Fisheries and aquaculture
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Resolution
-

Survival was recorded at the endpoint for all batches of each group (2n-control, 2n-wild, 2n-commercial, 2nR, 3nR and 3n-commercial). Similarly, initial and final yield were recorded, corresponding to the total weight of the live oysters at deployment and at the endpoint. Finally, shell length and total weight for individually recorded at reception and at the endpoint.
-

Long-term time series of coliform bacteria concentration (fecal coliform or Escherichia coli) in shellfish in four submarine areas (North Sea/Channel, Britany, Atlantic, Mediterranean).
-

Data were collected from the regional program LOUPE (Observation of the habitat and associated communities in the context of the fisheries of the Capbreton Canyon). It consisted in the observations of two métiers practiced around the canyon. The observations were carried out between July 2011 and April 2013 on coastal boats. Observations and interviews were made on board commercial vessels. The longlines used in the hake fishery are semi-pelagic and are deployed on the edge of the Capbreton Canyon. It is an emblematic and major métier benefiting from a particular regulation as they take advantage of a prohibition of net and trawl fishing on their fishing grounds. Between 8 and 14 costal boats practice this métier during the year and the fleet characteristics are homogeneous. Boats lay between 1,200 and 1,800 hooks per day, baited with frozen pilchard (Sardina pilchardus). Two or three men are on board these vessels. Fishing is mostly practiced in spring and summer but a small number of vessels work all year. Generally, trips last between ten and twelve hours; longline is set before sunrise and retrieved three or four hours later. Hake is the main targeted species; other targets are pollack (Pollachius pollachius), red sea bream (Pagellus bogaraveo) and conger (Conger conger). Netting is a major métier in terms of vessels involved and the number of trips. Crew composition varies and depends on boat length (from one to four men on average). This métier is practiced by 30 to 35 boats all year round, but fleet characteristics are less homogeneous than in the case of longliners . The strategy of these netters operating in the coastal area is based on the use of several types of nets (gillnets and trammel nets) targeting several species, often sold directly to consumers on the docks. Gillnets, consisting of a single mesh, target hake, sea bass and sea bream species (Diplodus spp, Sparus aurata, Litognathus mormyrus), while the trammel nets (three meshes) are used to capture benthic fish, such as common sole, monkfish (Lophius spp), turbot and brill (Scophthalmus rhombus). Generally, trips last less than twelve hours for coastal netters (less than 15 m), which predominate in the sector, and a few days for large netters. On average, the coastal vessels set 6000 to 8000 m. nets daily.
-
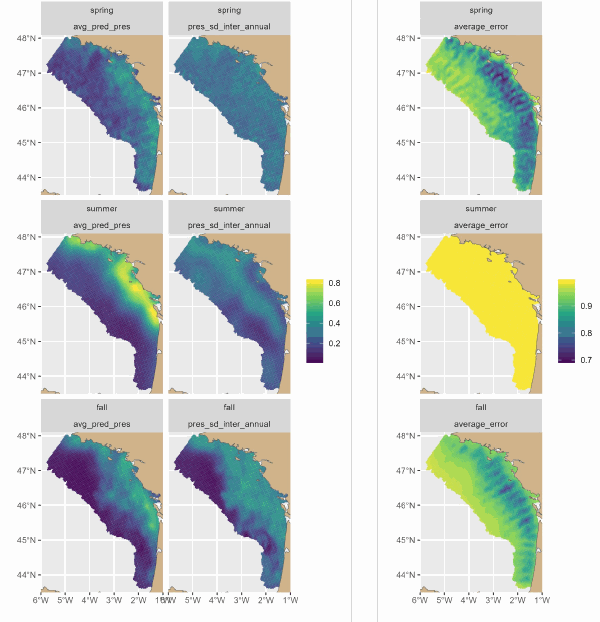
The Delmoges project aims to generate new ecological and fisheries knowledge to reduce dolphin bycatch in the Bay of Biscay (GoG). This dataset presents maps produced by a hierarchical model of the seasonal and interannual distribution of dolphins' main prey, small pelagic fish. The model integrates 3 types of data: presence-absence and biomass of fish from scientific campaigns and presence of fish from fishing data. For the first time, the model has provided a quantitative description of the seasonal spatial dynamics of sardines and associated fisheries. The main sardine distribution areas were coastal, from the mouth of the Gironde to south-west Brittany. On average, sardines were distributed over a wider area in small aggregations in spring. They seemed to concentrate in their main distribution areas in summer, and to disperse offshore in autumn, but to a lesser extent than in spring. Fishing was concentrated in the sardine's main coastal distribution areas, and was more intense in summer, then autumn, and less intense in spring.
-

The data come from organisms and pictures collected during the MEDITS annual bottom trawl surveys conducted between 2011 and 2013 (Bertrand et al. 2002). MEDITS surveys cover the continental shelf (10 m to 200 m depth) and the upper part of the continental slope (200 m to 800 m) on the Mediterranean. A total of 1511 individuals from 85 fish species were collected from seven Mediterranean areas (South Adriatic Sea, Sardinia, Gulf of Lions, around Cyprus, Mallorca, Tyrrhenian Sea, and North West Ionian Sea). A set of 14 morphological traits related to the habitat and the diet of the species were measured in the field and on pictures using the ImageJ software (version 1.47, http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/) (see Granger et al. 2015 and Brind'Amour et al. submitted for details) (Figure 1). Replicats of measures vary between 1 (e.g. Scorpaena loppei) to 53 (e.g. Serranus hepatus) according to fish species. Twelve of the chosen traits consist in continuous biological characteristics measured on each individual (measured in cm). The two remaining traits are categorical and determined at the species level.
-

The Mytilobs network, carried out by IFREMER (French Research Institute for Exploitation of the Sea), is a national network dedicated to building long-term physiological variations time series of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis), across a large spatial scale. This observation network, initially designed to survey production yields, also provides valuable data to track environmental variations of coastal ecosystems. Mussels exhibit high phenotypic plasticity in response to environmental variations. Collection of data describing phenotypic variations, over an extended period, reveals small-scale climate and habitat variations. With its broad deployment across time and space, the data produced under Mytilobs will be useful for the establishment of a baseline condition when studying the effect of a perturbation affecting an ecosystem’s functioning. Finally, the monitoring of mussel biometric traits and mortality was coupled with high-frequency measurements of salinity, temperature, and sea level, complementing this multi-layer observational framework.
-
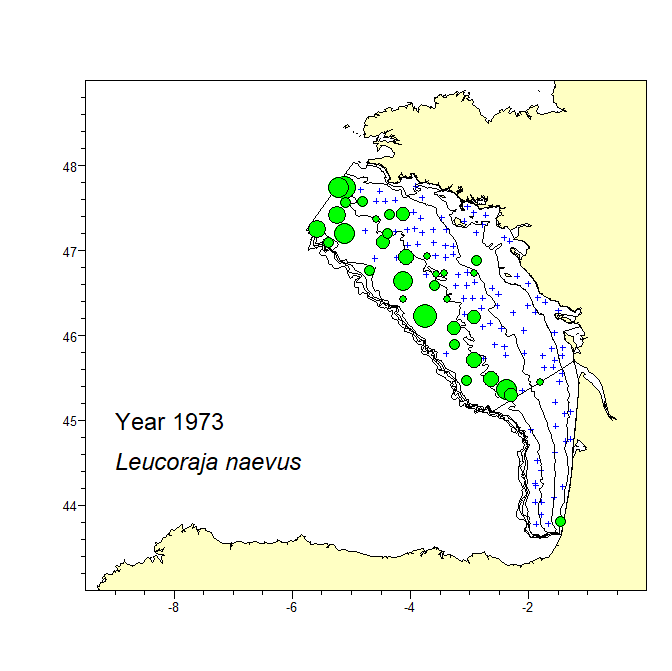
A consistent dataset of bottom trawl survey data spanning 47 years in the Bay of Biscay was assembled. The dataset includes data from the current EVHOE survey from 1987 to 2019 and two previous surveys carried out in 1973 and 1976. The recent EVHOE time-series from 1997 is also available from DATRAS (https://www.ices.dk/data/data-portals/Pages/DATRAS.aspx). The catch in numbers and weight (kg) per haul of all Rajiformes species caught in these surveys is provided. Haul information is provided for all hauls, including those with no catch of Rajiformes. Areas of the sampling strata of the survey and spatial polygones of these strata are provided in separate files.
-
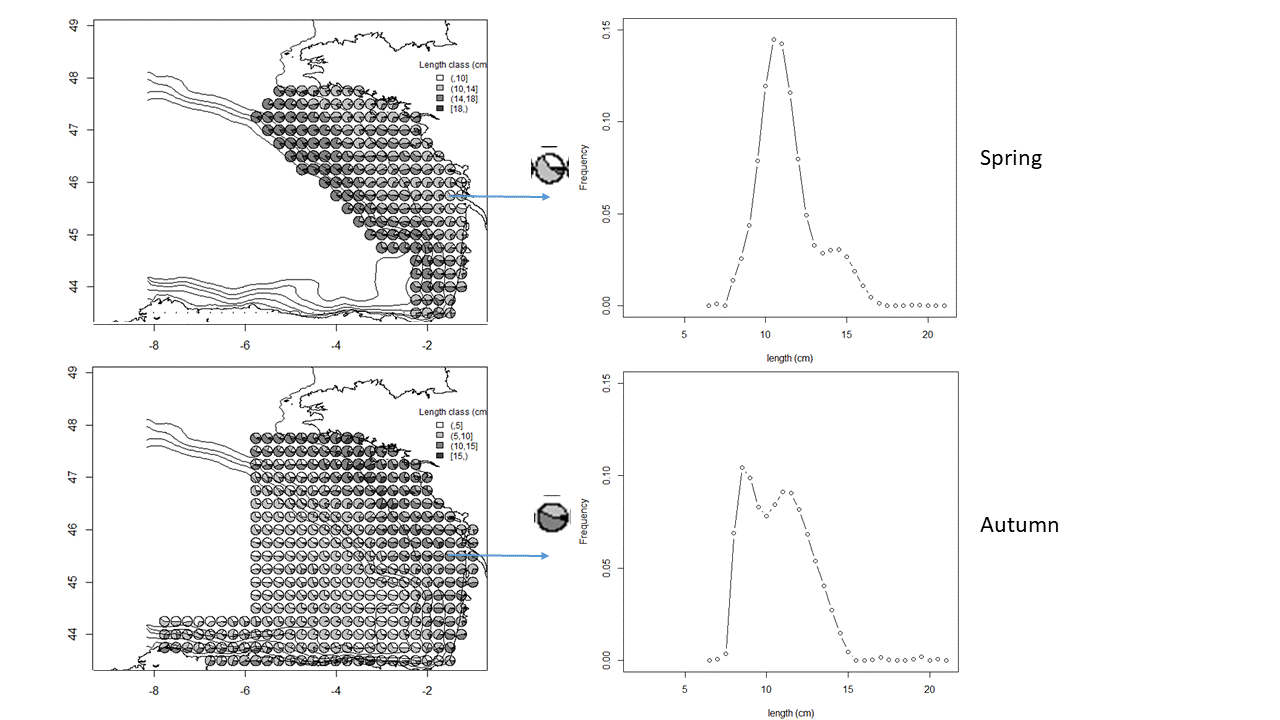
The anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) and sardine (Sardina pilchardus) populations in the Bay of Biscay are jointly surveyed each year in May since 2000 and in September since 2003 by means of acoustic surveys. The integrated survey PELGAS (Doray et al., 2018) is run in May by France and covers the French shelf of the Bay of Biscay. Its objectives are to monitor the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime and assess the biomass of its small pelagic fish species, including sardine and anchovy. Amongst many information on the ecosystem, the survey PELGAS provides knowledge on the adults of anchovy and sardine during their spawning in spring. The survey JUVENA (Boyra et al., 2013) is run in September by Spain. It has a larger spatial coverage than PELGAS, including part of the Spanish coast and open ocean outside the shelf because it targets juvenile anchovy. It also provides knowledge on sardine as well as other pelagic species. Both surveys are coordinated by the ICES Working Group on Acoustic and Egg Surveys for Small Pelagic Fish (WGACEGG), together with other pelagic surveys in ICES areas 7, 8 and 9. Survey protocoles are detailed in Doray et al. (2021). Briefly, fish backscatter data are recorded along the survey transect lines and pelagic trawl hauls are undertaken opportunistically to identify the echotraces to species and collect fish samples for biometric data. The trawl haul catches have provided the anchovy and sardine length data, from which the maps presented here are derived. At each trawl haul, the catch is sorted by species and weighted. A subsample by species is measured to estimate the species’ length distribution. The four maps presented here correspond to the average maps of anchovy and sardine length distributions in May and September, derived from the PELGAS and JUVENA trawl haul data series. The maps were obtained by kriging, following the procedure explained in Petitgas et al. (2011) for mapping functions instead of variables. For each species, the experimental length distribution at each haul was fitted by a linear combination of Legendre polynomials, the coefficients of which were co-kriged. The number of polynomials varied from 15 to 22 depending on the survey and species, with a higher number for sardine and in autumn. The length histogram at each grid node was then deduced from the mapped coefficients. When the length distribution at a given haul was estimated with less than 40 individual fish, the haul was not taken into account for mapping. This threshold defined presence and absence of the species in the haul data sets. The trawl hauls from 2000 to 2019 were pooled for the PELGAS series (1965 stations) and from 2003 to 2020 for JUVENA (852 stations). The mapping was performed on the same grid for both PELGAS and JUVENA and both species, and with similar moving kriging neighbourhoods. The grid has a mesh size of 0.25 x 0.25 decimal degree square. In addition to mapping the length distribution, presence/absence was mapped for each species by ordinary kriging on the same grid and with the same neighbourhoods as previously. The computations were performed in R (version 4.0.5) with the RGeostats package (version 13.0.1) freely available at http://rgeostats.free.fr. The map data files comprise for each species the following information: the geographical coordinates of the grid points, the probability of presence and the probability of each length class of width 0.5 cm ranging from 2.5 to 27 cm.
-

REPHYTOX dataset includes long-term time series on phycotoxins in marine bivalve molluscs, since 1987, along the whole French coast. The dataset covers results on lipophilic toxins, PSP toxins, ASP toxins, and palytoxins. REPHYTOX was a full part of the REPHY network until 2015. The whole dataset is available.
-

Ifremer conducts numerous fisheries surveys dedicated to benthic and demersal populations (commercial / non-commercial fishes and invertebrates). For several years, in application of the ecosystem approach, all benthic invertebrate fauna collected in fishing gear has been systematically monitored: megabenthic invertebrates captured have been sorted, identified, counted and weighted. All these surveys are based on fixed or random stratified sampling strategy with varying intensity depending on the covered survey area. These data are stored, in historical access-based databases or for the most recent years in the centralised “Harmonie” database held in the Ifremer Fishery Information Systeme (SIH). The species nomenclature used was standardized using WoRMS database. Taxa caught at least once a year are listed for each monitoring area on the basis of already available data series. In order to facilitate the identification of individuals sampled on board vessels and to improve the training of onboard scientists, the present work aims to define the minimum level of identification for each of them. The analysis identifies taxa that appears recurrently on available historical series or gathers them on less precise taxonomic levels if this is not the case, which may indicate potential identification difficulties. The following procedure was used: all taxa expressed at the species level were first aggregated at genus level if they occurred less 90% of the years over the available time series. For MEDITS, EPIBENGOL and ORHAGO, the occurrence threshold was set to 70% and to only 50% for NOURMONT because the datasets were less than 10 years long. Then to be kept at that taxonomic level, a given genus had to be observed over 90% of the time (for example over at least 9 years if the dataset contains 10 years). Otherwise it was iteratively regrouped into a higher taxonomic level (family, order, class, division) following the same criteria (Foveau et al, 2017). For instance, for the NOURSEINE survey, this resulted into the aggregation of the 103 origin taxa into 35 taxonomic groups. The name of the final taxon after data processing represents the minimum level of identification defined by the analysis. However, these results are very theoretical. This is why they were sent to scientists who embark regularly in order to refine the level of taxonomic identification with field experience. The first dataset is composed of 8 tables relevant to the different vessel surveys. The first column of each table represents the permanent code of the taxon in the Ifremer taxonomic referential, the second the systematic number and the third the species abbreviated code. The other columns are the different taxonomic levels of the taxon. The minimum level of identification at sea defined by the data processing appears in blue. The level determined by feedback of scientist’s field experience, which is the one to use at sea, appears in green. The second dataset summaries the results detailed in the first table and indicates directly for each taxon identified to far, the minimum level of identification required for the benthic invertebrates by-catch of each fisheries surveys studied.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA