Data
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Excel file containing CPR data from Standard Areas B4,C3,C4,D3,D4,D5,E4,F4 for the plankton Calanus finmarchicus and helgolandicus, total traverse (small) copepods, total large copepods, Phytoplankton Colour Index and Cnidaria (presence denoted by a 1, absence by a zero). All taxa are from 1980, except Cnidaria which are from 2011. Dataset is in the format of sample level data, with each row being a discrete sample, with a sample being 3m3 filtered seawater, and 10nm of tow. For each row, a sample has the following information, starting at column a: Standard area of sample, sample id, latitude (decimal degrees) of sample mid point, longitude (decimal degrees) of sample midpoint, sample midpoint date and local time, year of sample, month of sample, then plankton abundance values (or PCI index or cnidaria presence/absence). All taxa have been looked for during the period this dataset spans, so zero values represent true absence.
-

NOAA High-resolution Blended Analysis of Daily SST and Ice. Data is from Sep 1981 and is on a 1/4 deg global grid.
-
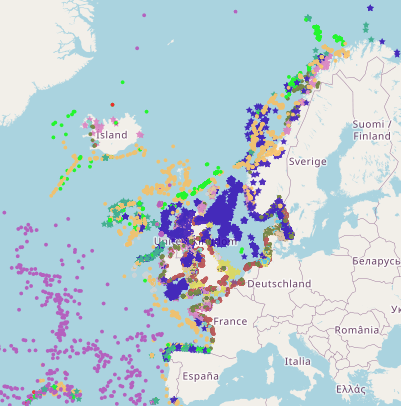
This is a compilation of OSPAR habitat point data for the northeast Atlantic submitted by OSPAR contracting parties. The compilation is coordinated by the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee, working with a representative from each of the OSPAR coastal contracting parties. This public dataset does not contain records relating to sensitive species (e.g. Ostrea edulis) in specific areas, or where data are restricted from public release by the owner's use limitations. This version (v2020) was published in July 2021.
-
This dataset containing traits of marine fish is based on fish taxa observed during international scientific bottom-trawl surveys regularly conducted in the Northeast Atlantic, Northwest Atlantic and the Northeast Pacific. These scientific surveys target primarily demersal (bottom-dwelling) fish species, but pelagic species are also regularly recorded. The overarching aim of this dataset was to collect information on ecological traits for as many fish taxa as possible and to find area-specific trait values to account for intraspecific variation in traits, especially for widely distributed species. We collected traits for species, genera and families. The majority of trait values were sourced from FishBase (Froese and Pauly, 2019), and have been supplemented with values from the primary literature.
-
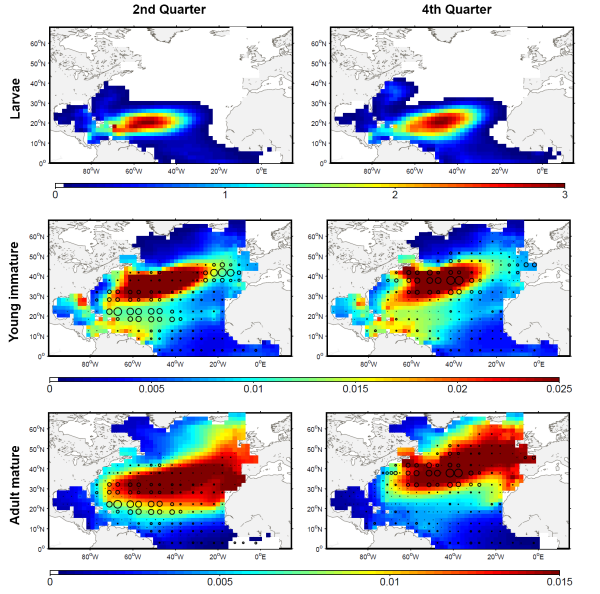
The development of the ecosystem approach and models for the management of ocean marine resources requires easy access to standard validated datasets of historical catch data for the main exploited species. They are used to measure the impact of biomass removal by fisheries and to evaluate the models skills, while the use of standard dataset facilitates models inter-comparison. North Atlantic albacore tuna is exploited all year round by longline and in summer and autumn by surface fisheries and fishery statistics compiled by the International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT). Catch and effort with geographical coordinates at monthly spatial resolution of 1° or 5° squares were extracted for this species with a careful definition of fisheries and data screening. In total, thirteen fisheries were defined for the period 1956-2010, with fishing gears longline, troll, mid-water trawl and bait fishing. However, the spatialized catch effort data available in ICCAT database represent a fraction of the entire total catch. Length frequencies of catch were also extracted according to the definition of fisheries above for the period 1956-2010 with a quarterly temporal resolution and spatial resolutions varying from 1°x 1° to 10°x 20°. The resolution used to measure the fish also varies with size-bins of 1, 2 or 5 cm (Fork Length). The screening of data allowed detecting inconsistencies with a relatively large number of samples larger than 150 cm while all studies on the growth of albacore suggest that fish rarely grow up over 130 cm. Therefore, a threshold value of 130 cm has been arbitrarily fixed and all length frequency data above this value removed from the original data set.
-
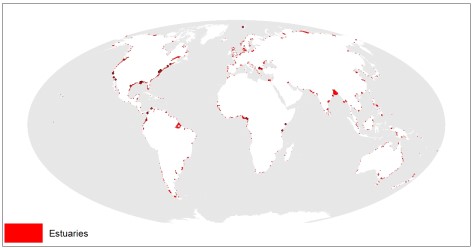
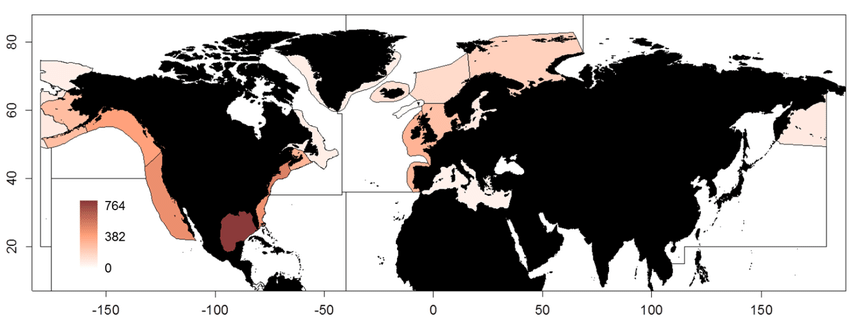
This dataset shows the global distribution of over 1,300 estuaries, including some lagoon systems and fjords. The majority of estuaries are represented by polygons, except for 44 records for which points are available. This dataset was developed by Sea Around Us (www.seaaroundus.org).
-

Portal to view and download observations of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystem (VME) indicators and habitats in the North Atlantic. A central portal for data on the distribution and abundance of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs), (and organisms considered to be indicators of VMEs) across the North Atlantic has been set up by the Joint ICES/NAFO Working Group on Deep-water Ecology (WGDEC). Criteria used to select habitats and indicators for inclusion in the database were those described in the FAO International Guidelines for the Management of Deep-sea Fisheries in the High Seas (FAO, 2009). The database is comprised of: - 'VME habitats' that are records for which there is unequivocal evidence for a VME, e.g. ROV observations of a coral reef - 'VME indicators' which are records that suggest the presence of a VME with varying degrees of uncertainty. For VME indicators a weighting system of vulnerability and uncertainty is provided as part of the database to aid interpretation. The VME database may be used for many purposes. ICES uses it when providing scientifically-robust advice on the distribution of VMEs and recommending possible management solutions such as bottom fishing closures within North East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) waters to protect VMEs.
-
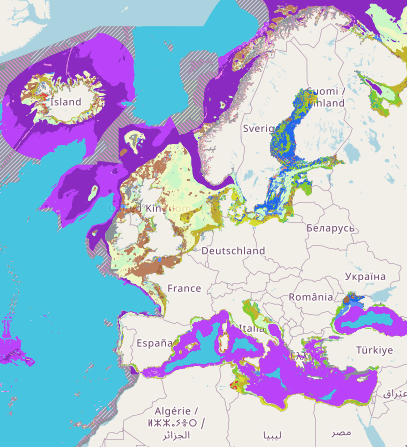
Output of the 2019 EUSeaMap broad-scale predictive model, produced by EMODnet Seabed Habitats and aggregated into the Benthic Broad Habitat Types of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (as defined in the Commission Decision 17 May 2017). The extent of the mapped area includes the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea, and areas of the North Eastern Atlantic extending from the Canary Islands in the south to the Barents Sea in the north. The map was produced using a "top-down" modelling approach using classified habitat descriptors to determine a final output habitat. Habitat descriptors differ per region but include: - Biological zone - Energy class - Oxygen regime - Salinity regime - Seabed substrate - Riverine input Habitat descriptors (excepting Substrate) are calculated using underlying physical data and thresholds derived from statistical analyses or expert judgement on known conditions.
-
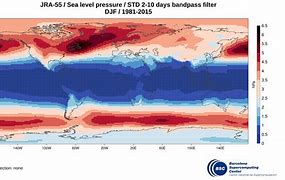
JRA55-do is a surface dataset for driving ocean-sea ice models and used in phase 2 of OMIP (OMIP-2). JRA55-do corrects the atmospheric reanalysis product JRA-55 (Kobayashi et al., 2015) using satellite and other atmospheric reanalysis products. The merits of JRA55-do are the high horizontal resolution (~55 km) and temporal interval (3 h). An assessment by Tsujino et al. (2020) implies that JRA55-do can suitably replace the current CORE/OMIP-1 dataset. This reanalysis of atmospheric variables is provided by the Japanese Meteorological Agency starting in the year 1958 and will be used to drive the coupled NEMO-ERSEM model in the hindcast configuration.
-
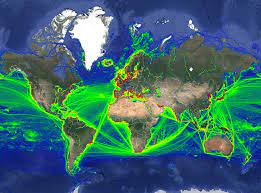
This data was obtained through a partnership with IMF, as part of IMF's World Seaborne Trade Monitoring System (Cerdeiro, Komaromi, Liu and Saeed, 2020). The data analysis was supported by the World Bank’s ESMAP and PROBLUE programs. The dataset contains 6 density layers, with vessel types aggregated to suit the needs of the WBG Offshore Wind Development Program: 1) Commercial ships 2) Fishing ships 3) Oil & Gas [note: this is just platforms, rigs, and FPSOs] 4) Passenger ships 5) Leisure vessels 6) GLOBAL ship density layers of all ship categories combined
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA