Historical
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Resolution
-
This L3U (Level 3 Uncollated) dataset contains global daily Sea Surface Temperature (SST) on a 0.02 degree grid resolution. It is produced by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Advanced Clear Sky Processor for Ocean (ACSPO) using L2P (Level 2 Preprocessed) product acquired from the Meteorological Operational satellite A (Metop-A) Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer 3 (AVHRR/3) (https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/AVHRRF_MA-STAR-L2P-v2.80 ) in Full Resolution Area Coverage (FRAC) mode as input. It is distributed as 10-minute granules in netCDF-4 format, compliant with the Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) Data Specification version 2 (GDS2). There are 144 granules per 24-hour interval. Fill values are reported in all invalid pixels, including land pixels with >5 km inland. For each valid water pixel (defined as ocean, sea, lake or river), and up to 5 km inland, the following major layers are reported: SSTs and ACSPO clear-sky mask (ACSM; provided in each grid as part of l2p_flags, which also includes day/night, land, ice, twilight, and glint flags). Only input L2P SSTs with QL=5 were gridded, so all valid SSTs are recommended for the users. Per GDS2 specifications, two additional Sensor-Specific Error Statistics layers (SSES bias and standard deviation) are reported in each pixel with valid SST. Ancillary layers include wind speed and ACSPO minus reference Canadian Meteorological Centre (CMC) Level 4 (L4) SST. The ACSPO Metop-A AVHRR FRAC L3U product is monitored and validated against iQuam in situ data https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/iquam , in the NOAA SST Quality Monitor (SQUAM) system https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/squam . SST imagery and clear-sky mask are evaluated, and checked for consistency with L2P and other satellites/sensors SST products, in the NOAA ACSPO Regional Monitor for SST (ARMS) system https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/arms . More information about the dataset is found at AVHRRF_MA-STAR-L2P-v2.80 and in (Pryamitsyn et al., 2021).
-
The MetOp First Generation (FG) is a European multi-satellite program jointly established by ESA and EUMETSAT, comprising three satellites, MetOp -A, -B and -C. The primary sensor onboard MetOp-FG, the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer/3 (AVHRR/3) contributed by NOAA, measures Earth emissions and reflectances in 5 out of 6 available bands (centered at 0.63, 0.83, 1.61, 3.7, 11 and 12 microns), in a swath of 2,600km from an 817km altitude. These data are collected in a Full Resolution Area Coverage (FRAC) mode, with pixel size of 1.1km at nadir. MetOp-A launched on 19 October 2006 is the first in the MetOp-FG series. The NOAA Advanced Clear-Sky Processor for Ocean (ACSPO) Level 2 Preprocessed (L2P) SST product is derived at the full AVHRR FRAC resolution and reported in 10 minute granules in NetCDF4 format, compliant with the GHRSST Data Specification version 2 (GDS2). Subskin SSTs are derived using the regression Nonlinear SST (NLSST) algorithm, which employs three bands (3.7, 11 and 12 microns) at night and two bands (11 and 12 microns) during the day. The ACSPO AVHRR FRAC L2P product is monitored and validated against quality controlled in situ data, provided by the NOAA in situ SST Quality Monitor system (iQuam) https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/iquam , in another NOAA system, SST Quality Monitor (SQUAM) https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/squam . SST imagery and clear-sky masking are continuously evaluated, and checked for consistency with other sensors and platforms, in the NOAA ACSPO Regional Monitor for SST (ARMS) system https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/arms . MetOp-A orbital characteristics and AVHRR/3 sensor performance are tracked in the NOAA 3S system ( https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/socd/sst/3s ).The L2P Near Real Time (NRT) SST files are archived at PO.DAAC with 3-6 hours latency, and then replaced by the Re-ANalysis (RAN) SST after about 2 months later with identical file names. Two features can be used to identify them: different file name time stamps and netCDF global attribute metadata source=NOAA-NCEP-GFS for NRT and source=MERRA-2 for RAN. A reduced size (0.45GB/day), equal-angle gridded (0.02-deg resolution) ACSPO L3U product is available at https://doi.org/10.5067/GHMTA-3US28
-
These products contain global non time critical (NTC) reprocessed (REP) Level 2P skin Sea Surface Temperature (SST) derived from SLSTR-A on Copernicus Sentinel-3 at full-resolution swath (1 km at nadir) in GHRSST compliant NetCDF format. All SSTs from the Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR) series of instruments are SST skin measurements. For more details please see “What is SST?” on the GHRSST web pages. At night, the skin temperature is typically a few tenths of a degree cooler than the temperature measured by in situ systems; in the day, the skin can be considerably higher if strong diurnal warming is present. The SLSTRs are dual-view self-calibrating radiometers with SST retrieved from spectral bands at nominally 3.74, 10.85 and 12 µm (referred to as S7, S8 & S9). Corrections for water vapour atmospheric absorption are performed using a triple window at night, and a split window during the day as the 3.7 µm channel is not used due to solar contamination. All pixels in the dual-view part of the swath are viewed twice, via nadir and oblique views with different atmospheric path lengths, allowing for correction for aerosol effects. Consequently, there are four possible retrieved SSTs, referred to as N2 (nadir-only 11 µm and 12 µm), N3 (nadir-only 3.7 µm, 11 µm and 12 µm), D2 (dual-view 11 µm and 12 µm) and D3 (dual-view 3.7 µm, 11 µm and 12 µm). The L2P file contains the best SST available for each pixel and flags are included to identify which retrieval is used. If the observation is in the nadir-only / single-view part of swath then "sst_algorithm_types" is N2 or N3, and if the observation is in the dual-view part of swath then "sst_algorithm_types" is D2 or D3. For D2 or D3 pixels it is possible to generate their N2 or N3 equivalent by subtracting the value in the "dual_nadir_sst_difference" field. Users are advised to use only QL = 5 dual-view SSTs for reference sensor applications and to use single-view (all quality levels) and quality level 3 and 4 dual-view data only for other qualitative analysis. Users are reminded to apply the SSES bias adjustments as SLSTR-B is harmonised to SLSTR-A through SSES. Users can consider using the "theoretical_uncertainty" for weighting observations rather than the simple SSES standard deviation values. Primary access to data is via the EUMETSAT Data Store (linked below). Other access methods can be found in the EUMETSAT Product Navigator https://navigator.eumetsat.int/product/EO:EUM:DAT:0582?query=slstr&results=22&s=advanced. Please also read the EUMETSAT SLSTR Product Notices (linked below) as they provide a lot of useful information. All products currently contain SLSTRA-MAR-L2P-v1.0 as the GHRSST Collection ID in the file metadata, which will be revised in a future release.
-
4-Dimensional Daily Temperature and Marine Heatwaves Categories from ESA/CAREHeat project, version 2

The 4D Marine Heatwaves (MHW) atlas contains 4D (x, y, z, t) **daily temperature and marine heatwaves categories** for global region [82.875°S-89.875°N, 0.125°E-359.875°E], from 0 to 300m depth and a spatial resolution of 1/8°. It covers the period 1993-2022. The MHW atlas has been computed from the temperature 4D fields of the ARMOR3D global product delivered in the Copernicus Marine Service (MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_TSUV_3D_MYNRT_015_012 - https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00052 ). The MHW categories are derived from the Hobday’s method [Hobday et al.,2018]. Each MHW event is classified among four categories (moderate to extreme), identified in terms of multiples of the local difference between the 90th percentile and climatological values, and defined as moderate (1-2×, Category I), strong (2-3×, Category II), severe (3-4×, Category III), and extreme (>4×, Category IV). When the category is zero, this means that there is no MHW. The period 1993-2021 is used as a baseline for defining the climatology to be as close as possible to the 30-year period suggested by Hobday. This choice is motivated by the need of altimetry data to constrain the vertical temperature reconstruction, which is required for most ocean reanalyses as well. Additionally, ancillary data are provided together with the data. It consists of 4D daily **temperature climatology** and **90 percentiles of the temperature**. These fields have been used to compute the MHW categories. They are delivered over the same domain as the MHW atlas. ARMOR3D **temperature uncertainties** are also supplied as they can help users to select only the most reliable events in the database. This dataset was generated by CLS (Collecte Localisation satellite) and is distributed by Ifremer /CERSAT in the frame of the CAREHeat project (CAREHeat Website) funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).
-
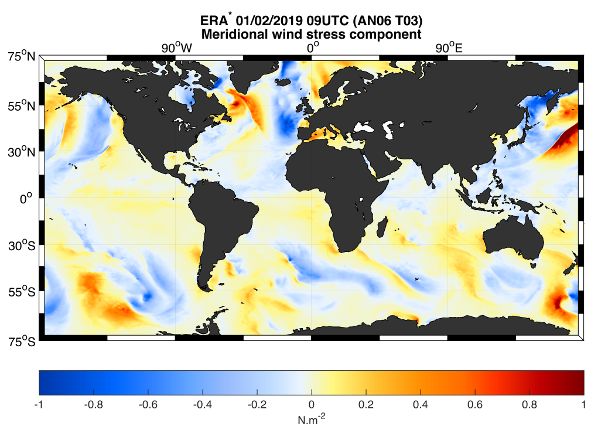
This dataset provides the meridional and zonal components of both the stress-equivalent wind (U10S) and wind stress (Tau) vectors. The ERA* product is a correction of the ECMWF Fifth Reanalysis (ERA5) output by means of geo-located scatterometer-ERA5 differences over a 15-day temporal window. The product also contains ERA5 U10S and Tau. The data are available through HTTP and FTP; access to the data is free and open. In order to be informed about changes and to help us keep track of data usage, we encourage users to register at: https://forms.ifremer.fr/lops-siam/access-to-esa-world-ocean-circulation-project-data/ This dataset was generated by ICM (Institute of Marine Sciences) / CSIC (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas) and is distributed by Ifremer / CERSAT in the frame of the World Ocean Circulation (WOC) project funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).
-
Satellite altimeters routinely supply sea surface height (SSH) measurements which are key observations to monitor ocean dynamics. However, below a wavelength of about 70 km, along-track altimeter measurements are often characterized by a dramatic drop in the signal-to-noise ratio, making it very challenging to fully exploit available altimeter observations to precisely analyze small mesoscale variations in SSH. Although various approaches have been proposed and applied to identify and filter noise from measurements, no distinctive methodology emerged to be systematically applied in operational products. To best cope with this unresolved issue, the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) actually provides simple band-pass filtered data to mitigate noise contamination in the along-track SSH signals and more innovative and adapted noise filtering methods are thus left to users seeking to unveil small-scale altimeter signals. Here demonstrated, a fully data-driven approach is developed and applied to provide robust estimates of noise-free Sea Level Anomaly (SLA) signals. The method combines Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD), to help analyze non-stationary and non-linear processes, and an adaptive noise filtering technique inspired by Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) decompositions. It is now found to best resolve the distribution of the sea surface height variability in the mesoscale 30-120 km wavelength band. A practical uncertainty variable is attached to the denoised SLA estimates that accounts for errors related to the local signal to noise ratio, but also for uncertainties in the denoising process, which assumes that SLA variability results in part from a stochastic process. Here, measurements from the Jason-3, Sentinel-3 A and SARAL/AltiKa altimeters are processed and analyzed, and their energy spectral and seasonal distributions characterized in the small mesoscale domain. Anticipating data from the upcoming Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission, these denoised SLA measurements for three reference altimeter missions already yield valuable opportunities to assess global small mesoscale kinetic energy distributions. This dataset was developed within the Ocean Surface Topography Science Team (OSTST) activities. A grant was awarded to the SASSA (Satellite Altimeter Short-scale Signals Analysis) project by the TOSCA board in the framework of the CNES/EUMETSAT call CNES-DSP/OT 12-2118. Altimeter data were provided by the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) and by the Sea State Climate Change Initiative (CCI) project.
-
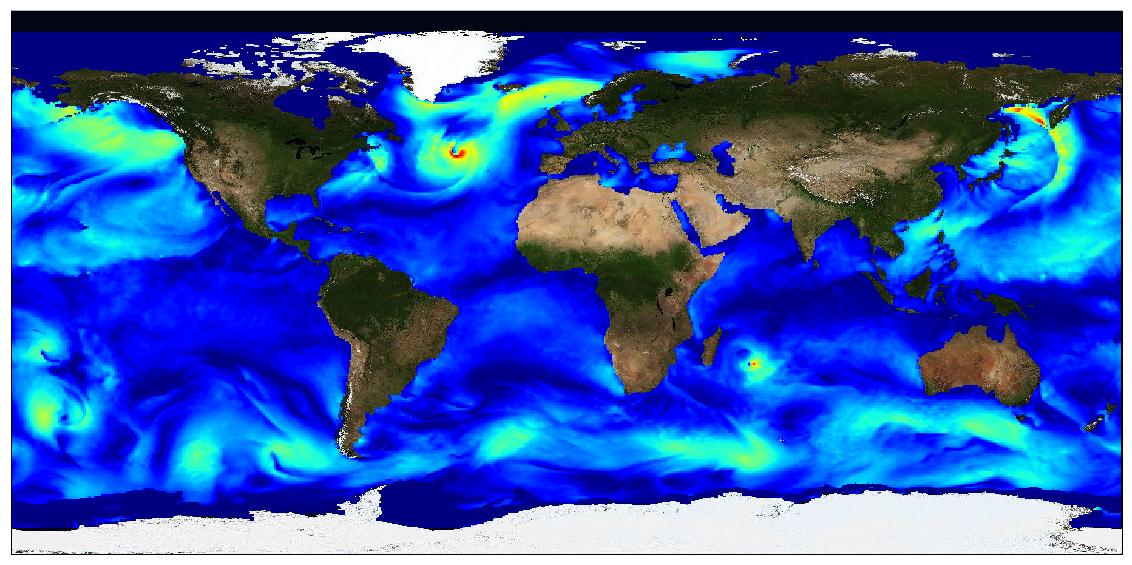
This dataset provides surface Stokes drift as retrieved from the wave energy spectrum computed by the spectral wave model WAVEWATCH-III (r), under NOAA license, discretized in wave numbers and directions and the water depth at each location. It is estimated at the sea surface and expressed in m.s-1. WAVEWATCH-III (r) model solves the random phase spectral action density balance equation for wavenumber-direction spectra. Please refer to the WAVEWATCH-III User Manual for fully detailed description of the wave model equations and numerical approaches. The data are available through HTTP and FTP; access to the data is free and open. In order to be informed about changes and to help us keep track of data usage, we encourage users to register at: https://forms.ifremer.fr/lops-siam/access-to-esa-world-ocean-circulation-project-data/ This dataset was generated by Ifremer / LOPS and is distributed by Ifremer / CERSAT in the frame of the World Ocean Circulation (WOC) project funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).
-
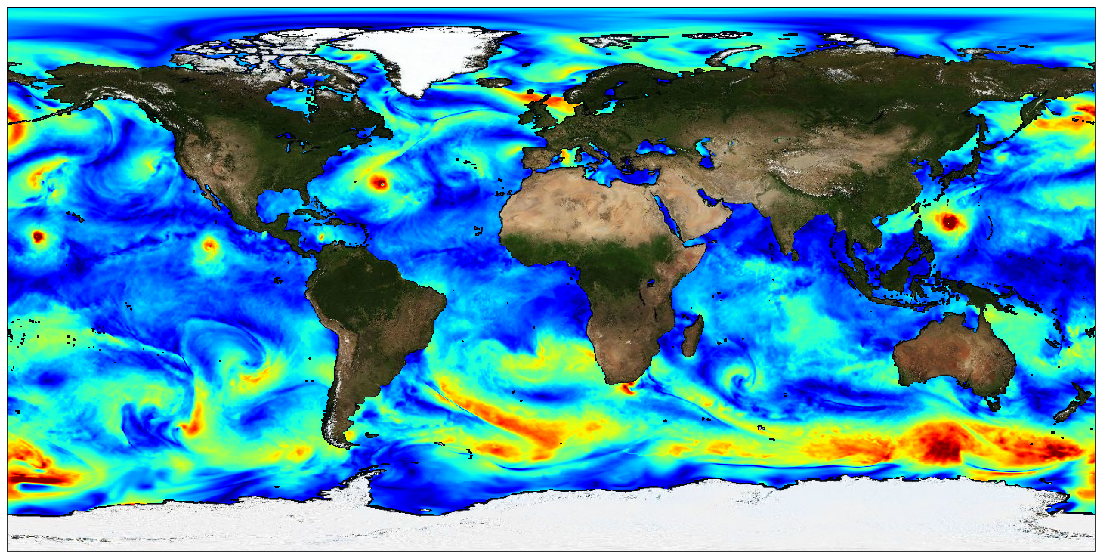
The Level 4 merged microwave wind product is a complete set of hourly global 10-m wind maps on a 0.25x0.25 degree latitude-longitude grid, spanning 1 Jan 2010 through the end of 2020. The product combines background neutral equivalent wind fields from ERA5, daily surface current fields from CMEMS, and stress equivalent winds obtained from several microwave passive and active sensors to produce hourly surface current relative stress equivalent wind analyses. The satellite winds include those from recently launched L-band passive sensors capable of measuring extreme winds in tropical cyclones, with little or no degradation from precipitation. All satellite winds used in the analyses have been recalibrated using a large set of collocated satellite-SFMR wind data in storm-centric coordinates. To maximize the use of the satellite microwave data, winds within a 24-hour window centered on the analysis time have been incorporated into each analysis. To accomodate the large time window, satellite wind speeds are transformed into deviations from ERA5 background wind speeds interpolated to the measurement times, and then an optical flow-based morphing technique is applied to these wind speed increments to propagate them from measurement to analysis time. These morphed wind speed increments are then added to the background wind speed at the analysis time to yield a set of total wind speeds fields for each sensor at the analysis time. These individual sensor wind speed fields are then combined with the background 10-m wind direction to yield vorticity and divergence fields for the individual sensor winds. From these, merged vorticity and divergence fields are computed as a weighted average of the individual vorticity and divergence fields. The final vector wind field is then obtained directly from these merged vorticity and divergence fields. Note that one consequence of producing the analyses in terms of vorticity and divergence is that there are no discontinuities in the wind speed fields at the (morphed) swath edges. There are two important points to be noted: the background ERA5 wind speed fields have been rescaled to be globally consistent with the recalibrated AMSR2 wind speeds. This rescaling involves a large increase in the ERA5 background winds beyond about 17 m/s. For example, an ERA5 10 m wind speed of 30 m/s is transformed into a wind speed of 41 m/s, and a wind speed of 34 m/s is transformed into a wind speed of about 48 m/s. Besides the current version of the product is calibrated for use within tropical cyclones and is not appropriate for use elsewhere. This dataset was produced in the frame of ESA MAXSS project. The primary objective of the ESA Marine Atmosphere eXtreme Satellite Synergy (MAXSS) project is to provide guidance and innovative methodologies to maximize the synergetic use of available Earth Observation data (satellite, in situ) to improve understanding about the multi-scale dynamical characteristics of extreme air-sea interaction.
-

In 1967, E.Postel, researcher at the OSTPM (Scientific and Technical Office for Maritime Fisheries) set up a data collection system on albacore catches by French fleets. JC Dao and FX Bard continued this work within CNEXO (National Center for the Exploitation of Oceans) and then at IFREMER from 1984. This information was transmitted by fishing professionals via logbooks, on the basis of volunteering (Dao, 1971, Bard, 1977). In 1982, the European Community put in place a mandatory system of declarations of fishing effort and catches via logbooks (EC Regulation No. 2057 in Sanchez and Santurtun, 2013). As a result, the two systems persisted between 1982 and 1986, with European logbooks gradually supplanting logbooks
-

The CDR-derived Wet Tropospheric Correction (WTC) Product V2 is generated from the Level-2+ along-track altimetry products version 2024 (L2P 2024) distributed by AVISO+ (www.aviso.altimetry.fr). It provides a long-term, homogenized estimation of the wet tropospheric correction based on Climate Data Records (CDRs) of atmospheric water vapour combined with high frequencies MWR data. Two independent CDRs datasets are used: - REMSS V7R2 (coverage until 2022) https://www.remss.com/measurements/atmospheric-water-vapor/tpw-1-deg-product/ - HOAPS V5 precursor CDR from EUMETSAT CM SAF (coverage until 2020) HOAPS V4/V5 data available via https://wui.cmsaf.eu Note: the HOAPS V5 precursor is not yet an official CM SAF product; full validation and public release are pending. The MWR/CDR WTC V2 estimates is derived using spatially varying but temporally constant polynomial coefficients (ai). 1. WTC V2 – Along-track L2P Product Data format: The WTC V2 product is delivered in Level-2+ (L2P) format, along the satellite ground track. Each mission is distributed as a compressed archive (.tar.gz) containing one NetCDF4 CF-1.8 file per mission cycle. Archive naming convention: <mission>_WTC_from_WV_CDR_<version>.tar.gz mission: TP (TOPEX/Poseidon), J1, J2, J3 version: product version (currently V2) File naming convention inside archives: <mission>_C<cycle>.nc cycle: 4-digit cycle index (e.g., C0001) Each NetCDF file contains: 1/ Along-track WTC estimate; 2/ Ancillary information; 3/ Space–time coordinates 2. WTC CDR Uncertainties – Gridded Product: A complementary product is provided, delivering regional trend estimates and associated uncertainties from the WTC Climate Data Record. The uncertainty product is distributed as a single NetCDF4 file: wtc_trend_uncertainties.nc . This file contains global gridded fields of WTC CDR trend and uncertainty parameters. Product content: This is the first dedicated version providing both: WTC CDR (HOAPS) linear trends, and Uncertainty estimates on these trends. Uncertainties are expressed as 1-sigma confidence intervals, and propagated using the methodology described in Section 2.3 of the Product User Manual. The product includes: - Total uncertainty on the WTC trend, propagated from all identified uncertainty sources in the WTC–TCWV regression. - Individual contributions of uncertainty sources (Uncertainties on regression coefficients: a0, a1 and their standard deviations; Uncertainties inherited from the HOAPS TCWV CDR) These fields enable users to assess the relative importance of each uncertainty component and recompute uncertainty propagation with alternative methods. Included regression input variables: To ensure transparency and reproducibility, the product provides: 1/ regression coefficients a0, a1; 2/ their associated uncertainties (std of a0, std of a1); 3/additional diagnostic fields required to recompute uncertainties if needed.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA