raw ages are indicated together with calibration calculations using the last two versions of the Calib software (http://calib.org/, Calib 7 and 8) to show the dispersion of ages linked to the updating of calibration curves (Marine13, Intcal13, Marine20, Intcal 20). The calibrated ages finally retained for publications (used in the related Seanoe document - https://doi.org/10.17882/104237 - and published in Eynaud et al., 2025 for the ST3c core, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2025.105039) are those obtained with the last Calib 8.1 version. Raw 14C ages were calibrated and converted to calendar ages using the IntCal20 calibration curve with a reservoir age correction of 400 years deduced from Radionuclide analyses (137Cs and 210Pb) at the top of the studied cores (see Schmidt, 2025, https://www.seanoe.org/data/00968/107979/).
-

As part of the European Horizon Europe FOCCUS project (https://foccus-project.eu/), the metadata inventory of European coastal platforms has been extracted. The inventory was based on the following History and Latest products, downloaded from the CMEMS website (https://marine.copernicus.eu/fr/acces-donnees) at: 1) Global Ocean-In-Situ Near-Real-Time Observation, 2) Atlantic Iberian Biscay Irish Ocean-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 3) Mediterranean Sea-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 4) Atlantic-European North West Shelf-Ocean In-Situ Near Real Time Observations. To carry out this inventory, it was decided to target only coastal platforms, located less than 200km from the coast and at a depth of less than 400m. For mobile platforms, it was also decided to focus only on the first position in the file. This data must be located within 200 km of the coast and at a depth of less than 400 m. In this inventory, FerryBox platforms have all been considered as coastal platforms. The following platforms were extracted from the products: BO (Bottles), CT (CTD), DB (Drifting Buoys), FB (Ferry Box), GL (Gliders), HF (High Frequency Radar), MO (Mooring), PF (Profiling Float), TG (Tide Gauge) and XB (XBT). Once the metadata had been extracted from the files, duplicates were removed (files with the same names). Duplicate platforms of type _TS_ and _WS_ were merged (date and parameters). Latest‘ files have been merged with ’History" files. Missing metadata have been replaced in the Excel file by ‘Missing Data’. Some old dates were also revised by hand because they had been badly extracted, as well as some institution names that included special characters. Platforms located on estuaries/rivers/lakes/ponds have also been removed by hand. This inventory identified a total of 10,479 coastal platforms.
-
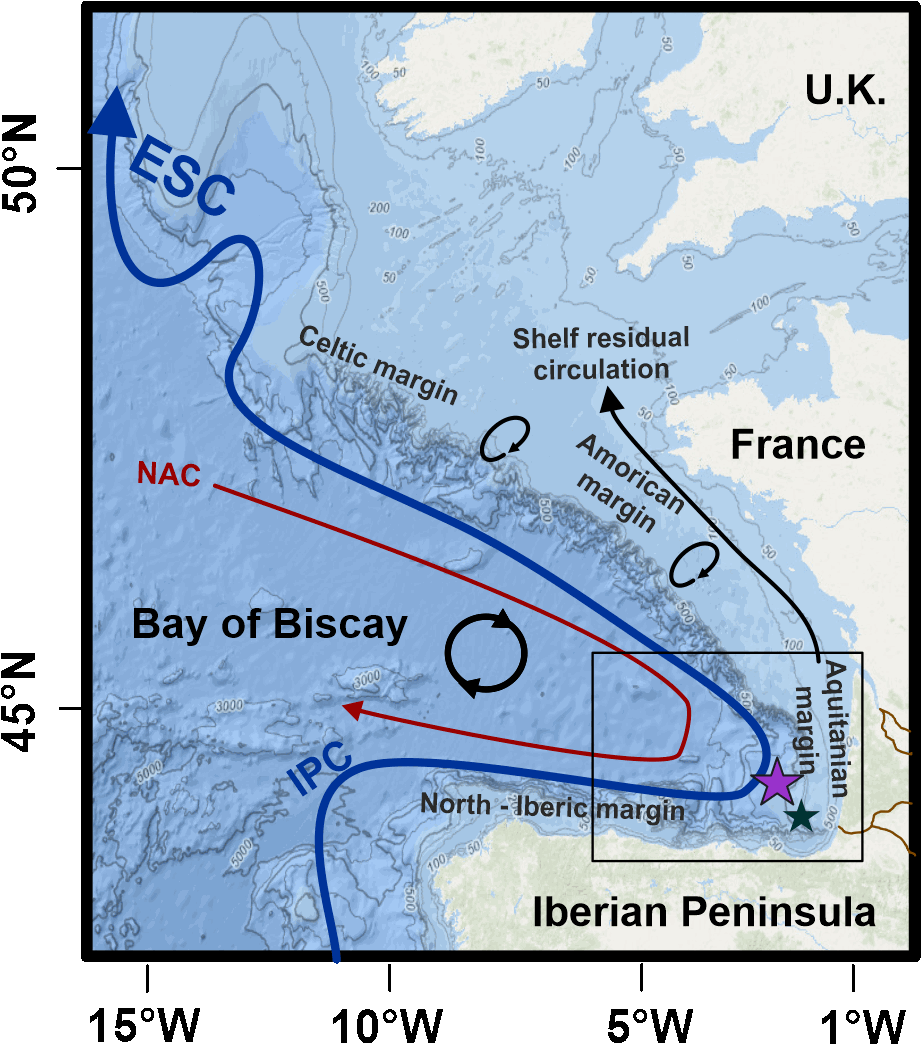
In the mid-latitudes of the northeast Atlantic, the study of the upper branch of the AMOC is poorly documented. This study provides a complete record of the glacial, deglacial and Holocene dynamics of the easternmost portion of the upper branch of the AMOC, namely the European Slope Current and its glacial equivalent know as the Glacial Eastern Boundary Current (GEBC). To do so, we use core SU81-44 (~1000 m water depth) from the of southern Bay of Biscay (BoB) upper slope, .The aim of this study is to reconstruct paleoenvironmental and hydrodynamic changes using a multiproxy approach (i.e. benthic foraminiferal assemblage, grain size proxies, oxygen and carbon stable isotopes, and foraminiferal εNd). During the glacial period and the onset of the deglaciation, our results show that the grain size proxies together with the relative densities of the high-energy indicator species Trifarina angulosa and the low oxygen tolerant Globobulimina spp. showed significant fluctuations. These were concomitant with the main climate changes recognized over this period and with the glacial slope paleoflow reconstruction from the northern BoB. This highlights a strong climatic/oceanographic forcing on the sedimentary characteristics of the region and a prominent forcing by changes in near-bottom flow speed. Our data also provide a new constraint on the strength of the slope current in the region during the late deglaciation and Holocene periods. We observe a reinvigoration of the upper branch of the AMOC during the Bølling-Allerød warming, preceding the abrupt resumption of the deeper branch of the AMOC in the western North Atlantic. This seems to confirm the crucial role of the European Slope Current in deep water formation, as it is the case today. Finally, our data show a progressive weakening of the ESC during the Holocene and we hypothesize a link with the long-term dynamics of the subpolar gyre.
-

Sardine physiological measurments from september to november 2020
-
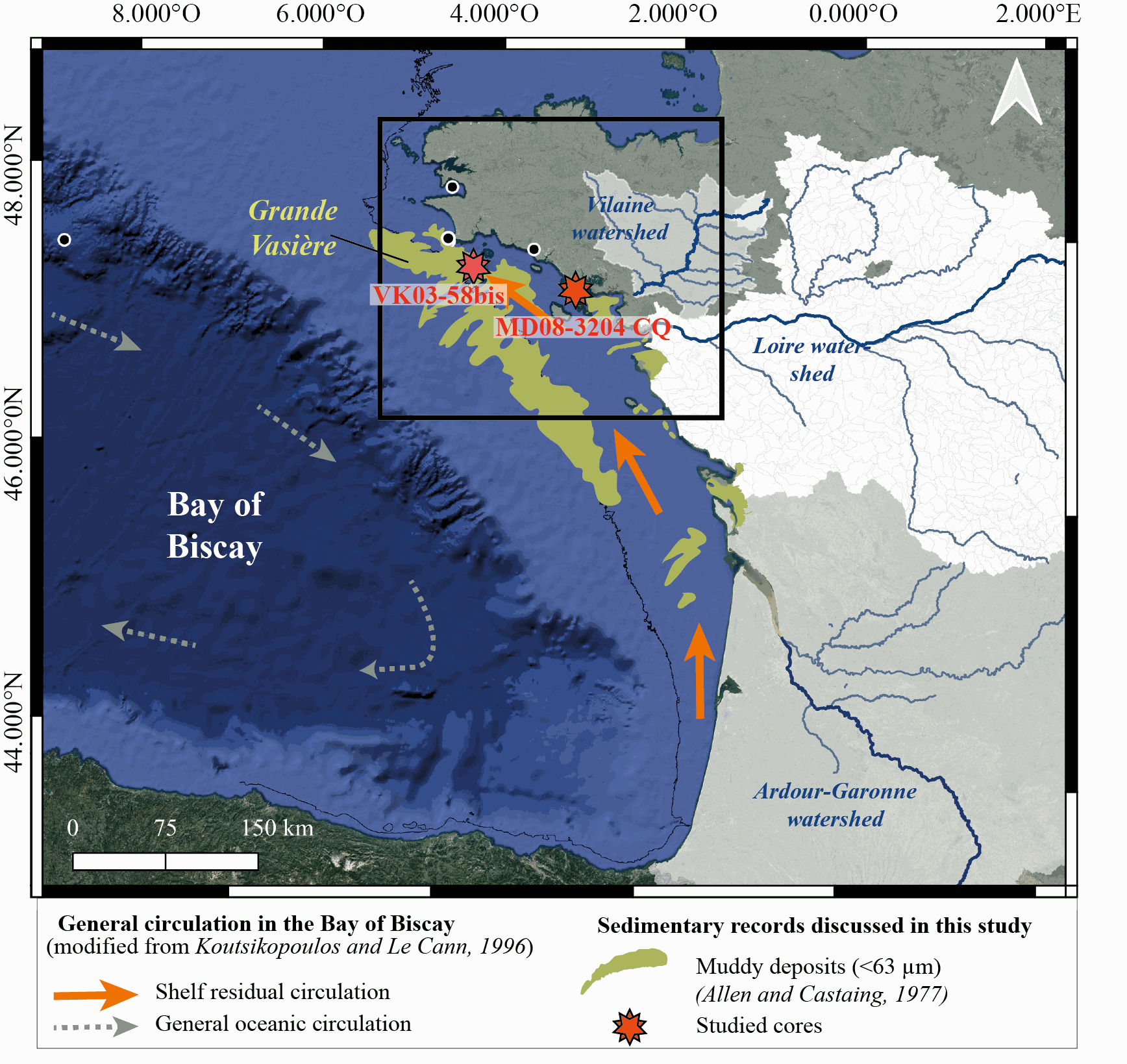
New results acquired in south-Brittany (MD08-3204 CQ core: Bay of Quiberon and VK03-58bis core: south Glénan islands) allow depicting Holocene paleoenvironmental changes from 8.5 ka BP to present through a multi-proxy dataset including sedimentological and palynological data. First, grain-size analyses and AMS-14C dates highlight a common sedimentary history for both study cores. The relative sea level (RSL) slowdown was accompanied by a significant drop of the sedimentation rates between ca. 8.3 and 5.7 ka BP, after being relatively higher at the onset of the Holocene. This interval led to the establishment of a shell-condensed level, identified in core VK03-58bis by the “Turritella layer” and interpreted as a marker for the maximum flooding surface. Palynological data (pollen grains and dinoflagellate cyst assemblages) acquired in core MD08-3204 CQ argue for an amplification of the fluvial influence since 5.7 ka BP; the establishment of the highstand system tract (i.e., mixed marine and fluviatile influences on the platform) then accompanying the slowdown of the RSL rise-rates. On the shelf, the amplification of Anthropogenic Pollen Indicators (API) is then better detected since 4.2 ka BP, not only due to human impact increase but also due to a stronger fluvial influence on the shelf during the Late Holocene. Palynological data, recorded on the 8.5–8.3 ka BP interval along an inshore-offshore gradient, also demonstrate the complexity of the palynological signal such as i) the fluvial influence that promotes some pollinic taxa (i.e., Corylus, Alnus) from proximal areas and ii) the macro-regionalization of palynomorph sources in distal cores. In addition, the comparison of palynological tracers, including API, over the last 7 kyrs, with south-Brittany coastal and mid-shelf sites subjected to northern vs. southern Loire catchment areas, allowed discussing a major hydro-climatic effect on the reconstructed palynological signals. Strengthened subpolar gyre dynamics (SPG), combined with recurrent positive North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) configurations, appear responsible for increased winter precipitations and fluvial discharges over northern Europe, such as in Brittany. Conversely, weakened SPG intervals, associated with negative NAO-like modes, are characterized by intensified winter fluvial discharges over southern Europe. Interestingly, we record, at an infra-orbital timescale, major peaks of API during periods of strengthened (/weakened) SPG dynamics in sites subjects to Brittany watersheds (/Loire watersheds) inputs.
-

The ARCHYD dataset, which have been collected since 1988, represents the longest long-term hydrologic data sets in Arcachon Bay. The objectives of this monitoring programme are to assess the influence of oceanic and continental inputs on the water quality of the bay and their implications on biological processes. It also aims to estimate the effectiveness of management policies in the bay by providing information on trends and/or shifts in pressure, state, and impact variables. Sampling is carried on stations spread across the entire bay, but since 1988, the number and location of stations have changed slightly to better take into account the gradient of ocean and continental inputs. In 2005, the ARCHYD network was reduced to 8 stations that are still sampled by Ifremer to date. All the stations are sampled at a weekly frequency, at midday, alternately around the low spring tide and the high neap tide. Data are complementary to REPHY dataset. Physico-chemical measures include temperature, salinity, turbidity, suspended matters (organic, mineral), dissolved oxygen and dissolved inorganic nutrients (ammonium, nitrite+nitrate, phosphate, silicate). Biological measures include pigment proxies of phytoplankton biomass and state (chlorophyll a and phaeopigment).
-
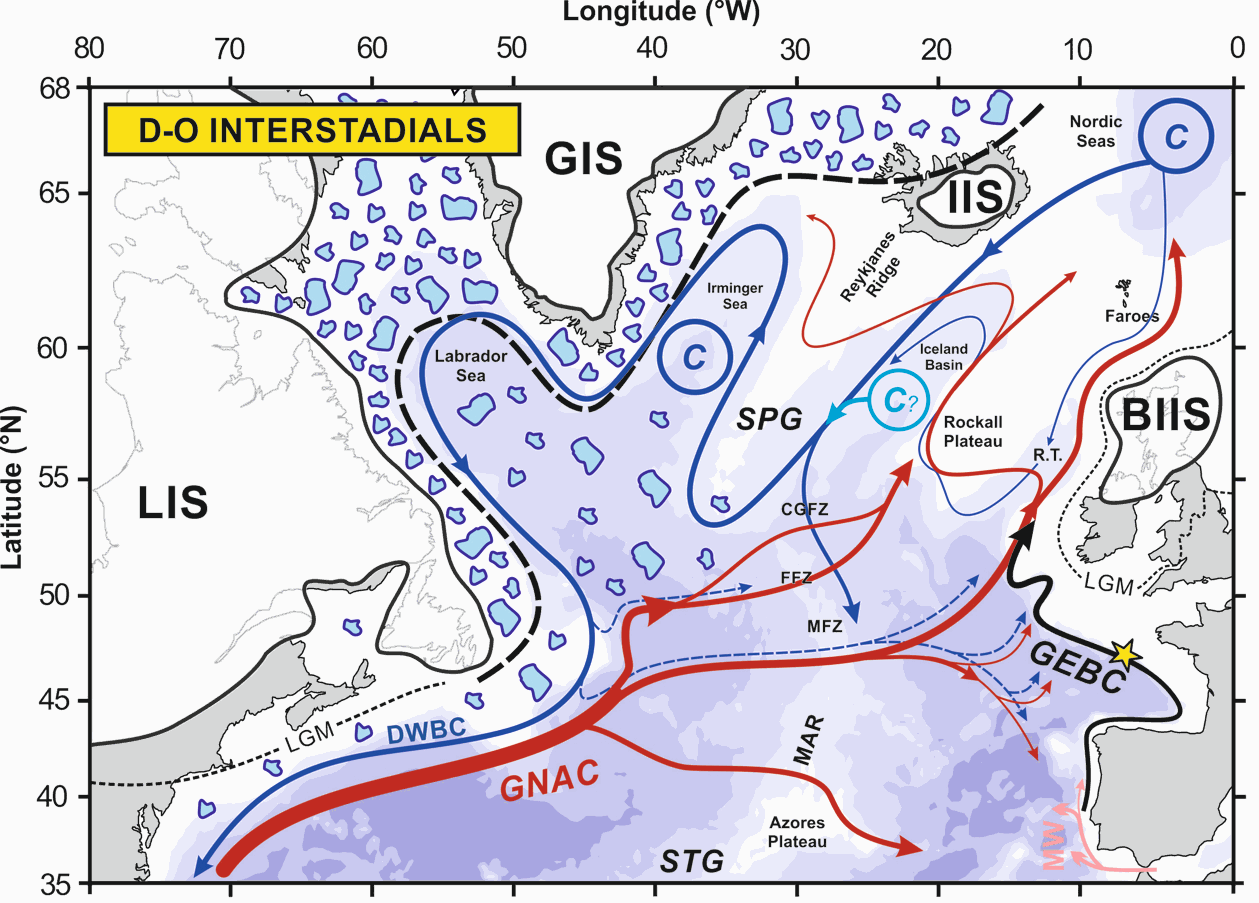
The upper branch of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) plays a critical role in ocean circulation and climate change, yet its variability during the last glacial period is poorly documented. Here, we investigate the northward-flowing Glacial Eastern Boundary Current (GEBC) in the North Atlantic, known today as the European Slope Current, and representing the easternmost portion of the upper branch of the AMOC. Based on flow speed (sortable silt, XRF) and radiogenic/stable isotopic records, we show that Dansgaard-Oeschger (D/O) interstadials (stadials) correspond to a faster (weaker) GEBC during the ~50-15 ka period. This, by analogy to present-day conditions, suggests enhanced (reduced) strength of the subpolar gyre and, by extension, of northern-sourced water production and AMOC during D-O interstadials (stadials). Concomitant fluctuations of both the European Ice Sheet and the GEBC between ~30 and 17 ka suggest an active role of the upper branch of AMOC in the poleward transport of heat and freshwater to the northern North Atlantic, with direct impacts on deep water formation and AMOC strength. Our GEBC reconstruction is the first physical (non-chemical) record documenting dynamic upper AMOC variability at high resolution in the eastern basin of the North Atlantic. Together with the deep North Atlantic records of northern-sourced water export, they confirm the central role of the AMOC in the generation of abrupt climate changes.
-
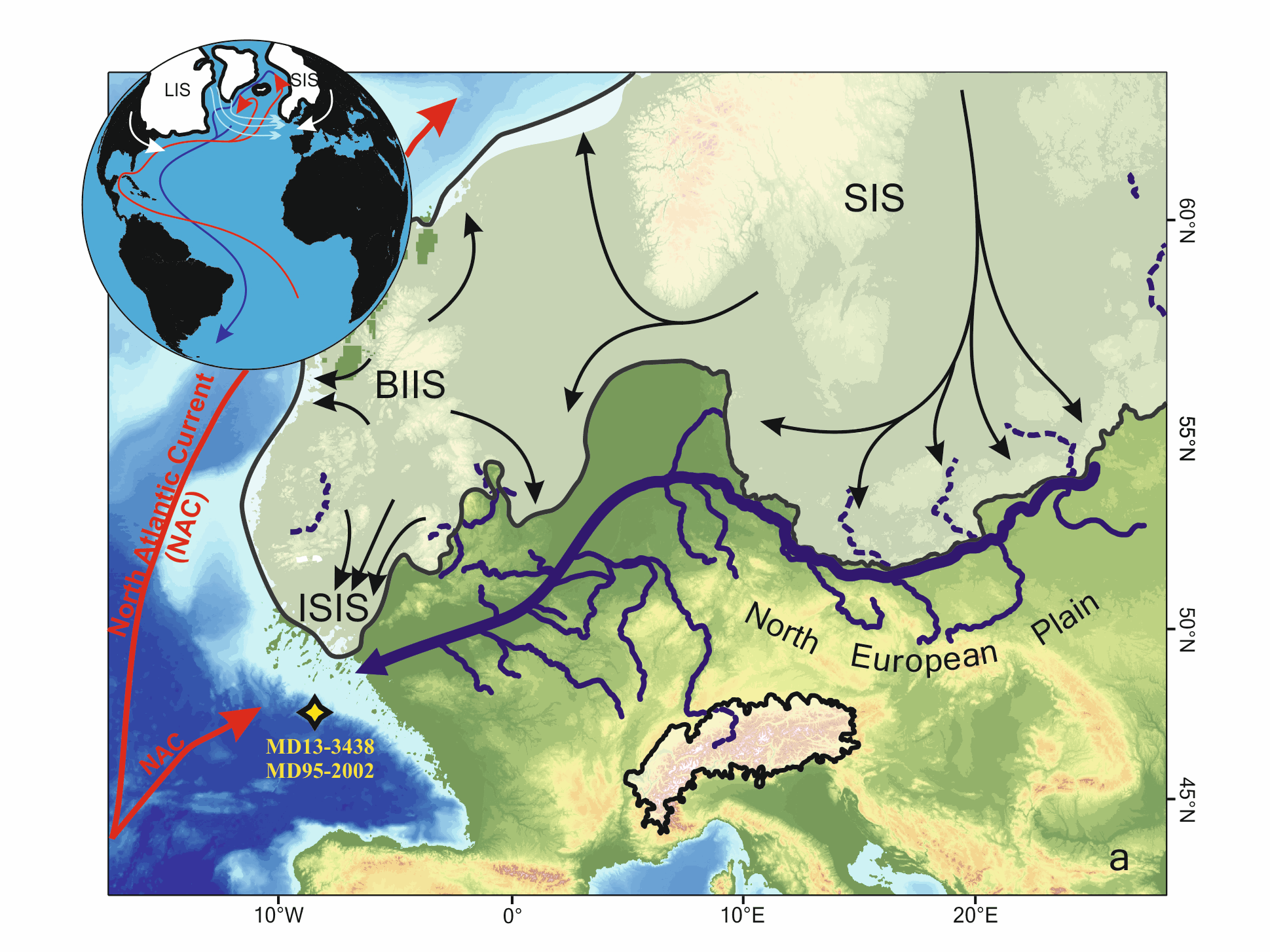
Marine microfossils (dinoflagellate cysts and planktonic foraminifera) and geochemical (XRF-Ti/Ca)-based climatic records from a core located off the Fleuve Manche (FM) paleo-mouth (MD13-3438) have revealed that sustained warm summer sea surface temperatures (SSTs) during sub-millennial climate changes within HS1 (~18–14.7 ka) may have played a key role in the FM regime related to the European Ice Sheet (EIS) melting rate. In this study, we have analyzed the MD13-3438 pollen content over the HS1 at a mean resolution of ~50 years to test whether vegetation-based air temperatures were coupled to SSTs face to this rapid climate variability. First, our results highlight two major phases of pollen sources at site MD13-3438, preventing the pollen record to be interpreted as a continuous record of the evolution of vegetation and climate occupying a single watershed across HS1. The first phase, i.e. the HS1-a interval (~18–16.8 ka), is marked by strong occurrences of boreal pollen taxa (especially Picea-Abies). Considering their spatial distribution and the coalescence of the British and Scandinavian ice sheets into the North Sea during the Last Glacial Maximum, these taxa probably originated from the North European Plain, i.e., eastern FM tributaries (east of the Rhine River), where cool-humid conditions generally prevailed. Then, the second phase, i.e. the HS1-b interval (~16.8–14.7 ka BP), is characterized by a deceleration of the EIS retreat and the drop of boreal pollen values at site MD13-3438 further signing a less influence of the upstream FM drainage system and thus a better characterization of pollen sources related with western FM tributaries. Superimposed to these two HS1 main phases, pollen fluctuations are concomitant with sub-millennial variability in the EIS deglaciation intensity. During the early HS1 (HS1-a), we discussed two short-term increases in the ratio between deciduous trees (Quercus-Corylus-Alnus) and herbaceous plants (Plantago-Amaranthaceae-Artemisia). These events were coeval with phases of increasing FM meltwater runoff and SST seasonality (i.e., dinocyst-based summer SST amplification). We associated these events with lower contribution of the upstream FM catchment as well as, possibly, atmospheric warming and regional sea-level positive oscillations. The HS1-b is composed of three main phases that appear more influenced by the downstream FM drainage system. HS1-b1 (16.8–16.3 ka BP) corresponds to the driest and coldest conditions west of the Rhine River. HS1-b2 (16.3–15.6 ka BP) is coeval with large arrivals of iceberg from the Hudson strait in the Bay of Biscay and thus likely to a major sea-level positive oscillation associated with a phase of FM valley reworking. HS1-b3 (15.6–14.7 ka BP) corresponds to persistent arid conditions that preceded the subsequent more humid conditions recorded from 14.7 ka BP at the start of the Bölling-Alleröd.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA