D4: Marine Food Webs
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
The aim of this project is to develop an eco-physiological model to predict production flow of certain species of planktonic Foraminifera, which are representative of the main ecological system, as well as their habitat (depth, season), from climate forcing. The eco-physiological and geochemical/isotopic characteristics must be determined by the data obtained during cruises. The data from closing nets and sediment traps will be used to evaluate flows from different Foraminifera and the acquisition of their isotope and geochemical signals according to the depth of their habitat and their development cycle. The project is linked to ANR FORCLIM (coordinator L.Labeyrie, LSCE). Data is organised into two parts : 1/ measurements of physiochemical and biogeochemical parameters in the water column ; inventory of planktonic Foraminifera - 2/ Measurements of biogeochemical parameters and the interface between sediment and water: inventory of benthic Foraminifera fauna. The campaign is connected to the STEEPL Observation Service (Temporal monitoring of benthic and planktonic ecosystems in the Landes plateau) – OSUNA funding (Nantes Angers Sciences of the Universe Observatory).
-
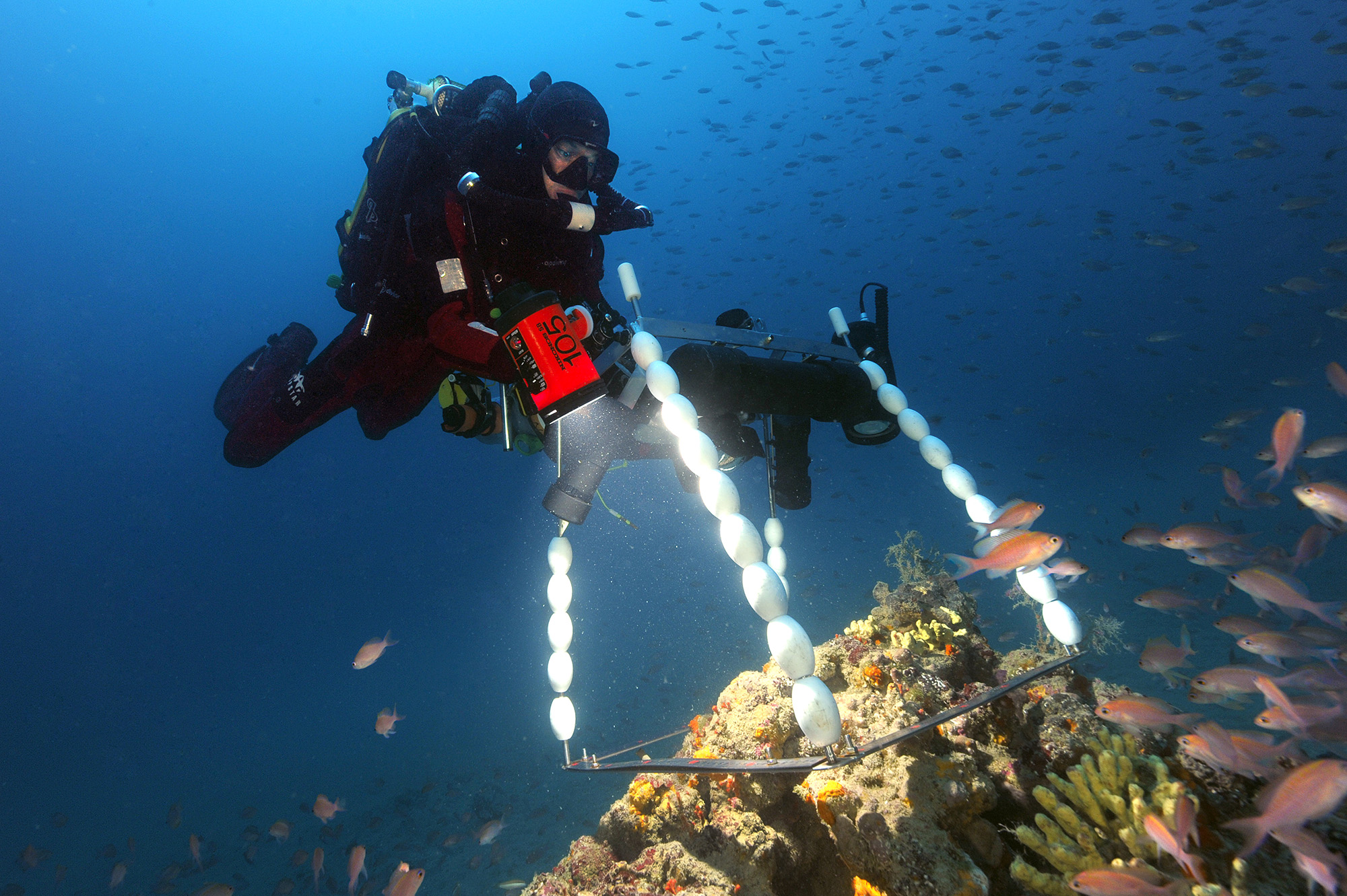

-
Upon building a new waste pool for waste from oyster farming, a zostera noltii seagrass meadow was destroyed by sediment deposits. This site is located in the Arcachon basin and has been monitored since 2005 in order to evaluate the impact this of this work and the recolonisation of the site by benthic macrofauna.
-
The effect of Maerl extraction on Benthic Communities in the Glénan Archipelago.
-
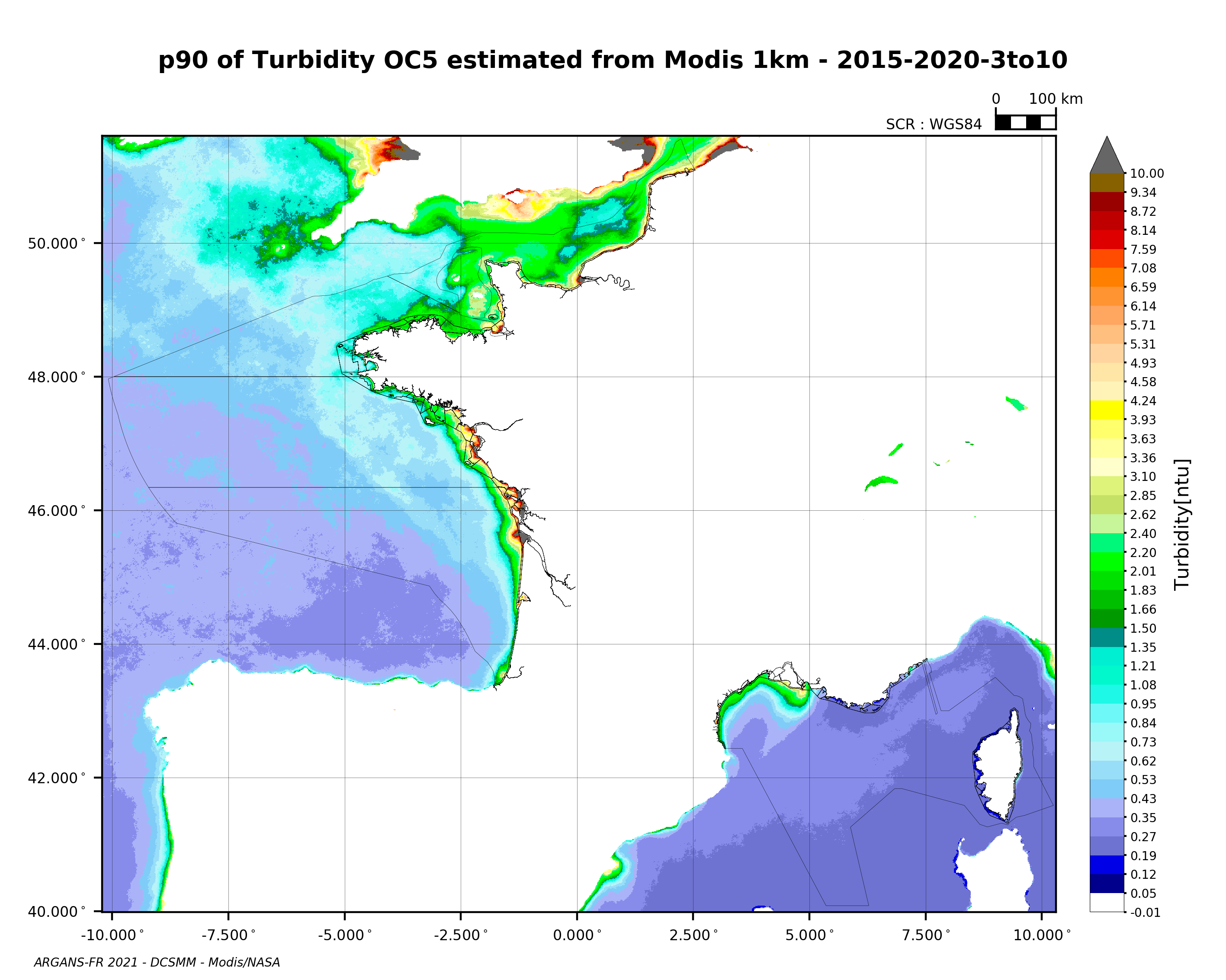
90th percentile of turbidity calculated during the productive period of the WFD (March-October) from 2015 to 2020, from the MODIS algorithm processed by OC5 IFREMER/ARGANS (Gohin et al 2002, Gohin 2011).
-
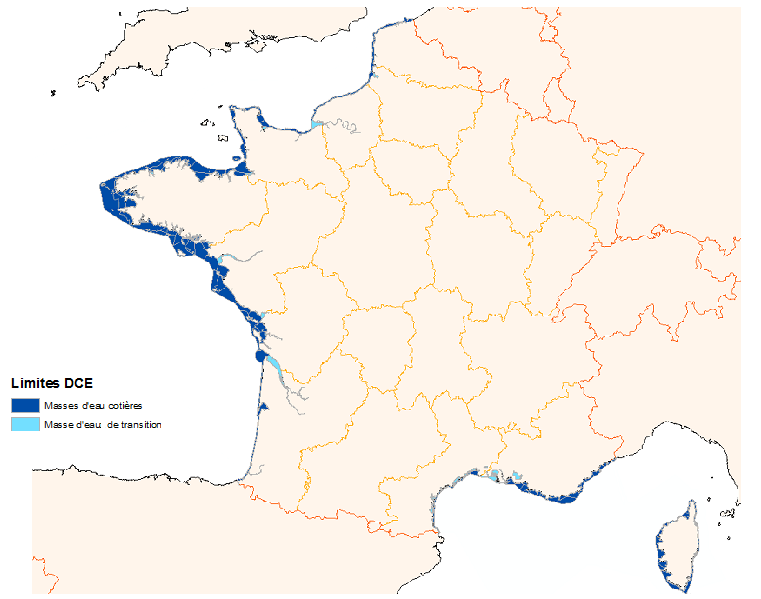
The Water Framework Directive 2000/60/CE is applied to all European Union member states and establishes a new framework for community policy in the water sector with a view to improving management of aquatic environments.
-
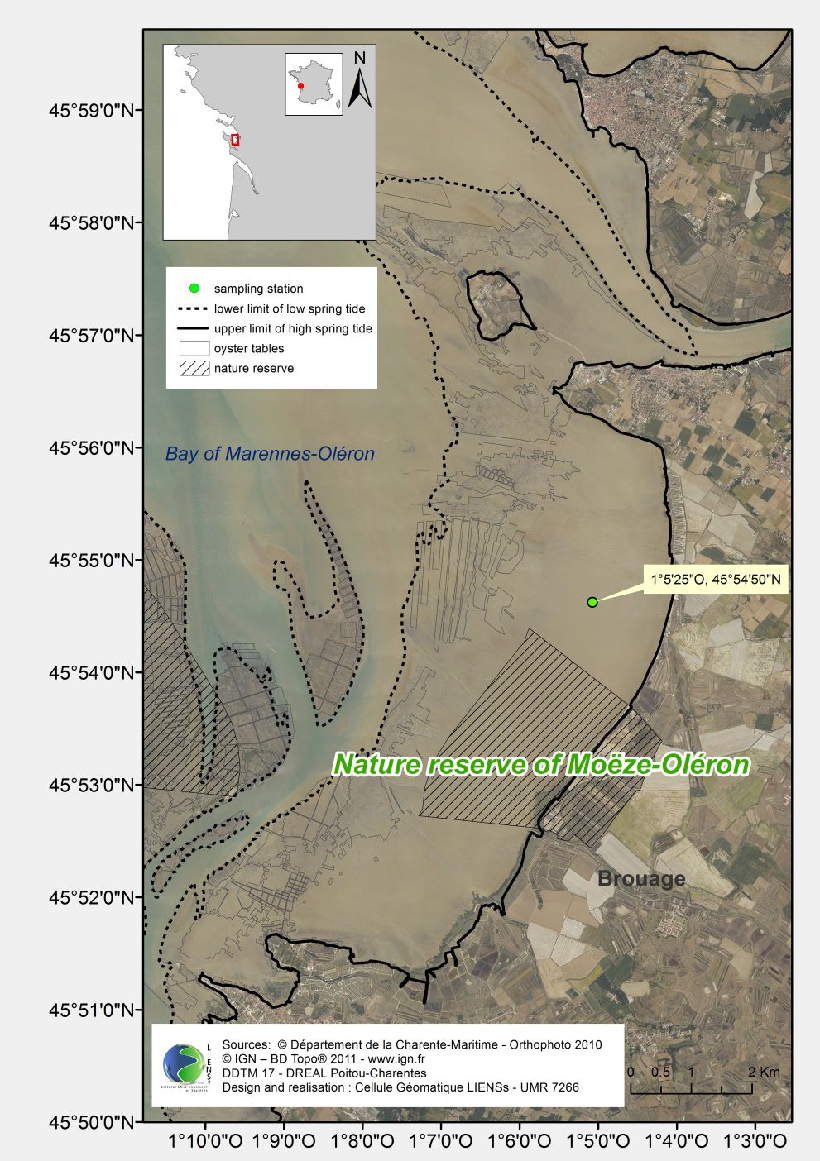
Intertidal mudflats are a key system of the network, being closely connected to ecosystems which form the transition between the watershed area and the ocean. Their high productivity is linked to activity within a diatom biofilm, the functioning and future of which have recently been the subject of many research programmes. However, the determinism and future of bacterial production associated with the secretion of ExoPolySaccharides within the biofilm is largely unknown. Early studies have nevertheless shown that this production is at least as high as that of diatoms. An integrated view of the ecological functioning of intertidal mudflats within a more global schema of carbon flow therefore needs to define and quantify the determinism of this bacterial production and it future within the ecosystem.
-
Zooplankton monitoring (essentially metazoal) – mesozooplankton in the Gironde estuary (3 stations) since 1997 Locations : 3 Stations pK86 : 45°31’N, 01°57’W, pK52 : 45°14’80’’N, 0°43’50’’W pK30 : 45°04’10’’N, 0°38’30’’W
-
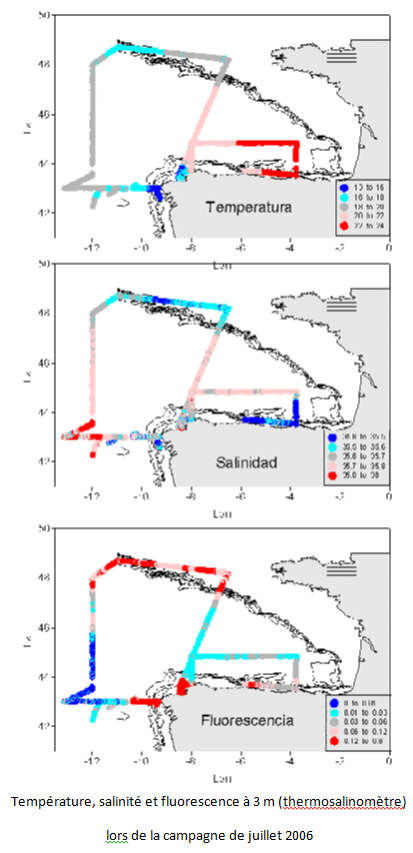
The aim of this project is to implement a sampling network in order to study climate variability in ocean water around the Iberian peninsula and the Bay of Biscay, to determine the flows of heat, freshwater, nutrients and C02 in wastewater, and relationship with NAO. This contributed to international climate change programmes and to the beginning of systematic study of the region. Furthermore, it facilitates the use of a digital model in the region. The main aim of the VACLAN project is to improve observation capacity and the use of the new tools available used to characterize climate change: remote sensing for the study of surface waters, drifting buoys for upper and mid waters, and moored instruments and hydrographic stations for studying the water column. The use of these tools along with digital modelling will make it possible to characterize CO2 flow and the physio-chemical flow in such a large area, where the border current is the Atlantic. Furthermore, once checked and validated, the data in this system will be made available for academic scientific communities and included in digital forecasting models.
-
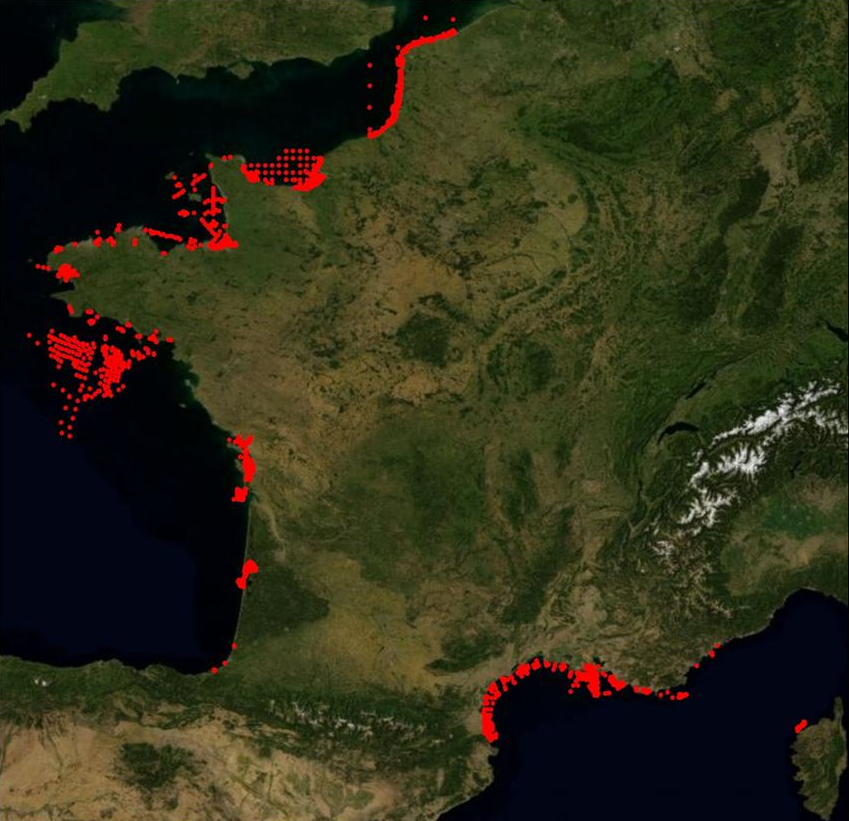
Resomar is a French national network of marine stations and observatories for exchanging and collaboration on scientific projects, studies and monitoring programmes. In 2007, the CNRS/INSU launched a programme with a view to giving new life to RESOMAR (formerly RNSM and then RNSLM), and to made it a strategic tool for enhancing coastal marine biology studies at a national level. This network has been given the task of scientifically collating and exploiting biological databased relating to the components of benthic and pelagic ecosystems on the French coast.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA