Kattegat
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

The raster dataset represents the intensity of species disturbance due to human presence along European coastlines. The dataset was created by combining the coastal urbanisation layer derived from Corine Land Cover 2012 (with the percentage of urbanised coastline per EEA 10 km grid cell) and the population density layer based on EUROSTAT NUTS 2016 data (with the population density in the NUTS 3 region corresponding to the coastal EEA 10 km grid cell). The dataset does not cover southern and western Mediterranean Sea, northern Black Sea and northernmost Atlantic Ocean. The dataset was prepared for the combined effect index produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-
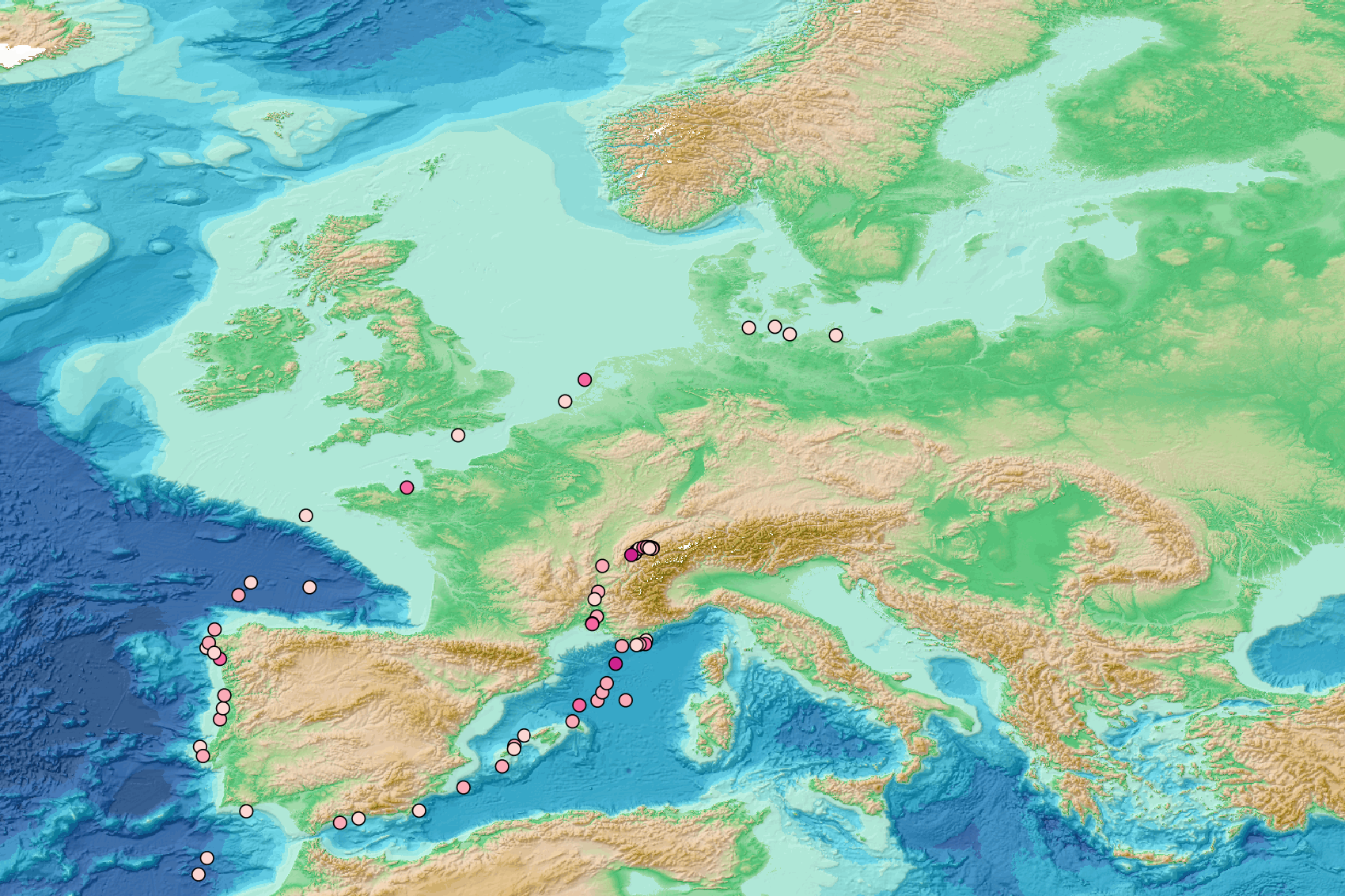
This visualization product displays the density of floating micro-litter per net normalized per km² per year from specific protocols different from research and monitoring protocols. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Before 2021, there was no coordinated effort at the regional or European scale for micro-litter. Given this situation, EMODnet Chemistry proposed to adopt the data gathering and data management approach as generally applied for marine data, i.e., populating metadata and data in the CDI Data Discovery and Access service using dedicated SeaDataNet data transport formats. EMODnet Chemistry is currently the official EU collector of micro-litter data from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) National Monitoring activities (descriptor 10). A series of specific standard vocabularies or standard terms related to micro-litter have been added to SeaDataNet NVS (NERC Vocabulary Server) Common Vocabularies to describe the micro-litter. European micro-litter data are collected by the National Oceanographic Data Centres (NODCs). Micro-litter map products are generated from NODCs data after a test of the aggregated collection including data and data format checks and data harmonization. A filter is applied to represent only micro-litter sampled according to a very specific protocol such as the Volvo Ocean Race (VOR) or Oceaneye. Densities were calculated for each net using the following calculation: Density (number of particles per km²) = Micro-litter count / (Sampling effort (km) * Net opening (cm) * 0.00001) When the number of microlitters or the net opening was not filled, the density could not be calculated. Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account data for all years. Warning: the absence of data on the map doesn't necessarily mean that they don't exist, but that no information has been entered in the National Oceanographic Data Centre (NODC) for this area.
-

This data set presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD), providing a mapping of contamination 'problem areas' and 'non-problem areas' based on measurements of biological effects. This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the of contaminant status of indicators of biological effects. The status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. Monitoring biological effects is restricted to a few indicators (e.g. imposex) and data coverage is currently limited. Biological effects have thus been addressed in only 134 assessment units, mostly in the Baltic Sea, the North Sea and the North-East Atlantic Ocean. This data set underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the EEA report “Contaminants in Europe’s seas” (No 25/2018). See the mentioned report for further information.
-

This raster dataset represents the Sea Surface Temperature (SST) anomalies, i.e. changes of sea temperatures, in the European Seas. The dataset is based on the map "Mean annual sea surface temperature trend in European seas" by Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), which depicts the linear trend in sea surface temperature (in °C/yr) for the European seas over the past 25 years (1989-2013). Since all changes of sea temperatures can be considered to have an impact on the marine environment, the pressure layer includes absolute values of SST anomalies, i.e. negative/decreasing temperature trends were changed to positive values so that they represent a pressure. The original data was in a 1° grid format but was converted to a 100 km resolution, adapted to the EEA 10 km grid and clipped with the area of interest. This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

The raster dataset represents bycatch fishing intensity (kilowatt per fishing hour) from bottom touching mobile gears in the European seas. The dataset has been derived from Automatic Identification System (AIS) based demersal fishing intensity data received from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre - Independent experts of the Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (JRC STECF) as well as Vessel Monitoring System (VMS) and logbook based demersal fishing intensity data downloaded from from OSPAR and HELCOM Commissions. The temporal extent varies between the data sources (between 2014 and 2017). OSPAR and HELCOM data superseded the JRC STECF data where they overlapped spatially. The cell values have been transformed into a logarithmic scale (ln1). This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

The raster dataset represents fishing intensity (kilowatt per fishing hour) by pelagic towed gears in the European seas. The dataset has been derived from Automatic Identification System (AIS) based pelagic fishing intensity data received from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre - Independent experts of the Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (JRC STECF), as well as from Vessel Monitoring System (VMS) and logbook based pelagic fishing effort data from HELCOM Commission. The temporal extent varies between the data sources (between 2013 and 2015). The dataset has been transformed to a logarithmic scale (ln1). This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

This metadata describes the ICES data on the temporal development of the Lusitanian/Boreal species ratio in the period from 19657 to 2016. Key message: The ratio between the number of Lusitanian (warm-favouring) and Boreal (cool-favouring) species are significantly increasing in several North-East Atlantic marine areas whereas there is no significant changes in all the southern areas. Changes in ratios are most apparent in the North Sea, Irish Sea and West of Scotland. Furthermore, it seems that Lusitanian species have not spread in all northward directions, but have followed two particular routes, through the English Channel and north around Scotland Blue dots indicates L/B ratios below 1 (dominance of Boreal species) Yellow dots indicates L/B ratios >=1 and <2 (dominance of Lusitanian species) Red dots indicates L/B ratios >=2 (high dominance of Lusitanian species) The dataset is derived from the ICES data portal 'DATRAS' (the Database of Trawl Surveys). DATRAS is an online database of trawl surveys with access to standard data products. DATRAS stores data collected primarily from bottom trawl fish surveys coordinated by ICES expert groups. The survey data are covering the Baltic Sea, Skagerrak, Kattegat, North Sea, English Channel, Celtic Sea, Irish Sea, Bay of Biscay and the eastern Atlantic from the Shetlands to Gibraltar. At present, there are more than 56 years of continuous time series data in DATRAS, and survey data are continuously updated by national institutions. The dataset has been used in the EEA Indicator "Changes in fish distribution in European seas" https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/fish-distribution-shifts/assessment-1. The dataset has been used for this static map: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/changes-in-fish-distribution-in/temporal-development-of-the-ratio
-

This data set presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD), with a mapping of contamination 'problem areas' and ‘non-problem areas’ based on measurements in the matrix 'biota'. This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the biota matrix. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. Monitoring and assessment for the matrix 'biota' has been carried out in the North-East Atlantic Ocean (482 assessment units), Baltic sea (198 assessment units), Mediterranean Sea (161 assessment units) and Black sea (12 assessment units). This data set underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the EEA report “Contaminants in Europe’s seas” (No 25/2018): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/contaminants-in-europes-seas. See the mentioned report for further information as well as examples of classification excluding specific groups of substances (e.g. metals, PBDEs).
-

This raster dataset represents physical disturbance to the seabed in the European seas. Several human activities disturb the seabed either directly or indirectly. Alteration of benthic living conditions as a result of increased sedimentation or attenuation of light penetration, abrasion of the seabed and exploitation of benthic biota, temporarily disturb the benthic habitat quality. The dataset is an aggregation of several different human activities that cause physical disturbance to the seabed: aquaculture, demersal fishing, dredging and dumping of dredged material, oil and gas rigs, offshore installations, ports, sand and gravel extraction, shellfish mariculture, shipping in shallow waters and windfarms. The resulting dataset is a raster (10km grid cell) derived from EMODnet, MED-IAMER, JRC-STECF, OSPAR, HELCOM and 4C Offshore datasets, and with reference temporal coverage from 2012 to 2017. This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
-

The dataset presents the results of classification of eutrophication status of the European seas using the HEAT+ tool. Eutrophication status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. Besides the overall Eutrophication status (HEAT+) are the results shown for three aspects of eutrophication: C1) Nutrient Concentrations C2) Direct Effects C3) Indirect Effects This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Nutrient enrichment and eutrophication in Europe's seas" (EEA, 2019): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/nutrient-enrichment-and-eutrophication-in.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA