/Physical Environment/Hydrodynamics/Water Column
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
GOSUD aims at assembling in-situ observations of the world ocean surface collected by a variety of ships and at distributing quality controlled datasets. At present time the variables considered by GOSUD are temperature and salinity. The GOSUD data are mostly collected using thermosalinographs (TSG) installed on research vessels, on commercial ships and in some cases on sailing exploration ships. GOSUD manages both near-real time (RT and NRT) data and delayed mode (DM-reprocessed) data. The GOSUD GDAC is hosted by the Coriolis data centre (France) and a back-up (permanent archived) is performed on a daily basis by NCEIS (NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information).
-
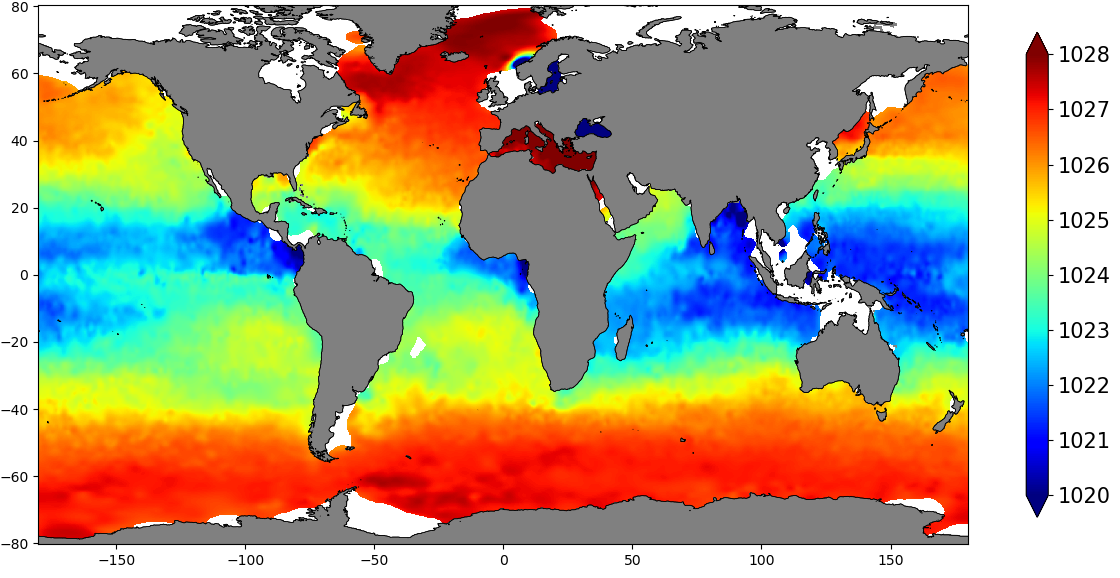
The SDC_GLO_CLIM_Dens product contains global monthly climatological estimates of in situ density using Temperature and Salinity from profiling floats contained in the World Ocean Data 18 (WOD18) database. The profiles were first quality controlled with a Nonlinear Quality control procedure. The climatology considers observations from surface to 2000 m for the time period 2003-2017. Density profiles are computed using UNESCO 1983 (EOS 80) equation from in situ temperature, salinity and pressure measurements by the PFL. Only profiles with both T,S values were used. The gridded fields are computed using DIVAnd (Data Interpolating Variational Analysis) version 2.3.1.
-
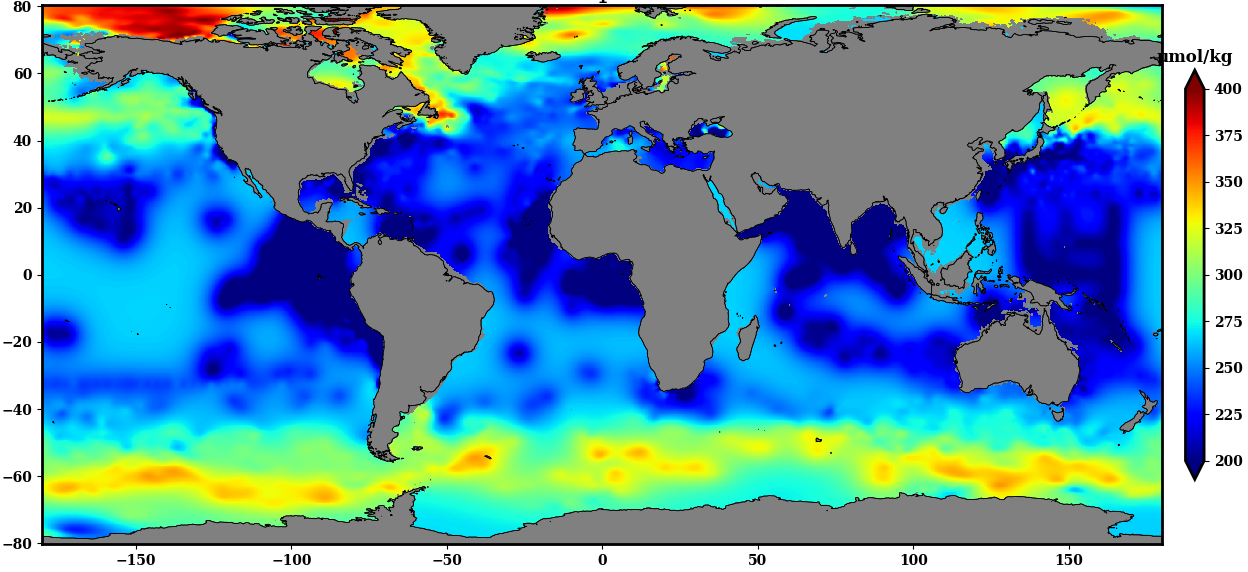
The SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2_AOU product contains two different monthly climatology for dissolved Oxygen and Apparent Oxygen Utilization, SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2 and SDC_GLO_CLIM_AOU respectively from the World Ocean Data (WOD) database. Only basic quality control flags from the WOD are used. The first climatology, SDC_GLO_CLIM_O2, considers Dissolved Oxygen profiles casted together with temperature and salinity from CTD, Profiling Floats (PFL) and Ocean Station Data (OSD) for time duration 2003 to 2017. The second climatology, SDC_GLO_CLIM_AOU, apparent Oxygen utilization, is computed as a difference of dissolved oxygen and saturation O2 profiles. The gridded fields are computed using DIVAnd (Data Interpolating Variational Analysis) version 2.3.1.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA