turbidity
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
Resolution
-
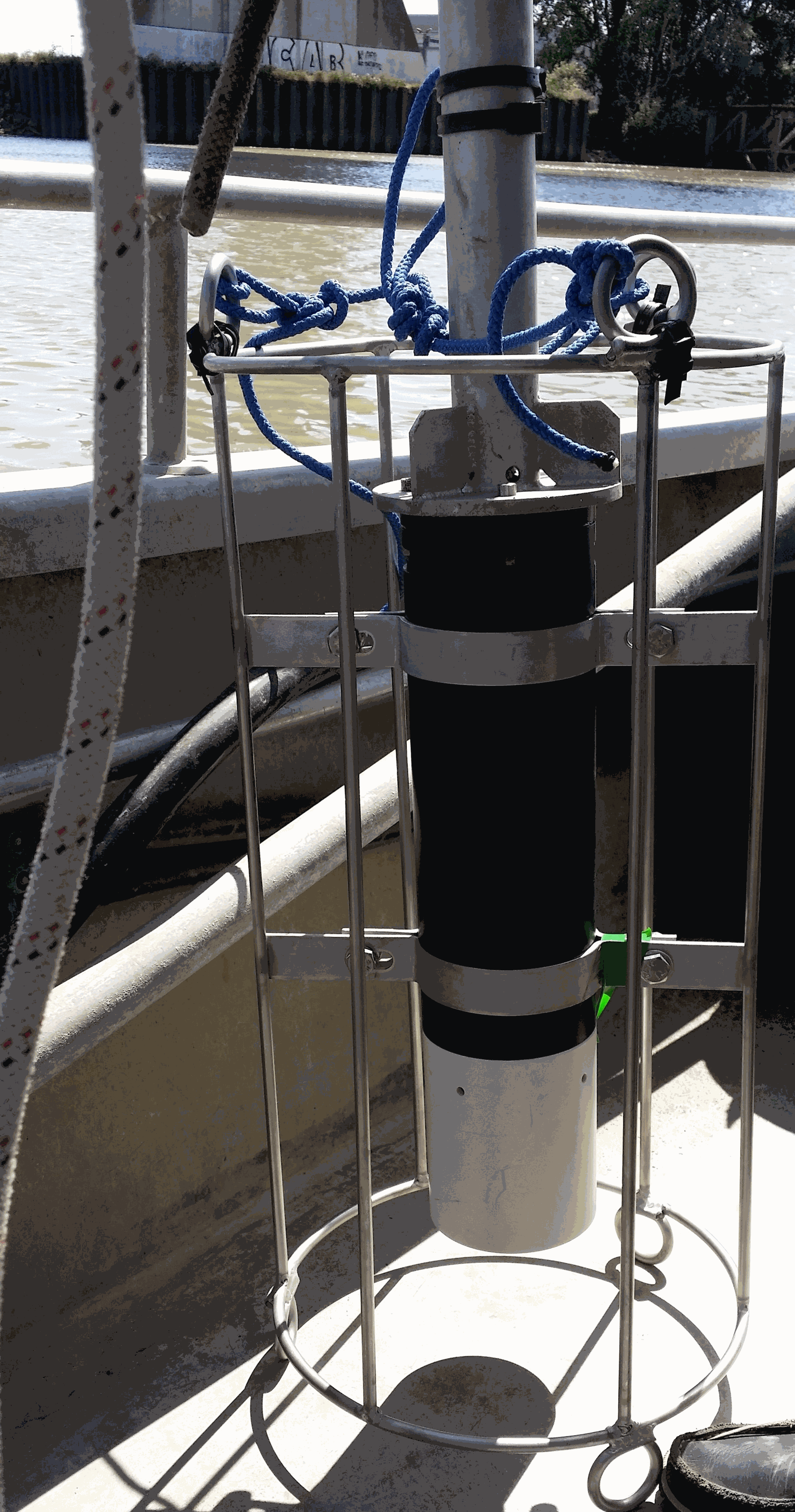
Key physico-chemical parameters (salinity, temperature, turbidity and dissolved oxygen) were measured in surface water during longitudinal transects in the Loire and Gironde estuaries in summers 2017 and 2018. This objective of this work was to determine the distribution of the dissolved oxygen and to detect potential severe desoxygenation. The transects were scheduled in order to begin the measurements at high tide from a site located upstream of an area where severe deoxygenation have been already been reported. Then, the transect was realised by sailing at low speed downstream with a multiparameter probe SAMBAT, maintained at 0.5 m below the surface, that collected a measurement every 2 minutes.
-
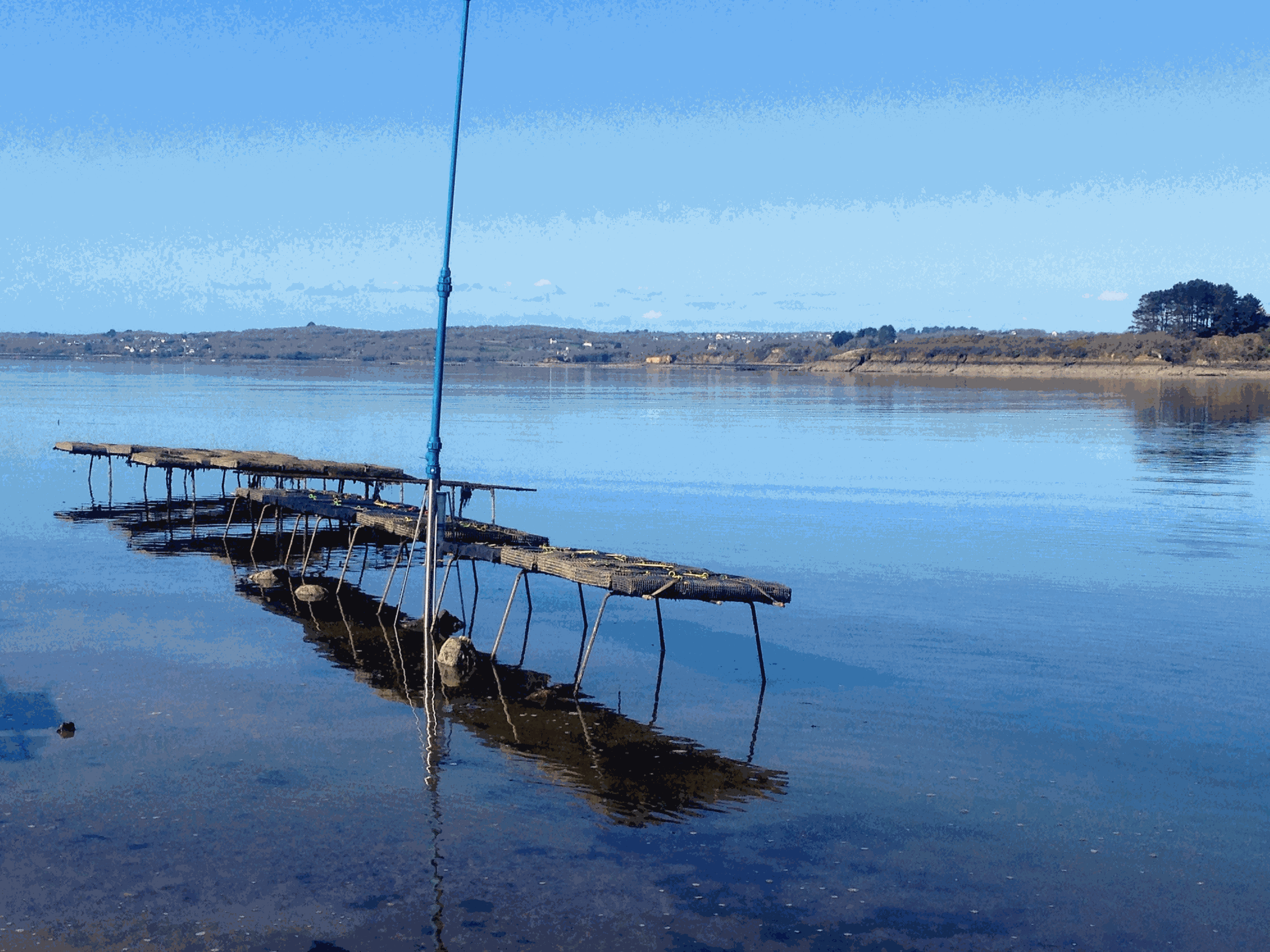
Based on the consolidation of the Ifremer networks RESCO (https://doi.org/10.17882/53007) and VELYGER (https://doi.org/10.17882/41888), the general objective of the ECOSCOPA project is to analyze the causes of spatio-temporal variability of the main life traits (Larval stage - Recruitment - Reproduction - Growth – Survival – Cytogenetic anomalies) of the Pacific oyster in France and follow their evolution over the long term in the context of climate change. The high frequency environmental data are monitored since 2010 at several stations next to oyster farm areas in eight bays of the French coast (from south to north): Thau Lagoon and bays of Arcachon, Marennes Oléron, Bourgneuf, Vilaine, Brest, Mont Saint-Michel and Veys (see map below). Sea temperature and practical salinity are recorded at 15-mins frequency. For several sites, fluorescence and turbidity data are also available. Data are acquired with automatic probes directly put in oyster bags or fixed on metallic structure at 50 cm over the sediment bottom, except for Thau Lagoon whose probes are deployed at 2m below sea surface. Since 2010, several types of probes were used: STP2, STPS, SMATCH or WiSens CTD from NKE (www.nke-instrumentation.fr) and recently ECO FLNTU (www.seabird.com). The probes are regularly qualified by calibrations in the Ifremer coastal laboratories. Precision estimated of the complete data collection process is: temperature (±0.1°C), salinity (±0.5psu), in vivo fluorescence (±10%), turbidity (±10%). The data are qualified into several levels: 0-No Quality Check performed, 1-Good data, 2-Probably good data, 3-Probably bad data, 4-Bad data, 5-Value changed, 7-Nominal value, 8-Interpolated value, 9-Missing value.
-
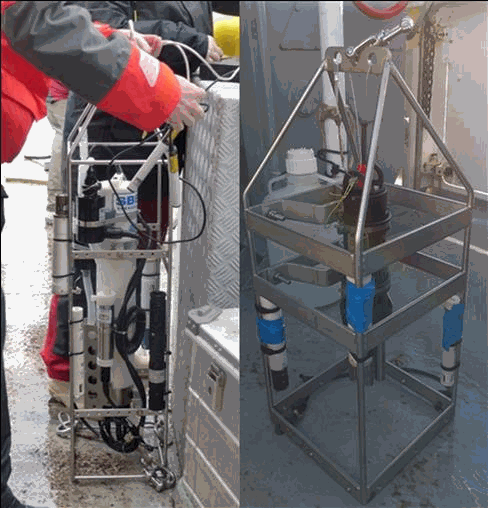
The aim of this work was to document the seasonal and inter-annual dynamic of dissolved oxygen and ancillary data (T, S, Chl-a, turbidity, pH) along a cross-shelf transect off the Gironde estuary. This work has been motivated by recent simulations that suggest the occurrence of seasonal bottom deoxygenations in this River-dominated Ocean Margin (Riomar); but unfortunately there were no data sets to test this hypothesis until now. Profiles of temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen were performed in the water column of the West Gironde Mud Patch off the Gironde estuary (from 45°46.383’N – 1°28.925’W to 45°35.524’N - 1°50.689’W) during seven cruises on the R/V Côte de la Manche (doi: 10.18142/284 ; 10.17600/18000861) between 2016 and 2021 (October 2016, August 2017, January 2018, April 2018, July 2019, April 2021, October 2021). Turbidity was measured in January and April 2018, July 2019 and October 2021, Chl-a in October 2016, August 2017, January 2018, April 2018 and July 2019 and pH in October 2021. This dataset had permitted to validate the occurrence of bottom deoxygenations when the water column is stratified.
-
The French Atlantic coast hosts numerous macrotidal and turbid estuaries that flow into the Bay of Biscay that are natural corridors for migratory fishes. The two best known are those of the Gironde and the Loire. However, there are also a dozen estuaries set geographically among them, of a smaller scale. The physico-chemical quality of estuarine waters is a necessary support element for biological life and determines the distribution of species, on which many ecosystem services (e.g. professional or recreational fishing) depend. With rising temperatures and water levels, declining precipitation and population growth projected for the New Aquitaine region by 2030, the question of how the quality and ecological status of estuarine waters will evolve becomes increasingly critical. The MAGEST (Mesures Automatisées pour l’observation et la Gestion des ESTuaires nord aquitains) high-frequency monitoring of key physico-chemical parameters was first developed in the Gironde estuary in 2004 ; the Seudre and Charente estuaries were instrumented late 2020. First based on real-time automated systems, MAGEST is now equipped by autonomous multiparameter sensors. Depending of the stations, an optode is also deployed to secure dissolved oxygen measurement. By the end of 2020, MAGEST had 12 instrumented sites. Portets is a measuring station located in the upper Gironde estuary (Garonne subestuary, about 20 km upstream of the Bordeaux metropolis.
-
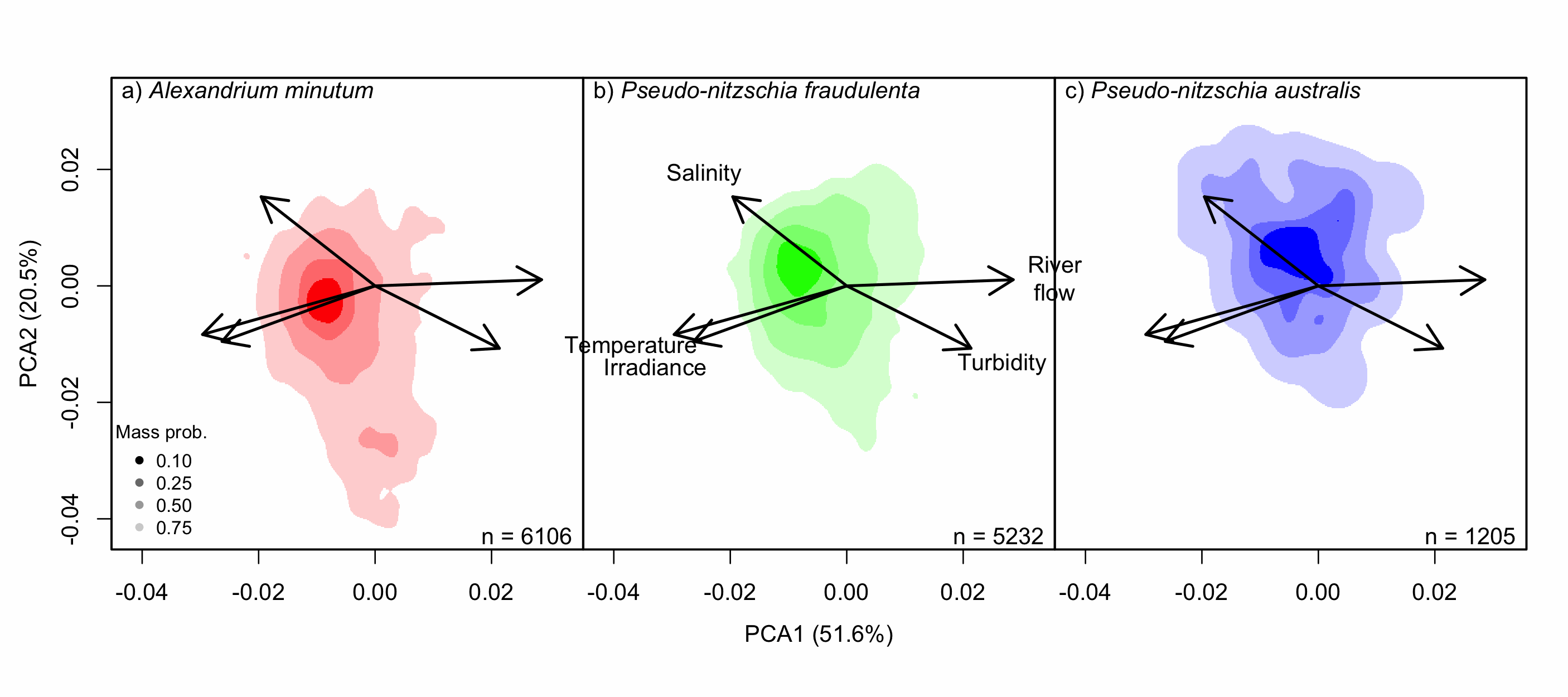
Understanding the spatial and temporal preferences of toxic phytoplankton species is of paramount importance in managing and predicting harmful events in aquatic ecosystems. In this study we address the realised niche of the species Alexandrium minutum, Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta and P. australis. We used them to highlight distribution patterns at different scales and determine possible drivers. To achieve this, we have developed original procedures coupling niche theory and habitat suitability modelling using abundance data in four consecutive steps: 1) Estimate the realised niche applying kernel functions. 2) Assess differences between the species’ niche as a whole and at the local level. 3) Develop habitat and temporal suitability models using niche overlap procedures. 4) Explore species temporal and spatial distributions to highlight possible drivers. Data used are species abundance and environmental variables collected over 27 years (1988-2014) and include 139 coastal water sampling sites along the French Atlantic coast. Results show that A. minutum and P. australis niches are very different, although both species have preference for warmer months. They both respond to decadal summer NAO but in the opposite way. P. fraudulenta realised niche lies in between the two other species niches. It also prefers warmer months but does not respond to decadal summer NAO. The Brittany peninsula is now classified as an area of prevalence for the three species. The methodology used here will allow to anticipate species distribution in the event of future environmental challenges resulting from climate change scenarios.
-

This vector dataset represents the benthic broad habitat types in Europe Seas potentially affected by the ship wakes. When navigating, the propellers of ships generate a turbulent mixing of the water that can produce sediment re-suspension in soft bottoms of shallow areas. This can increase the turbidity in those areas, affecting the seafloor organisms (especially those that are directly dependent on light, such as aquatic plants). It may also contribute to an increase of the the eutrophication level of the ecosystem (since the turbid waters may become warmer, which may turn into a reduction of dissolved oxygen in water). Finally, turbidity can produce an increase in the inputs of contaminants and microbial pathogens, since those can become attached to the suspended solids. The dataset has been prepared in the context of the development of the first European Maritime Transport Environmental Report (https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/maritime-transport).
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA