Sedimentary fluxes
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Resolution
-
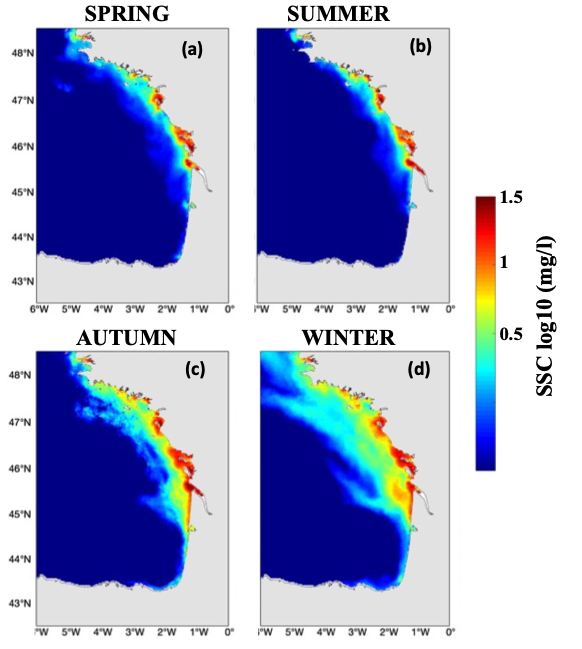
Hydrodynamic and sediment dynamic hindcast modelling with a resolution of 2.5 km in the Bay of Biscay and Channel, produced by coupling the hydrodynamic model CROCO with the sediment dynamic module MUSTANG.
-
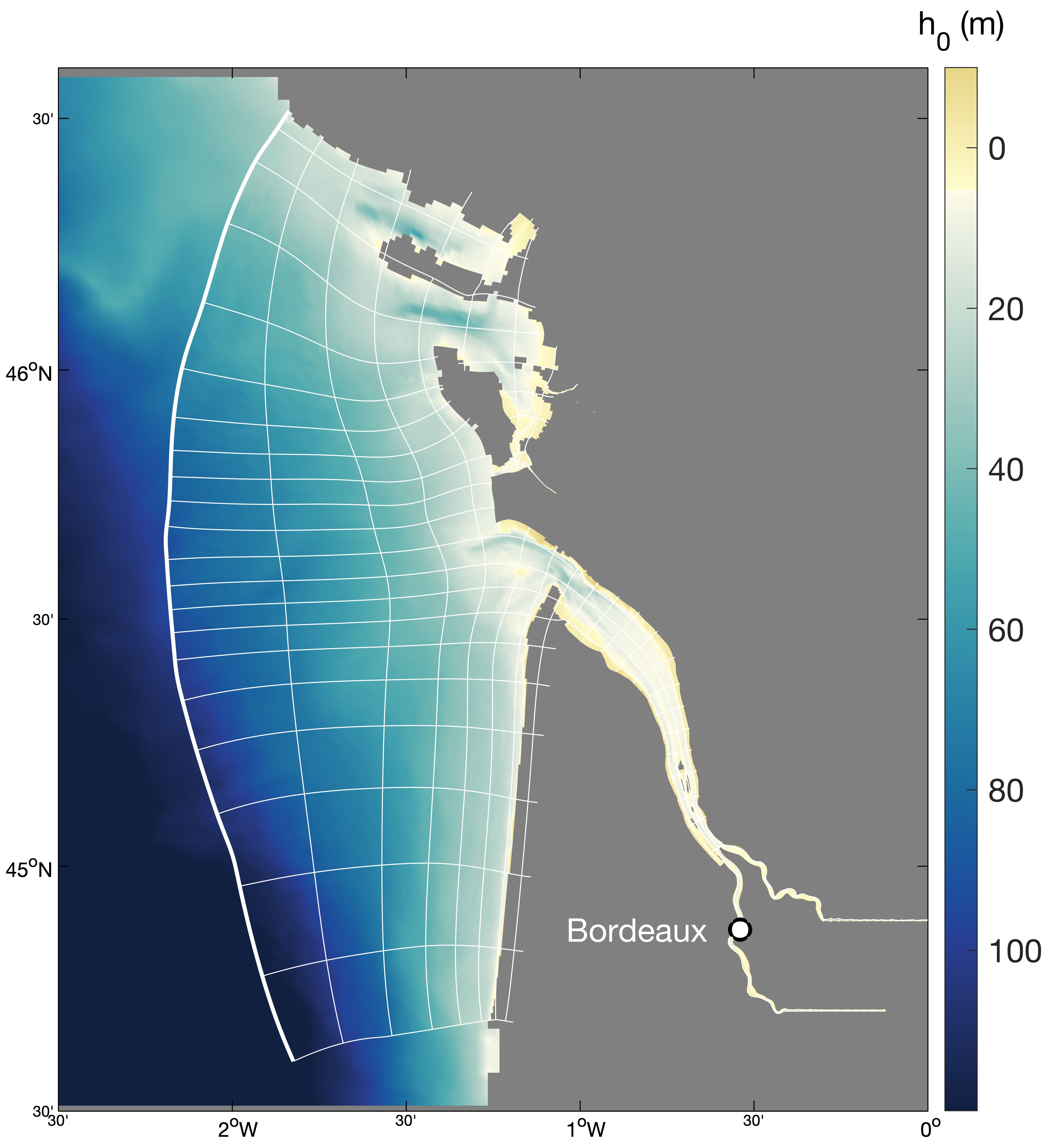
Hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics hindcast in the Gironde Estuary (France), produced by coupling the hydrodynamics model MARS3D (with sediment dynamics module MUSTANG) and wave spectral model WAVEWATCH III®.
-
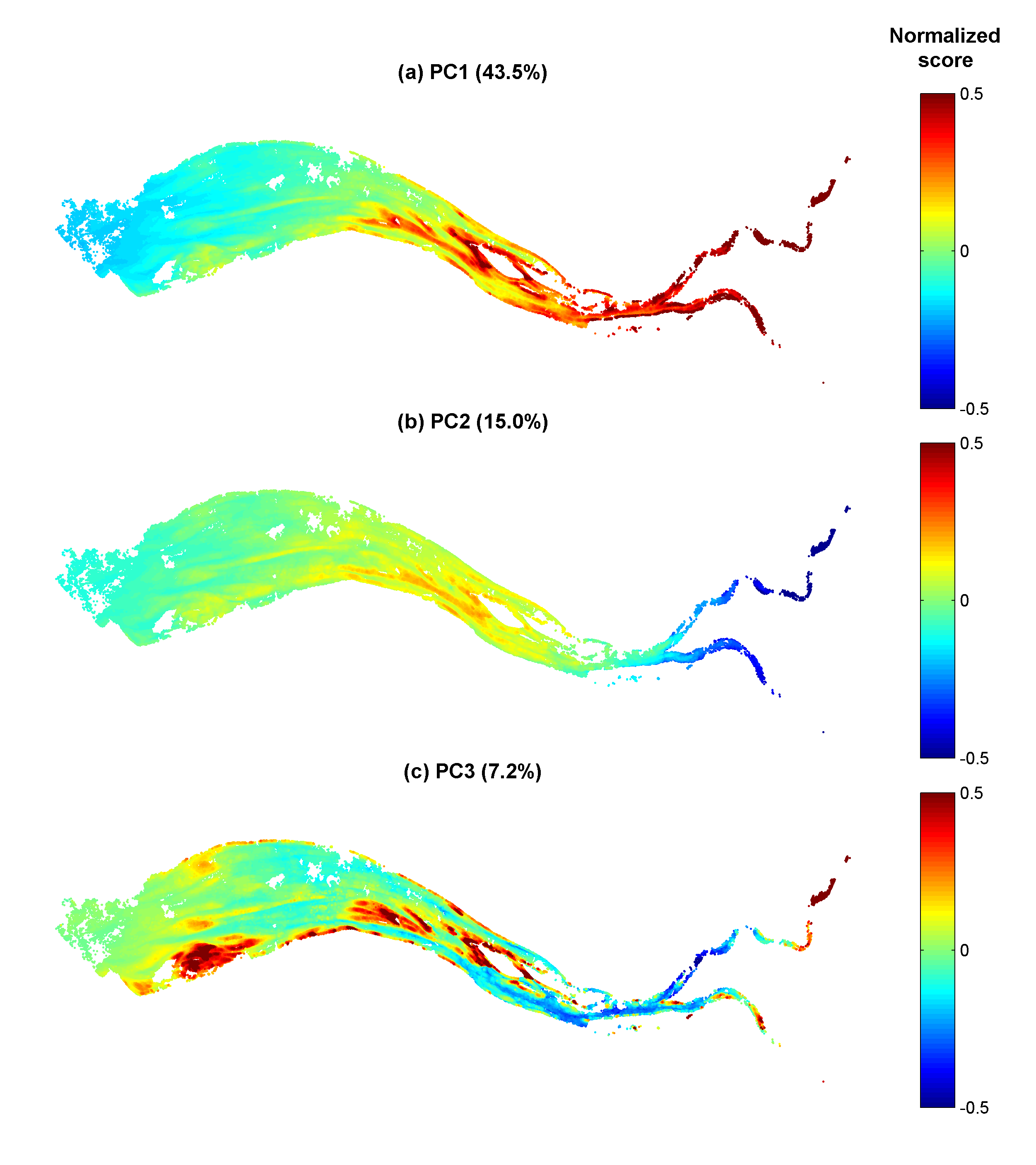
Gironde estuary environmental parameters and SPM maps generated from 41 Landsat-8/OLI and Sentinel-2/MSI images acquired over the period 2013-2018. Except bathymetry and daily river discharge data, that are accessible on public platforms, the dataset includes all of the time seris used in the publication: Analysis of suspended sediment variability in a large highly-turbid estuary using a 5-year-long remotely-sensed data archive at high resolution, Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, DOI:10.1029/2019JC015417.
-
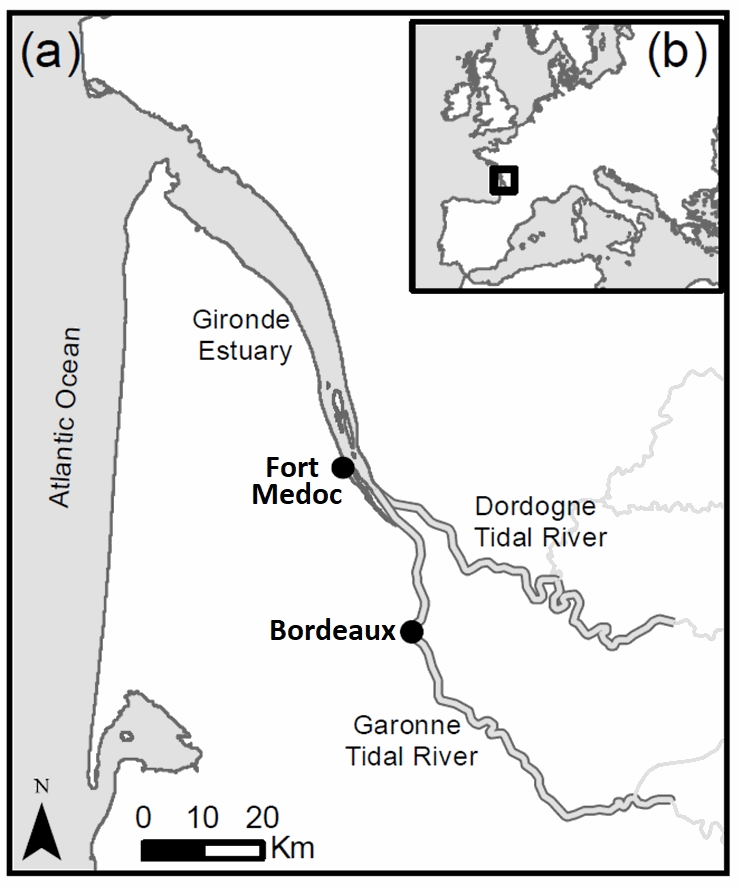
In the context of EMPHASE project (ANR-FRQ), two fields campaigns were carried out to determine the settling velocity and properties of suspended sediments during a semi-diurnal tidal cycle, as well as hydrodynamic conditions and water properties. The two sampling stations Bordeaux (Garonne Tidal River) and Fort Medoc (Gironde EStuary) were representative of two regions: a tidal river dominated by fresh water and an estuary affected by salty or brackish waters, inside the same land-sea continuum. Quasi in-situ measurements of settling velocity were carried out with a recently-patented instrument named System for the Characterisation of Aggregates and Flocs (SCAF).
-
The West Gironde Mud Patch (WGMP) is a 420-km2 mud belt in the Bay of Biscay, located 25 km off the mouth of the Gironde estuary. This clay-silt feature of 4 m in thickness extends between 30 and 75m water depth, surrounded by the sands and gravels that cover the North Aquitaine continental shelf. Interface cores were collected during JERICOBent-1 cruise (October 2016; Deflandre (2016) doi.org/10.17600/16010400) along two cross-shelf transects for a total of 9 sites. Each sediment core was carefully extruded every 0.5 cm from the top core to 4 cm and every 1 cm below until the core bottom. The sediment layers were used to determine dry bulk density, grain size and selected radioisotope activities (210Pb, 226Ra, 137Cs, 228Th, K).
-

The West Gironde Mud Patch (WGMP) is a mud deposit located 25 km from the mouth of the Gironde Estuary in the Bay of Biscay. This 4-metre-thick clay-silt feature, which extends over an area of 420 km2, is found at depths between 30 and 80 meters. The main objectives of the JERICObent7 cruise, in July 2019, were to characterise the evolution of the WGMP’s benthic ecosystem in terms of its sedimentary, biogeochemical and ecological properties and to reconstruct climate variations and identify potential anthropogenic impacts over the last few centuries. To this end, a precise chronological framework was established for the sedimentary archives of the last few decades using 210Pbxs (T1/2 = 22.3 years). Interface cores were collected at stations 1, 3 and 4 along a cross-shelf transect. Twin Kullenberg cores were collected at sites 3 and 4 for geochemical (KGL) and palaeoceanographic (JB7-ST) investigations. Each interface core was carefully extruded at 0.5 cm intervals from the top of the core to 4 cm, and then at 1 cm intervals until the bottom was reached. Kullenberg cores were only collected at sites 3 and 4. Depending on their intended use, the Kullenberg cores were sampled at different resolutions, the depth of each sediment layer corresponded to the depth from the top of the core. These layers were then used to determine the dry bulk density and radioisotope activities of interest (210Pb, 226Ra, 228Th, 137Cs, 40K). Excess 210Pb was used to establish the realignment and chronological framework of the interface and Kullenberg cores.
-
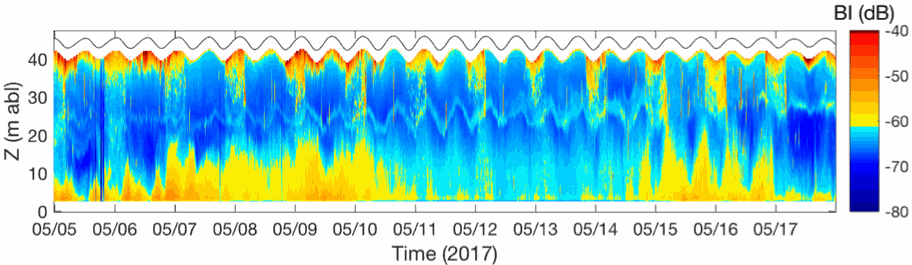
In the framework of the ANR AMORAD project, the METEOR cruises (Grasso, 2017) aimed at deploying the ‘Gironde Estuary Mouth MEasurement Stations’ (GEMMES) to measure hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics at the mouth of the Gironde Estuary and on the West Gironde Mud Patch (SW France, Bay of Biscay). Measurements were carried out between November 2016 and December 2017: i) from a buoy station around 20-m water depth (GEMMES-20), collecting sub-surface data of temperature, salinity and turbidity; and ii) a benthic station around 40-m water depth (GEMMES-40), collecting data of current velocity and turbidity. Bottom and surface water samples were regularly collected to calibrate turbidity measurements to SPM concentrations.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA