IFREMER, Univ. Brest, CNRS UMR 6523, IRD, Laboratoire d'Océanographie Physique et Spatiale (LOPS), IUEM, 29280, Plouzané, France
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
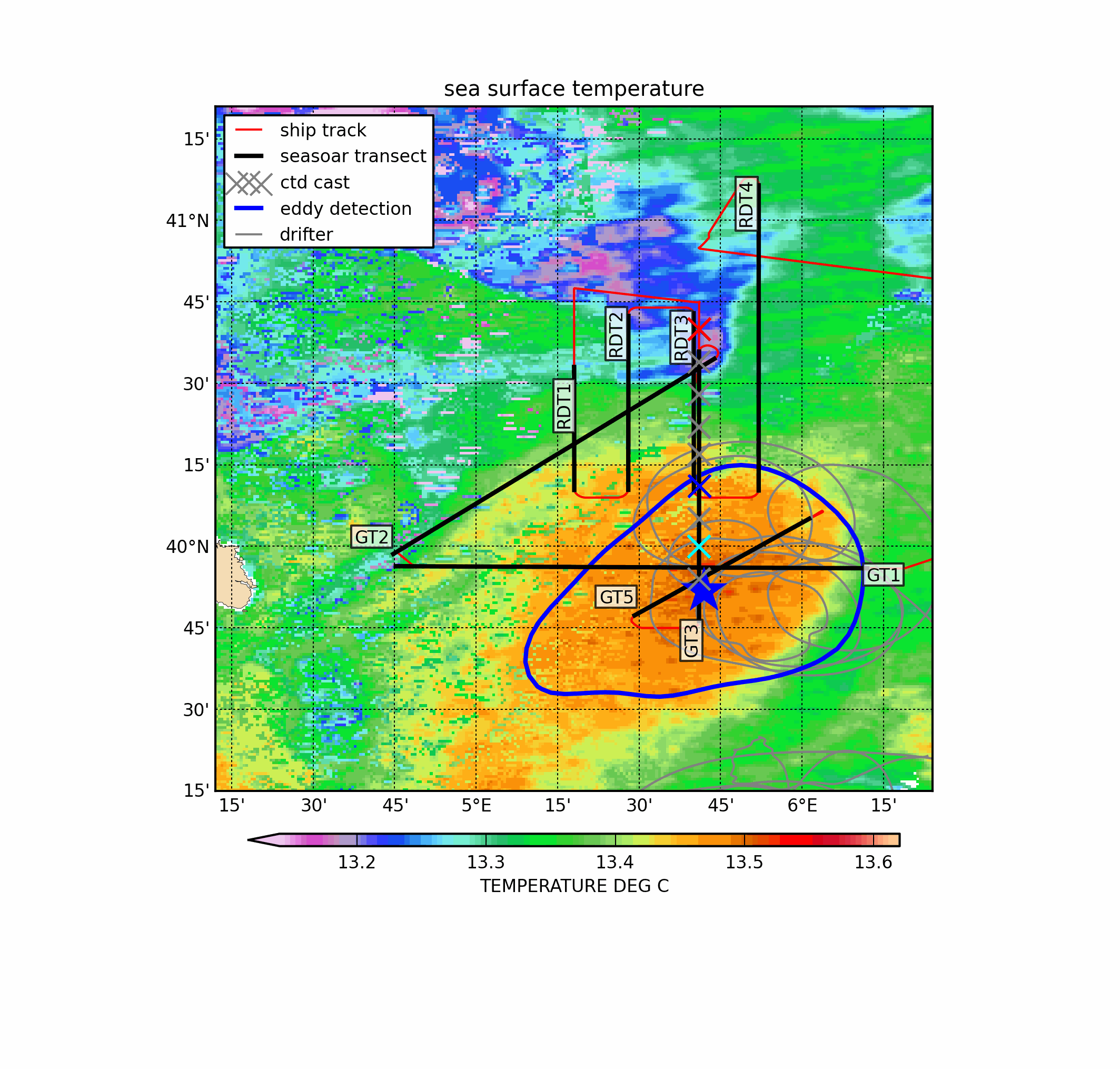
Mesoscale dynamics in the Mediterranean Sea have been investigated for years and anticyclonic eddies are regularly observed features in the Algerian Basin. In early spring 2016, a field experiment during the ProtevsMed 2016 cruise thoroughly investigated this specific eddy, when it was located near the North Balearic Front, taking high-resolution (Seasoar) hydrological transects, several CTD casts and LADCP measurements. In addition, four drifting buoys were released in the eddy core. These in situ measurements revealed that the vertical structure of this anticyclone was made of two water lenses of very different origins (Atlantic Water above and Western Intermediate Water below) spinning together. In the vicinity of the North Balearic Front, which may act as a dynamical barrier for structures, the eddy interacted with a subsurface anticyclonic eddy made of modal water, which fostered cross-front exchanges generating filaments by stirring. The high-resolution sampling revealed fine scales structures both adjacent to the eddy and within its core. The eddy has been targeted from 21 March to 1 April 2016 taking advantage of a meteorological window. It has been sampled with: - a towed undulating vehicle, the SeaSoar designed and built by Chelsea Instruments; it gets mounted on its sides two Sea-bird SBE-9 (SBE 3 temperature and SBE 4 conductivity sensors) and a Wetlabs Fluorometer of type ChloroA WetStar - CTD casts performed with a Sea-bird SBE-9 (SBE 3 temperature and SBE 4 conductivity sensor) and an RDI 150 kHz current profiler mounted in a general oceanics 12-place rosette, with12l Niskin bottles - drifters with holey-sock positioned at 50 m deep below the expected Ekman layer thickness (remaining in the eddy until mid May).
-

From 2015 to 2018 five field experiments (9 legs) have been performed in the Western Mediterranean Basin during winter or early spring. Thanks to the intensive use of a towed vehicle undulating in the upper oceanic layer between 0 and 400 meter depth (i.e. a Seasoar), a large amount of very high resolution hydrographic transects have been performed, to measure the mesoscale dynamics (slope current and its instabilities, anticyclonic eddies, sub-mesoscale coherent vortices, frontal dynamics convection events, strait outflows) and sub-mesoscale processes like stirring, mixed layer or symmetric instabilities. When available, the data were completed with velocities recorded by Vessel Mounted Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (VMADCP) and by surface salinity and temperature recorded by ThermosalinoGraph (TSG). Some CTD casts have also been performed giving the background hydrography of the deep layers. In 2017, a Moving Vessel Profiler (MVP) has been deployed to manage even higher horizontal resolution. This data set is an unprecedented opportunity to investigate the very fine scale processes as the Mediterranean Sea is known for its intense and contrasted dynamics. It should be useful for modellers (who reduce the grid size below a few hundred meters) and expect to properly catch finer scale dynamics. Likewise, theoretical work could also be illustrated by in situ evidence embedded in this data set.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA