South Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Resolution
-

This is the FAO Fishery and Aquaculture Reference Data repository: Codes and reference data for fishing gear, species, currencies, commodities, countries and others.
-

The Commission for the Conservation Southern Bluefin Tuna collects a variety of data types from its Members and Cooperating Non-Members, including total catch, catch and effort data, and catch at size data. Catch, size and trade information is also collected through the Commission's Catch Documentation Scheme, Japanese import statistics, and other monitoring programs. Annual catches provided on this page are reported on a calendar year basis. CCSBT Members use quota years (not calendar years) for managing catching limits, but quota years differ between Members, so calendar years are used to provide catches on a common timescale. Relevant subsets and summaries of these data are provided below. All figures are subject to change as improved data or estimates become available. In particular, reviews of SBT data in 2006 indicated that southern bluefin tuna catches may have been substantially under-reported over the previous 10-20 years and the data presented here do not include estimates for this unreported catch. Also, data for the last reported year of catch (2020) are preliminary and are subject to revision. Any latitudes and longitudes presented in these summaries represent the north western corner of the relevant grid, which is a 5*5 grid unless otherwise specified. Other information on Members and Cooperating Non-Members fishing activities appears in the reports of the Extended Scientific Committee, Compliance Committee and Extended Commission.
-

Several climate indices, regarding Atlantic Basin: - North Atlantic Oscillation - Southern Oscillation Index - Bivariate ENSO Timeseries - Tropical Northern Atlantic Index - Tropical Southern Atlantic Index - Oceanic Niño Index - Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI V2) - North Tropical Atlantic SST Index - ENSO precipitation index - Northeast Brazil Rainfall Anomaly - Solar Flux (10.7cm) - Global Mean Lan/Ocean Temperature
-
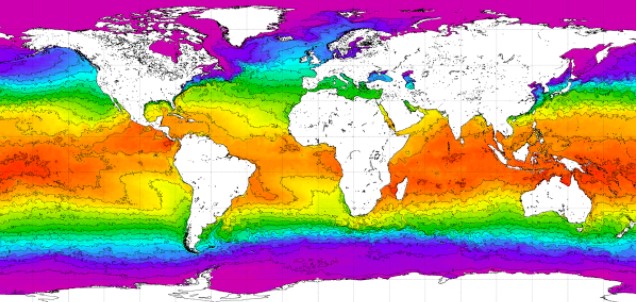
World Ocean Atlas 2018 (WOA18) is a set of objectively analyzed (one degree grid and quarter degree grid) climatological fields of in situ temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, Apparent Oxygen Utilization (AOU), percent oxygen saturation, phosphate, silicate, and nitrate at standard depth levels for annual, seasonal, and monthly compositing periods for the World Ocean. Quarter degree fields are for temperature and salinity only. It also includes associated statistical fields of observed oceanographic profile data interpolated to standard depth levels on quarter degree, one degree, and five degree grids. Temperature and salinity fields are available for six decades (1955-1964, 1965-1974, 1975-1984, 1985-1994, 1995-2004, and 2005-2017) an average of all decades representing the period 1955-2017, as well as a thirty year "climate normal" period 1981-2010. Oxygen fields (as well as AOU and percent oxygen saturation) are available using all quality controlled data 1960-2017, nutrient fields using all quality controlled data from the entire sampling period 1878-2017. This accession is a product generated by the National Centers for Environmental Information's (NCEI) Ocean Climate Laboratory Team. The analyses are derived from the NCEI World Ocean Database 2018.
-

3-D habitat suitability maps (HSM) or probability of occurrence maps, built using Shape-Constrained Generalized Additive Models (SC-GAMs) for the 30 main commercial species of the Atlantic region. Predictor variables for each species were selected from: sea water temperature, salinity, nitrate, net primary productivity, distance to seafloor, distance to coast, and relative position to mixed layer depth. Each species HSM contains 47 maps, one per depth level from 0 to 1000 m. Probability values of each map range from 0 (unsuitable habitat) to 1 (optimal habitat). For depth levels below the 0.99 quantile of the depth values found on the species occurrence data, NA values were assigned. Maps have been masked to species native range regions. See Valle et al. (2024) in Ecological Modelling 490:110632 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2024.110632 ), for more details.
-

Classification of the Atlantic Ocean seabed into broad-scale benthic habitats employing a hierarchical top-down clustering approach aimed at informing Marine Spatial Planning. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021 with data provided by a wide group of partners representing the nations surrounding the Atlantic Ocean. It classifies continuous environmental data into discrete classes that can be compared to observed biogeographical patterns at various scales. It has 3 levels of classification. For ease of use, a layer is provided for each level. Level 1 has 4 classes. Level 2 has 15 classes nested within level 1. Layers indices are 2 digits (1[level1 class index]1[level 2 class index]). Level 3 has 157 classes nested within level 2 and class names have 4 digits (1digit[level1 class index]1[level 2 class index]2[level 3 class index]). Note that the classification was performed for the whole world and thus it has more classes than in the presented layer.
-

Climatological monthly means output (physical variables) from the global hydrodynamic-biogeochemical model (NEMO-ERSEM) by the Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) within the framework of the project Mission Atlantic (https://missionatlantic.eu/). This 40-year monthly means netcdf file of 1 degree regular grid resolution is a sample aiming to show the results of the model in the geonode. The variables included in this netcdf are: sea water absolute salinity (so_abs, units: psu), sea water conservative temperature (thetao_con, units: C°), mixed layer depth (mldr10_1, units: m), latitude (lat, units: degrees), longitude (lon, units: degrees), time (time, units: seconds since 1900-01-01 00:00:00), depth [height] (z, units: m). The original model output files are stored with the data provider at the Plymouth Marine Laboratory.
-

Classification of the seabed in the Atlantic Ocean into broad-scale benthic habitats employing a non-hierarchical top-down clustering approach aimed at informing Marine Spatial Planning. This work was performed at the University of Plymouth in 2021 with data provided by a wide group of partners representing the nations surrounding the Atlantic Ocean. It classifies continuous environmental data into discrete classes that can be compared to observed biogeographical patterns at various scales. It has 3 levels of classification. The numbers in the raster layer correspond to individual classes. Description of these classes is given in McQuaid, K.A. et al. (2023).
-

This dataset comprises the global frequency, classification and distribution of marine heat waves (MHWs) from 1996-2020, in Chauhan et al. 2023 (https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1177571). The classification was done based on their attributes and using different baselines. Daily SST values were extracted from the NOAA-OISST v2 high-resolution (0.25°) dataset from 1982-2020. MHWs were detected using the method presented by Hobday et al. 2016 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2015.12.014), and by using the 95th percentile of the accumulated temperature distribution to flag the extreme events. A shifting baseline of 8-year rolling period was selected between the years 1982-1996, since this period shows relatively stable maximum values of temperature across different ocean regions. The shifting baseline aims to account for the decadal changes of westerly winds, temperatures and ocean gyres circulations. The classification was done using the KMeans clustering algorithm to identify the relevant features of MHWs and classify them into separate groups based on feature similarities. This algorithm takes MHW features, namely duration, maximum intensity, rate onset and rate decline, as input vectors and applies clustering in the 4-dimensional feature space where each data point represents an MHW event. Note that all the MHWs features are standardized because unequal variances can put more weight on variables with smaller variances. This record comprehends the geospatial datasets of: Average number of MHW days per year (i.e., the sum of all MHW days divided by the total number of years, 1996-2020). Average cumulative intensity per year (i.e., the sum of cumulative intensity divided by the total number of years, 1996-2020). Total number of MHW events across the different periods averaged on the total number of years (1989-2020). The period 1982-1988 was only used as an initial baseline without calculating MHWs. Spatial distribution of three MHW categories: moderate MHWs, abrupt and Intense MHWs and extreme MHWs; displaying the total number of MHW days normalized by the number of years considered (i.e., 1989-2020). Distribution of Extreme MHWs across the different periods (A) 1989-1996, (B) 1997-2004, (C) 2005-2012, (D) 2013-2020. The relative frequency (γ) is a ratio of extreme MHWs in a specific period and all extreme MHWs in the same cluster for all periods.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA