/Biological Environment/Habitats
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
-
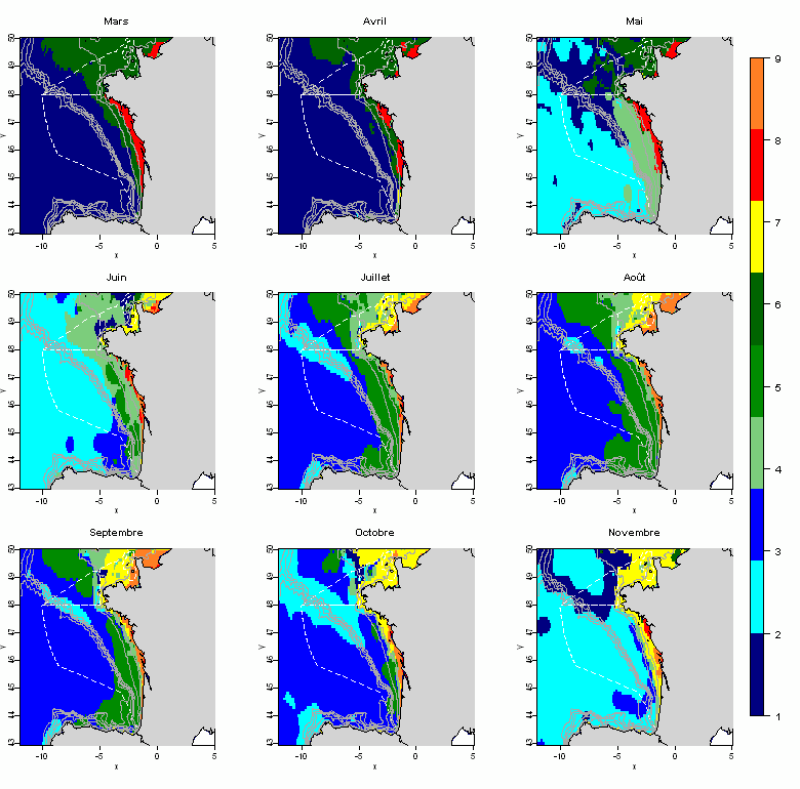
The statistical analysis used (Principal Component Analysis followed by a classification method) to identify groups common to all months and describe the evolution of these groups during the year. The data used allows for monthly tables showing the selected parameters, calculated over the entire geographic area with a resolution of 0.1 °. This method identifies 10 hydrological landscapes present at various times of the year, and characterized by homogeneous hydrological conditions.
-
-
-
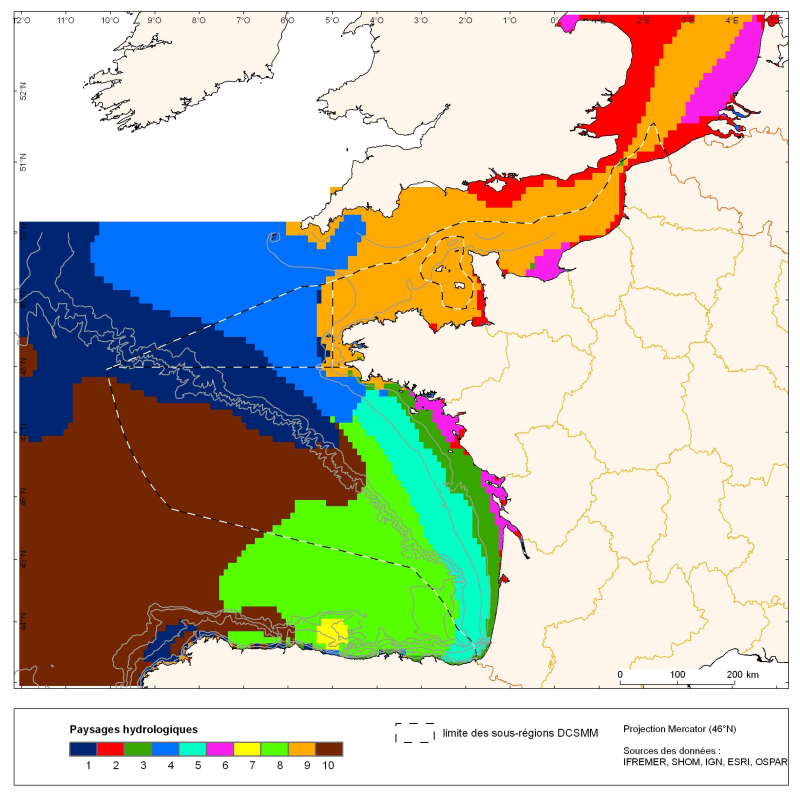
The distribution of hydrological landscapes is determined by a method of comparing multi-tables, to identify groups of individuals with similar variability of hydrological conditions during the year. The data used provides monthly tables showing the selected parameters, calculated over the entire geographic area with a resolution of 0.1 °. The variable chlorophyll-a is extra: it does not contribute to the discrimination of groups. This method identifies 10 hydrological landscapes with a similar annual variability of hydrological conditions.
-
-

Portal to view and download observations of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystem (VME) indicators and habitats in the North Atlantic. A central portal for data on the distribution and abundance of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs), (and organisms considered to be indicators of VMEs) across the North Atlantic has been set up by the Joint ICES/NAFO Working Group on Deep-water Ecology (WGDEC). Criteria used to select habitats and indicators for inclusion in the database were those described in the FAO International Guidelines for the Management of Deep-sea Fisheries in the High Seas (FAO, 2009). The database is comprised of: - 'VME habitats' that are records for which there is unequivocal evidence for a VME, e.g. ROV observations of a coral reef - 'VME indicators' which are records that suggest the presence of a VME with varying degrees of uncertainty. For VME indicators a weighting system of vulnerability and uncertainty is provided as part of the database to aid interpretation. The VME database may be used for many purposes. ICES uses it when providing scientifically-robust advice on the distribution of VMEs and recommending possible management solutions such as bottom fishing closures within North East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) waters to protect VMEs.
-
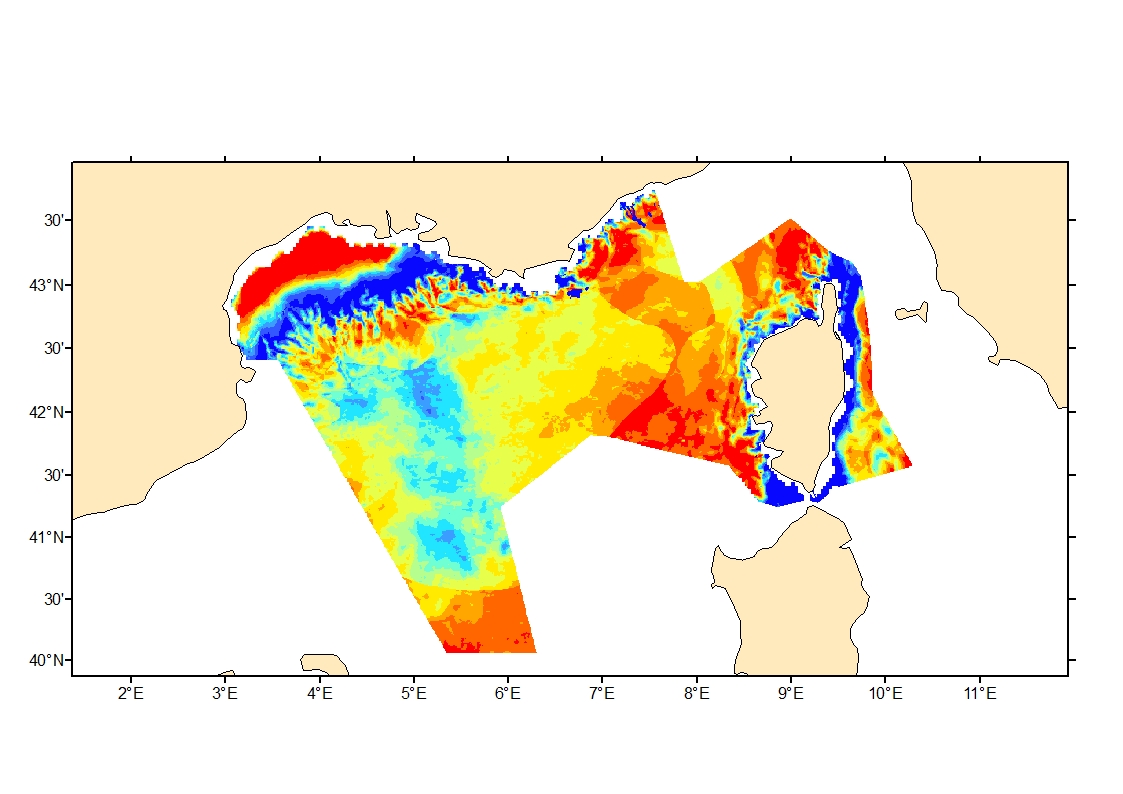
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-
-
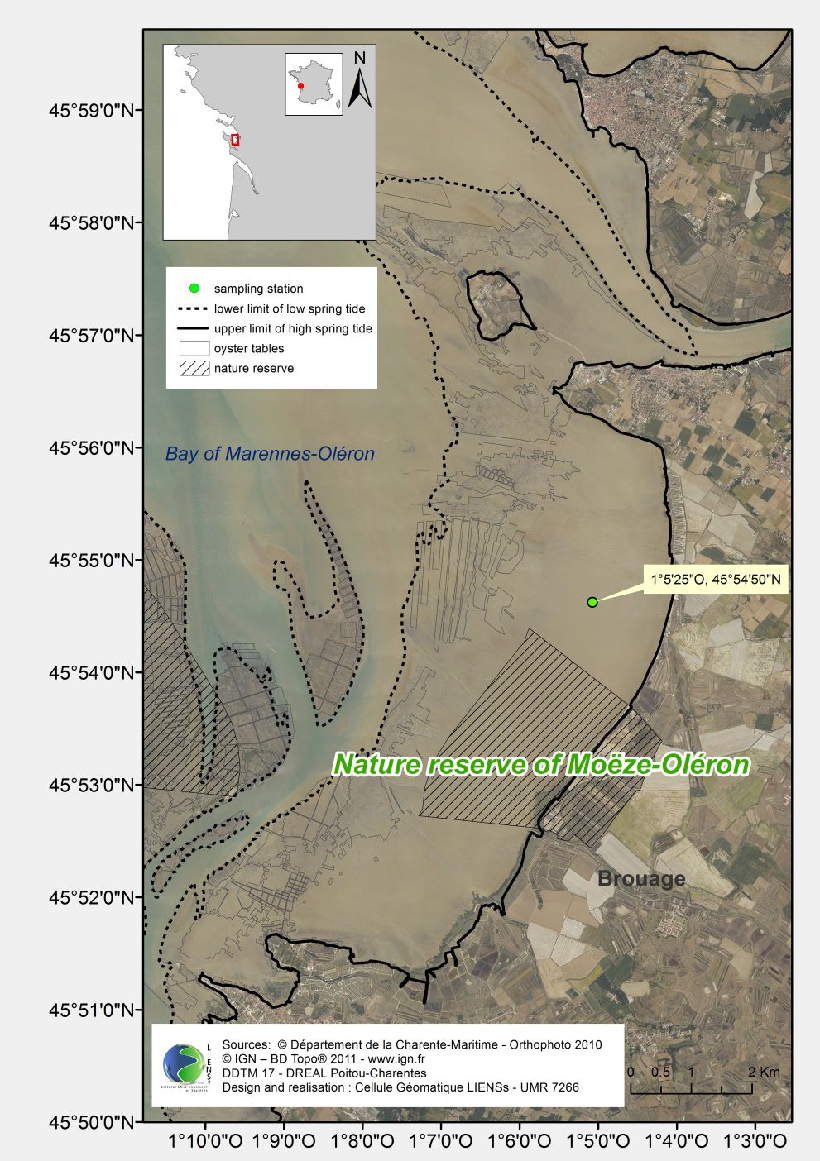
Intertidal mudflats are a key system of the network, being closely connected to ecosystems which form the transition between the watershed area and the ocean. Their high productivity is linked to activity within a diatom biofilm, the functioning and future of which have recently been the subject of many research programmes. However, the determinism and future of bacterial production associated with the secretion of ExoPolySaccharides within the biofilm is largely unknown. Early studies have nevertheless shown that this production is at least as high as that of diatoms. An integrated view of the ecological functioning of intertidal mudflats within a more global schema of carbon flow therefore needs to define and quantify the determinism of this bacterial production and it future within the ecosystem.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA